AAV/HBV induced Chronic HBV Infection Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established and comprehensive animal models to evaluate the efficacy of therapeutic interventions for Hepatitis B, including drug testing and immunotherapy evaluation. These models provide critical insights for the development of effective HBV treatments.
Introduction
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that primarily affects the liver. It can range from an acute self-limiting illness to a chronic infection that may lead to serious liver diseases, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HBV is transmitted through contact with infectious body fluids, including blood, semen, and vaginal fluids. It is a major global health concern, particularly in regions such as sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia, where it is endemic. The infection can be asymptomatic or result in symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal pain. Chronic infection can lead to persistent liver inflammation and long-term complications such as fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Despite the availability of vaccines and antiviral treatments, Hepatitis B remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Management strategies focus on antiviral therapy to reduce viral replication, alleviate liver damage, and prevent progression to liver failure or cancer. Early detection and monitoring of disease progression are critical in the management of chronic HBV infection.
Disease Models and Applications
The AAV/HBV induced Chronic HBV Infection Model is a widely used approach to study chronic hepatitis B. This model is established by using adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to deliver HBV genes into the liver, inducing persistent viral infection. AAV vectors are particularly effective due to their ability to efficiently transduce liver cells without causing significant immune reactions, making them ideal for long-term studies. This model mimics the chronic phase of HBV infection, closely resembling the disease in humans, with persistent viral replication and immune-mediated liver injury. The advantages of this model include its high reproducibility and suitability for studying the progression of HBV-related liver diseases. However, the limitation is the need for careful optimization of viral load to avoid acute immune responses, which can interfere with chronic infection. This model is critical for testing antiviral drugs, immunotherapies, and liver protective agents in preclinical stages.
- Simulates: This model simulates chronic hepatitis B infection, including HBV induced liver inflammation, viral persistence, and immune responses, closely mimicking the natural progression of the disease.
- Evaluates Drugs: The AAV/HBV induced chronic HBV infection model is used to evaluate antiviral agents, including nucleos(t)ide analogs and immune-modulating drugs, aimed at controlling HBV replication, reducing liver inflammation, and preventing fibrosis and HCC development.
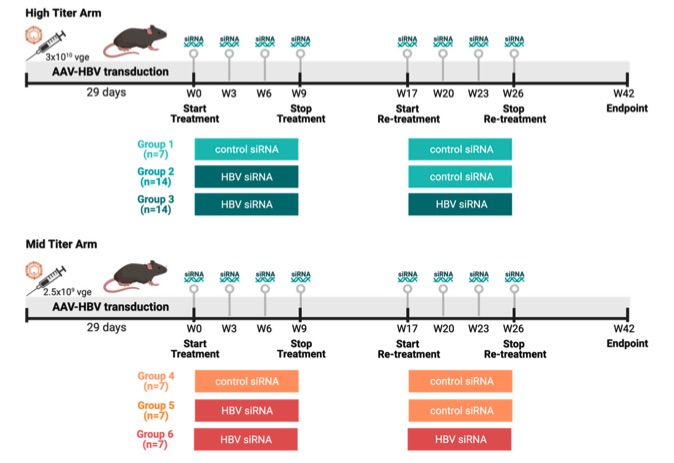 Fig.1 C57BL/6 mice were transduced with different titers of AAV-HBV.1
Fig.1 C57BL/6 mice were transduced with different titers of AAV-HBV.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the AAV/HBV induced Chronic HBV Infection Model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight, mortality rate, stool consistency, and liver function tests.
- Histopathology: Liver tissue examination for necrosis, inflammation, and fibrosis.
- Cytokine profiling: Measurement of inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β using ELISA.
- HBV DNA quantification: PCR-based methods to measure HBV replication levels in the liver and serum.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of HBV antigens and immune cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in liver tissues.
- Gene and protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blotting for viral and immune-related markers.
In addition to these established methods, we offer customizations based on the specific needs of your study, ensuring precise and tailored approaches to evaluating the effects of your candidate drugs.
Related Services
In addition to the AAV/HBV induced model, our company also offers services using other methods to induce chronic HBV infection. These include the hydrodynamic injection method, which delivers HBV DNA directly into the liver, and the transgenic mouse model expressing HBV proteins. Each method offers distinct advantages and can be chosen based on the research objectives and required outcomes.
- HBV Transgenic Mouse Model
- Hydrodynamic Injection HBV Model
- Hepatitis B Humanized Mouse Model
- Chronic Hepatitis B Woodchuck Model
Advantages
- Expertise: Our team of scientists has years of experience in developing and optimizing HBV models for drug discovery.
- Tailored Approach: We work closely with clients to customize models and experimental designs to suit specific research needs.
- Comprehensive Services: From model establishment to drug testing and data analysis, we provide a complete service package.
- High Reproducibility: Our models have been validated for reproducibility, ensuring reliable results.
- Cutting-edge Technology: We utilize the latest in molecular and imaging techniques to ensure accurate and timely data.
- Fast Turnaround: We offer efficient study timelines without compromising quality, enabling faster drug development processes.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the typical duration for a chronic HBV infection study?
Studies typically last from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the specific experimental design and drug evaluation requirements.
-
2. Can this model be used for testing immune-modulating therapies?
Yes, the model is ideal for evaluating both antiviral and immune-modulating therapies targeting chronic HBV infection.
-
3. Do you offer long-term study options?
We offer long-term studies for monitoring the progression of liver damage and fibrosis over extended periods.
-
4. How do you handle variability between animal subjects?
Our team ensures consistent results by using well-characterized strains and optimizing the model to minimize subject variability.
Published Data
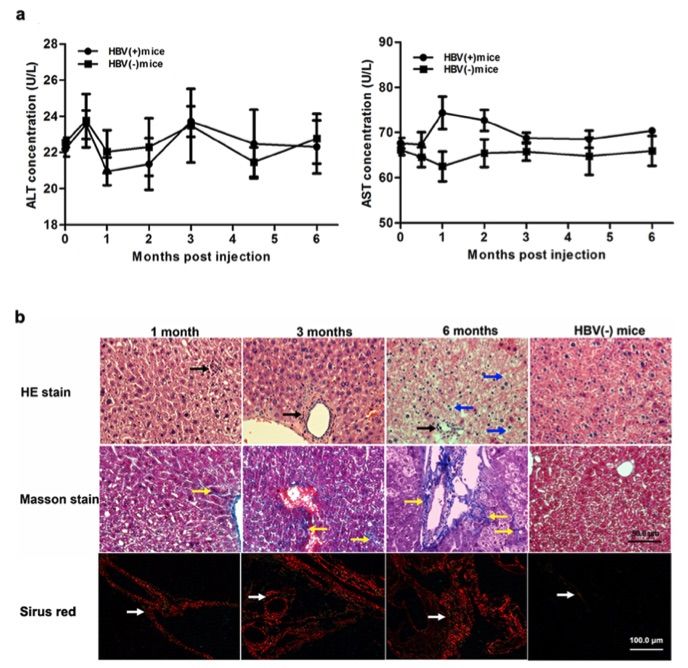 Fig. 2 Injection AAV-HBV induces chronic liver injury but not acute inflammation.2
Fig. 2 Injection AAV-HBV induces chronic liver injury but not acute inflammation.2
Compared to HBV (-) mice, AAV8-1.2HBV infection did not result in increased serum ALT levels over a 6-month period (Fig. 2a). To assess whether liver fibrosis and chronic liver injury were present following AAV8-1.2HBV transduction, histopathological changes in liver sections were evaluated at various time points using H&E, Masson's trichrome staining, and Sirius Red staining. As shown in Fig. 2b, mild inflammation and hepatic necrosis were observed. Inflammatory cell infiltration surrounding the portal area (indicated by the black arrow) was detected by H&E staining at 1, 3, and 6 months post-infection (p.i.). Hepatocytes appeared normal up to 3 months p.i. At 6 months p.i., however, significant damage to the hepatic lobular structure was observed, with ground-glass-like hepatocytes (indicated by the blue arrow) and macrovesicular steatosis degeneration. Additionally, vascular and portal areas were notably broadened.
References
- Van Gulck, Ellen et al. "Retreatment with HBV siRNA Results in Additional Reduction in HBV Antigenemia and Immune Stimulation in the AAV-HBV Mouse Model." Viruses vol. 16,3 347. 23 Feb. 2024, DOI:10.3390/v16030347. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Ye, Lei et al. "Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Mediated Delivery of the HBV Genome Induces Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Liver Fibrosis in Mice." PloS one vol. 10,6 e0130052. 15 Jun. 2015, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130052. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
