PTCH1 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs has extensive experience to offer drug discovery services for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. We have the capability to enable you to free up your time for core work and projects. Here we describe the PTCH1 gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Introduction of PTCH1
Encoded by the PTCH1 gene, protein patched homolog 1 is a protein that belongs to the patched family. The PTCH1 protein is a transmembrane (TM) glycoprotein encoding 1447 amino acids. Sonic hedgehog is a secreted molecule involved in embryonic structure formation and tumorigenesis. As a receptor of sonic hedgehog, PTCH1 can release smoothened and signal cell proliferation by binding to the sonic hedgehog.
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway is an important regulator involved in animal development. This pathway, which transmits information to embryonic cells required for normal cell differentiation, also plays an important role in adults. Therefore, malfunction of this pathway can lead to the occurrence of a series of diseases, especially cancer. In general, there are three hedgehog ligands, including sonic hedgehog (SHH), indian hedgehog (IHH), and desert hedgehog (DHH) ligands. When these Hh ligands bind to PTCH1, the Hh pathway is activated and leads to the activation of the GLI family of transcription factors. At the same time, GLI1 regulates the expression of many genes involved in cell cycle progression, including members of the Hh pathway.
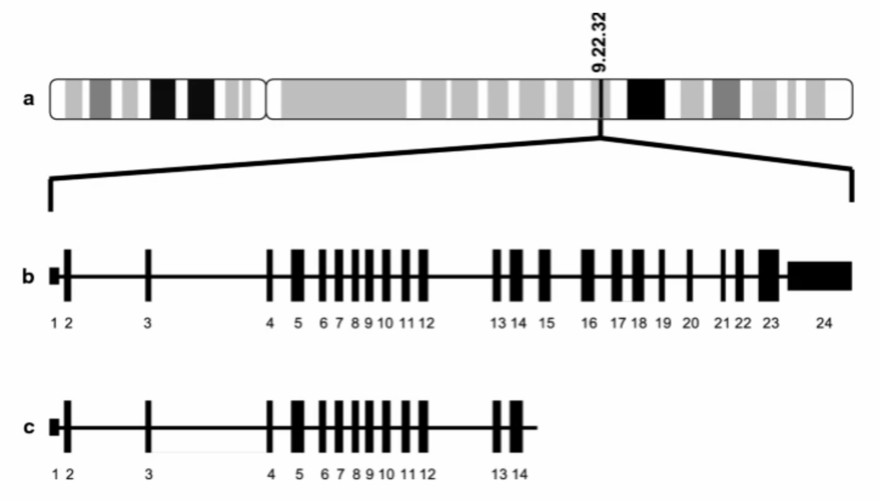 Fig.1 PTCH1 gene schematic. a PTCH1 origin on q arm of chromosome 9, b full length transcript with 24 exons and c mutant PTCH1 with deletion of exons 15–24. (Banerjee, 2019)
Fig.1 PTCH1 gene schematic. a PTCH1 origin on q arm of chromosome 9, b full length transcript with 24 exons and c mutant PTCH1 with deletion of exons 15–24. (Banerjee, 2019)
PTCH1 and Cancer
Studies have shown that mutations in the PTCH1 gene have been linked to a variety of cancers, such as Gorlin syndrome, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinomas of the bladder, medulloblastoma, and holoprosencephaly. Most of these mutations are clustered in two large extracellular loops and a large intracellular loop.
In the previous research, 29 novel PTCH1 mutations have been identified, which include truncation, non-truncation, as well as splice-site mutations. For example, nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS) is a classical inherited disease caused by mutations in the PTCH1 gene. Therefore, genetic analysis of the PTCH1 gene may be used for early diagnosis of NBCCS.
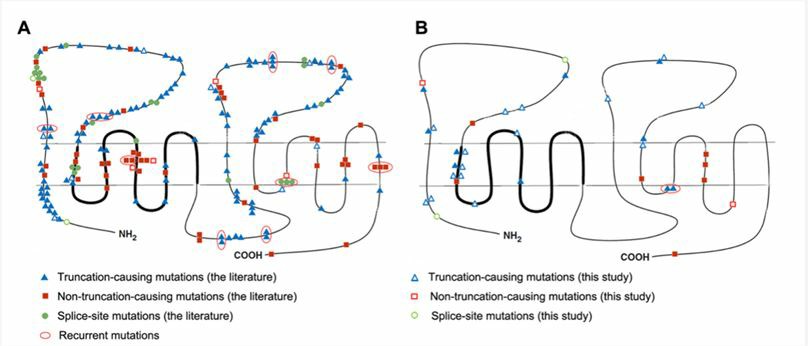 Fig.2 Distribution pattern of PTCH1 mutations in relation to the different domains of the Patched protein. (Guo, 2013)
Fig.2 Distribution pattern of PTCH1 mutations in relation to the different domains of the Patched protein. (Guo, 2013)
Related Services
- Viral Vector Design and Construction
- mRNA Therapeutics
- siRNA In Vitro Screening Service
- ASO In Vitro Screening Service
If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
References
- Guo, YY. et al. PTCH1 gene mutations in Keratocystic odontogenic tumors: a study of 43 Chinese patients and a systematic review. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 21;8(10):e77305. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Banerjee, S.; et al. Loss of the PTCH1 tumor suppressor defines a new subset of plexiform fibromyxoma. Journal of translational medicine. 2019 Dec;17(1):1-8. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
