KMT2A and Associated Diseases
According to years of experience in the field of gene therapy, excellent scientists in our Creative Biolabs are good at transforming basic science and personalized medicine research through classical and contemporary approaches and provide detailed and one-stop services for our clients.
Overview of KMT2A
In humans, Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A, also known as MLL1, ALL-1, or zinc finger protein HRX) is an enzyme encoded by the KMT2A gene located on chromosome 11 at q23. KMT2A, a histone methyltransferase of histone-modifying enzymes, is regarded as a positive regulator of gene transcription during early development and hematopoiesis. KMT2A contains transactivation domain 9aaTAD and is related to the epigenetic maintenance of transcriptional memory. KMT2A plays an important role in neuronal function and complex behaviors as an epigenetic regulator.
KMT2A in Disease
Chromosomal translocations involving are associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemias and acute myeloid leukemias. Ectopic expression of KMT2A is related to Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome and melanoma.
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemias
The rearrangements of KMT2A are highly pathogenic drivers of acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALL). KMT2A rearranged ALL (KMT2Ar ALL) is a high-risk genomic subtype of leukemias and the long-term survival rate of KMT2Ar ALL is less than 60%. KMT2A rearranged ALL has high-risk clinical features and the tendency of aggressive relapse. The transgenic KMT2Ar ALL mouse model performs long latency and mixed phenotype which is different from the clinically observed features. KMT2Ar ALL is the main cause of ALL in infants carrying a few leukemia-associated cooperative mutations. Other mutants such as PI3K-RAS pathway variants are associated with the occurrence of KMT2Ar ALL in adults. The comprehension of underlying biology is important in improving long-term outcomes in patients with KMT2Ar ALL.
- Melanoma
KMT2A promotes the growth of melanoma by activating the hTERT signal pathway. Melanoma is one of the most aggressive cutaneous malignancies. According to the siRNA library screening, KMT2A is identified and chosen for evaluation. Knockdown of KMT2A can significantly inhibit cell viability, cell migration, formation of tumorsphere, the expression of markers of cancer stem cells, and induce cell apoptosis, which is associated with inhibited promoter activity of hTERT. Overexpression of hTERT can rescue it. Overexpression of KMT2A can effectively enhance cell proliferation in different melanoma cell lines via hTERT signaling. Upregulated expression of KMT2A predicts a poor prognosis in patients with melanoma. Taken together, KMT2A/hTERT signaling pathway can be a potential target for melanoma therapy.
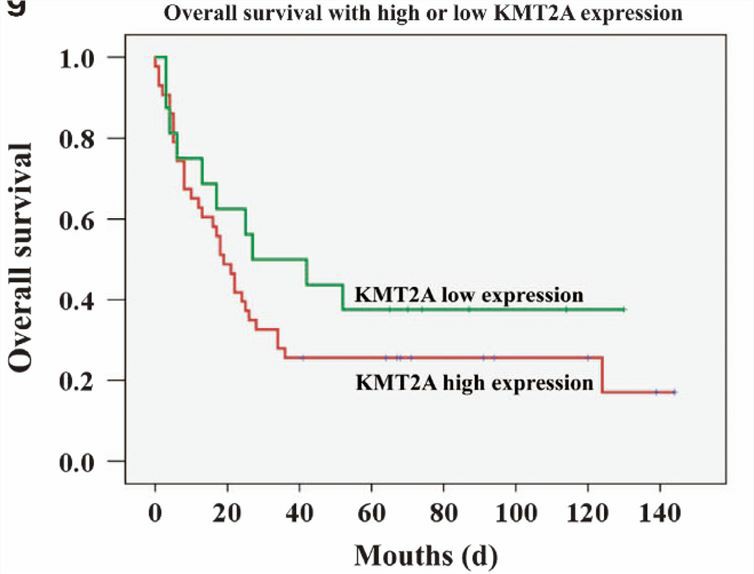 Fig.1 Patients with high expression of KMT2A have poor overall survival. (Zhang, 2017)
Fig.1 Patients with high expression of KMT2A have poor overall survival. (Zhang, 2017)
As a world-trusted biotechnology company, Creative Biolabs has a skilled team of well-trained scientists and well-established platforms. For all your questions about gene therapy, please feel free to contact us for more details about your KMT2A project.
Reference
- Zhang, C.; et al. KMT2A promotes melanoma cell growth by targeting hTERT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8: e2940–e2940. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
