x
-
Research Models
-
Ex Vivo Tissue Model
- Ex Vivo Human Skin System Tissue Model
- Ex Vivo Neurological System Model
- Ex Vivo Human Digestive System Model
- Ex Vivo Human Musculoskeletal System Tissue Model
- Ex Vivo Human Respiratory System Tissue Model
- Ex Vivo Human Genitourinary Tissue Model
- Ex Vivo Human Endocrine System Tissue Model
- Ex Vivo Human Cardiovascular Tissue Model
- Precision-Cut Tissue Slicing Model
- 3D Spheroid Model
- 3D Organoid Model
- Organ-on-a-Chip Model Introduction
-
Ex Vivo Tissue Model
-
Services
- 3D Biology Based Biomarker Discovery Services
-
3D Biology Based Drug Discovery and Development Services
- 3D Biology Based Immuno-Oncology Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Neurological Disorder Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Inflammation & Immunological Disease Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Metabolic Disease Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Urological System Disease Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Digestive System Disease Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Ocular Disease Drug Discovery and Development
- 3D Biology Based Musculoskeletal Disease Drug Discovery and Development
-
3D Biology Based Toxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Ocular Toxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Skin Toxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Cardiotoxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Hepatotoxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology-Based Neurotoxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology-Based Nephrotoxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology-Based Gastrointestinal Toxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Phototoxicity & Photoallergy Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Pancreatic Endocrine Toxicity Evaluation Service
- 3D Biology Based Inhalation Toxicity Evaluation Services
- 3D Biology Based Oral Irritation Evaluation Services
- Supporting Assay Services
-
Products
- Body Fluids
-
Cells
- Cardiomyocytes
- Bone Cells & Chondrocytes
- Neural Cells
- Preadipocytes & Adipocytes
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs)
- Purified Immune Cell Populations
- Tissue Resident Immune Cells
- Bone Marrow-derived Cells
- Primary Epithelial Cells
- Primary Endothelial Cells
- Primary Fibroblasts
- Primary Smooth Muscle Cells
- Macrophages
- Stem Cells
- Hepatocytes and Non-Parenchymal Cells
- Islet Cells
- GFP-expressing Stable Cells
- RFP-expressing Stable Cells
- Luciferase-expressing Stable Cells
- Cas9-expressing Stable Cells
- Cre-expressing Stable Cells
- Immortalized GFP-expressing Stable Cells
- Immortalized Primary Cells
- Genetically Modified Cells
- 3D Models
- 3D Cultures
- Nucleic Acids
- Subcellular Samples
- Tissues
- Cell & Tissue Lysates
- Recombinant Proteins
- Resource
- Company
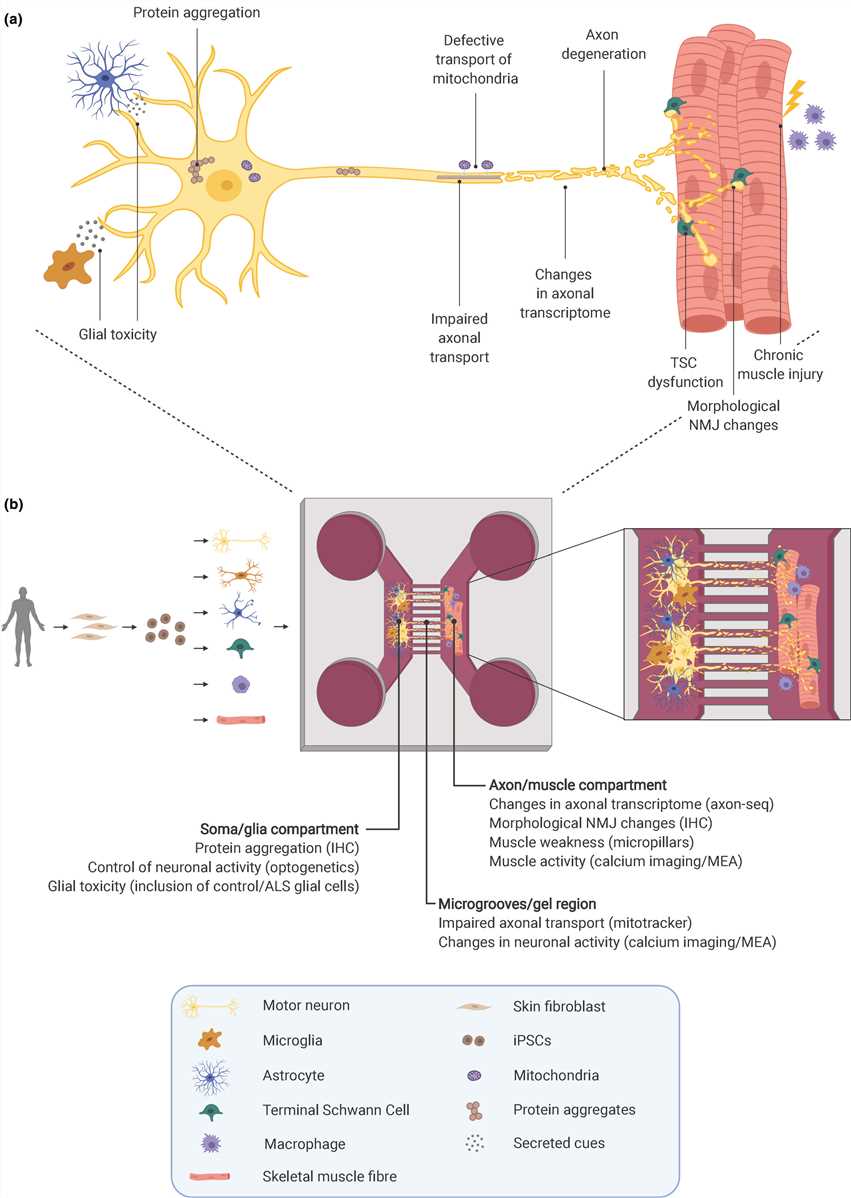 Fig 1. Analysis of ALS disease mechanisms in microfluidic devices.1
Fig 1. Analysis of ALS disease mechanisms in microfluidic devices.1