POLR2A and Associated Diseases
After decades of development and expansion, Creative Biolabs has gradually gained an excellent reputation in the field of gene therapy. With our highly specialized technical capabilities and expertise in gene therapy, we are well-positioned to facilitate collaborations in the fast-growing field of gene therapy. Here, we provide a brief introduction to the RNA polymerase II subunit A (POLR2A) gene.
Introduction of POLR2A
POLR2A is a protein-coding gene that encodes the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, a polymerase that plays an important role in the synthesis of messenger RNA in eukaryotes. Furthermore, this subunit involves a carboxy-terminal domain consisting of repeats essential for polymerase activity. These repeats involve serine and threonine residues that are phosphorylated by actively transcribing RNA polymerase. In addition, the product of this gene is involved in the formation of the DNA-binding domain of the polymerase, the groove in which the DNA template is transcribed into RNA. POLR3A is an important paralog of the gene. Notably, gene ontology (GO) annotations associated with this gene include DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity and RNA binding.
POLR2A and Associated Diseases
POLR2A is closely linked to many diseases, such as neurodevelopmental disorders with hypotonia and meningiomas. In addition, accumulating evidence revealed that POLR2A mutation is a risk factor for tumor recurrence.
- POLR2A and meningioma
Mutations in genes can affect gene transcription. POLR2A mutations are present in 6% of meningiomas. Meningiomas, the most common type of tumor in the head, can put pressure on the adjacent brain, nerves, and blood vessels. In general, obvious signs and symptoms do not appear in slow-growing meningiomas, so they usually do not require immediate treatment and can be monitored over time. Furthermore, some studies reported that POLR2A mutations could serve as a potential marker for meningiomas with poor prognosis.
- POLR2A and gastric cancer (GC)
Studies demonstrated that POLR2A was highly expressed in GC tissues and facilitated GCs proliferation. Furthermore, POLR2A contributes to the cell cycle progression of GCs by promoting the transcription of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). In addition, POLR2A plays a crucial role in accelerating GC cell migration. Taken together, POLR2A is an important indicator involved in GC occurrence and development.
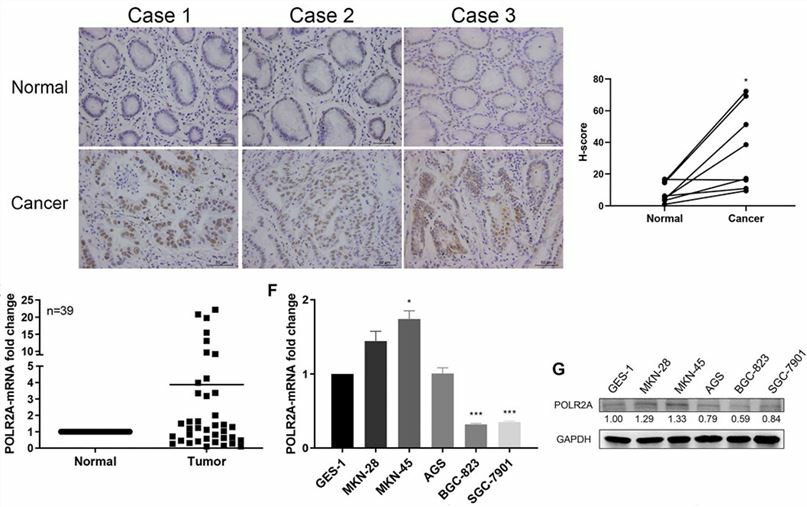 Fig.1 POLR2A was highly expressed in GC tissues. (Jiang, 2021)
Fig.1 POLR2A was highly expressed in GC tissues. (Jiang, 2021)
POLR2A Related Pathways in Cancers
POLR2A is an essential neighbor gene of tumor protein p53 (TP53). POLR2A was identified as always co-deleted with TP53 in various human cancers, including colorectal, ovarian, kidney, and pancreatic cancers. TP53 is a tumor suppressor gene that prevents the formation of tumors. Mutations or deletions of the TP53 gene are involved in more than half of all human tumors. The researchers found that co-depletion of TP53 and POLR2A renders cancer cells highly susceptible to POLR2A inhibition, thus providing an attractive therapeutic strategy for tumors harboring such genomic alterations.
For decades, Creative Biolabs has been at the forefront of the field of gene therapy. We continuously improve quality and provide services for research to support our global clients with high quality results. If you are interested in our gene therapy-related services, please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Jiang, Q.; et al. POLR2A Promotes the Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells by Advancing the Overall Cell Cycle Progression. Frontiers in genetics. 2021, 12. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
