COL4A1 and Associated Diseases
Description ofCOL4A1
The COL4A1 gene encodes the α-1 subunit of collagen type IV, a major structural component of basement membranes. Types I, II, and III collagen, the so-called interstitial collagens, are distinct from basement membrane collagen. Type IV collagen does not form ordered fibrillar structures; rather, a meshwork formed by 4 molecules held together at the ends. Both disulfide and typical lysyl-derived collagen crosslinks are involved. The protein encoded by the COL4A1 gene is widely distributed in diverse tissues and cell types, exerting significant actions in angiogenesis.
Scientists (Poschl, 1988) isolated and sequenced a 2.2-kb genomic fragment that contained the 5-prime terminal exons of both COL4A1 and COL4A2. The 2 genes were found to be arranged in opposite directions, head-to-head, separated only by 127 bp. The connecting segment apparently contained promoters of both genes as indicated by the existence of typical sequence motifs.
 Fig. 1 Structure of COL4A1. (Wikipedia)
Fig. 1 Structure of COL4A1. (Wikipedia)
COL4A1-Related Disorders
Collagen IV is the most abundant constituent of basement membranes of the extracellular matrix (ECM). COL4A1 mutations have been identified in vascular abnormalities, myopathy, and nephropathy.
- Porencephaly
Porencephaly is a rare neurological disease, typically manifest in infants, which is characterized by the existence of degenerative cavities in the brain. It has been demonstrated in a mouse mutant that vascular defects were caused by a semi-dominant mutation in the procollagen type IV α 1 gene (Col4a1) in mice, which inhibited the secretion of mutant and normal type IV collagen.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer. Scientists (Wang, 2020) have screened all 44 collagen members in HCC using whole transcriptome sequencing data from the public datasets, and it was collagen type IV α 1 chain (COL4A1) that was identified as the most significantly differentially expressed gene. Upregulation of COL4A1 facilitated the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells through FAK-Src signaling. The expression of COL4A1 is upregulated by runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) in HCC. HCC cells with high COL4A1 expression are sensitive to the treatment with FAK or Src inhibitor.
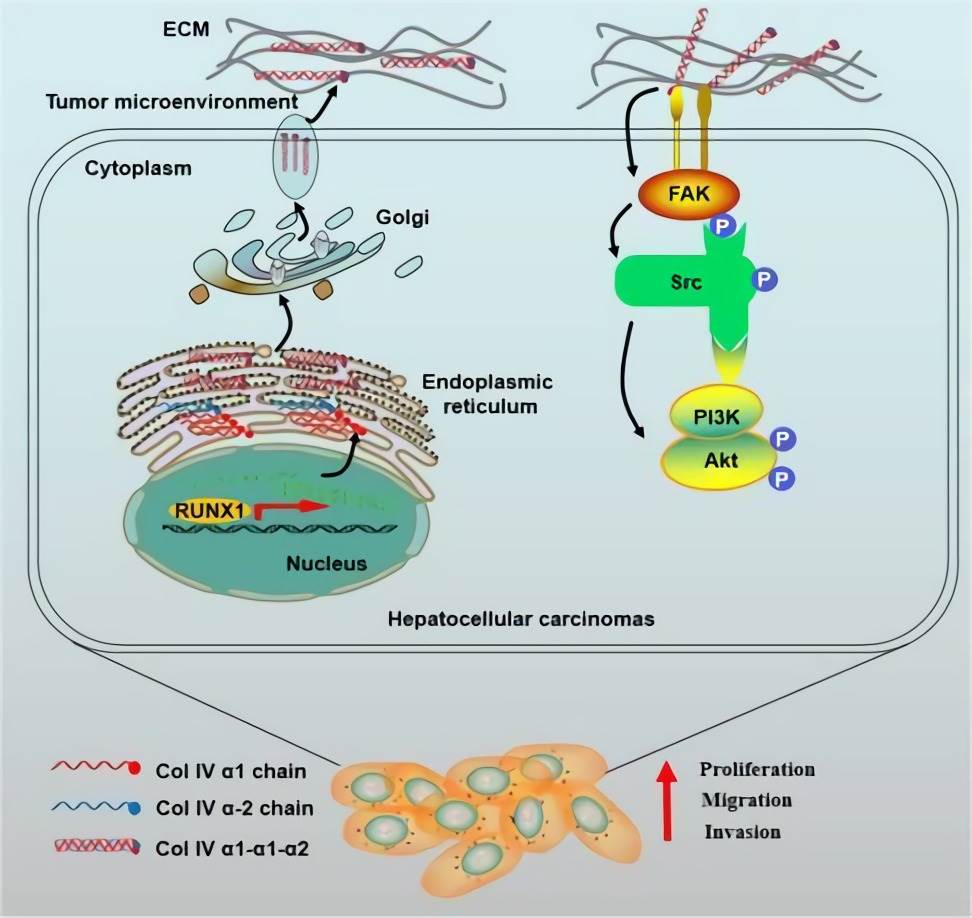 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of COL4A1 promoting the growth and metastasis of HCC cells. (Wang, 2020)
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of COL4A1 promoting the growth and metastasis of HCC cells. (Wang, 2020)
- Unexplained familial syndromes
Plaisier et al. (Plaisier, 2007) performed linkage studies involving microsatellite markers flanking the COL4A1-COL4A2 locus followed by sequence analysis of COL4A1 cDNA extracted from skin-fibroblast specimens from the subjects. By this approach, they identified 3 closely located glycine mutations in exons 24 and 25 of the COL4A1 gene. They concluded that COL4A1 may be a candidate gene in unexplained familial syndromes with autosomal dominant hematuria, cystic kidney disease, intracranial aneurysms, and muscle cramps.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide genetically modified gene therapy services to our clients all over the world. If you are interested in our Gene Editing for Gene Therapy services to study the role of COL4A1 and related disease, please feel free to contact us for more.
References
- From Wikipedia: Emw, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_COL4A2_PDB_1li1.png.
- Wang T.; et al. COL4A1 promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating FAK-Src signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020, 39(1): 148. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
