ACTN4 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating the development of gene therapy. Based on our understanding of gene therapy and potential target genes, we now describe the ACTN4 gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Overview of ACTN4
Belongs to the spectrin gene superfamily, alpha-actinin is an actin-binding protein consisting of an N-terminal actin-binding domain (ABD), four spectrin-like repeats (SRs), as well as a C-terminal EF-hands (calmodulin-like domain). Moderately calcium-sensitive ACTN4 is widely expressed as a member of the alpha-actinin (ACTN1-4) family, and the human phenotype associated with ACTN4 mutation is manifested only in the kidney.
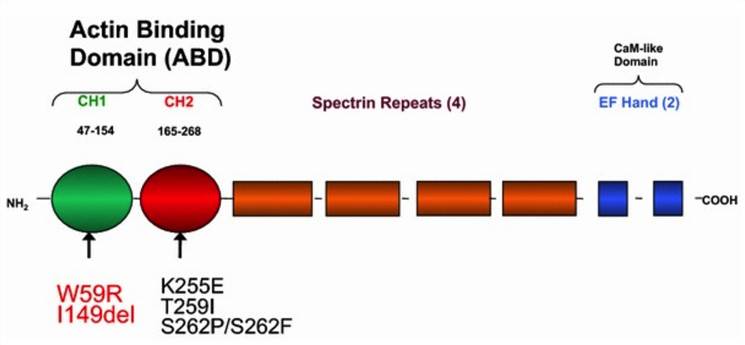 Fig.1 Functional domains of the human ACTN4 protein. (Feng, 2015)
Fig.1 Functional domains of the human ACTN4 protein. (Feng, 2015)
Functions of ACTN4
ACTN4 interacts with various proteins and plays a role in multiple cellular functions.
- Cell adhesion - Alpha actinin interacts directly with β1-integrin, vinculin, zyxin, and kindlin-1 to link the cytoskeleton with the extracellular matrix.
- Cell junction - ACTN4 acts as a linker between F-actin and other adhesion junction proteins.
- Cell signaling - ACTN4 interacts with PI3 kinase (PI3K) downstream kinase Akt to mediate cell proliferation.
- Nuclear transcription activator - ACTN4 is the transcription activator to regulate the transcription activity of multiple genes, such as the estrogen receptor (ERα), the vitamin D receptor, the myocyte enhancer factor (MEF), the androgen receptor, and the retinoic acid receptor (RAR).
ACTN4 Mutations with FSGS in Human
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a type of glomerular disease that is always associated with kidney failure and progressive chronic kidney disease. FSGS can be classified into primary and secondary forms, while secondary FSGS is caused by a variety of systemic diseases. Recent studies have shown that ACTN4 mutations are associated with FSGS and nephrotic syndrome. The identified mutations K255E, T259I, and S262P all lie within an evolutionarily conserved ABD. These mutations increase the binding affinity of ACTN4 protein to F-actin. What’s more, the mutations W59R and I149del in the ABD are also proven to be disease-causing.
In particular, compared with wild-type ACTN4, the K255E mutant ACTN4 presents greater binding affinity to F-actin and is not Ca2+ regulated in vitro. Bulk rheological experiments showed that the dissociation rate of mutant K255E ACTN4 from actin was much slower than that of wild-type ACTN4. Taken together, mutations within the ABD of ACTN4 lead to greater degradation of the protein in cells and prevent ACTN4 from acting as a transcriptional co-regulator.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Feng, D.; et al. The role of alpha-actinin-4 in human kidney disease. Cell & bioscience. 2015, 5(1): 1-7. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
