CHD4 and Associated Diseases
An overview of CHD4
As a multi-subunit complex, the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) complex participates in histone deacetylation, demethylation, and nucleosome mobilization. As shown in Figure 1, the detailed structure of the NuRD complex consists of six unique subunits, each with a different function. Among them, the chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 4 (CHD4) is a crucial protein that existed in almost all species. CHD4 is encoded by the CHD4 gene, an ATP-dependent remodeling enzyme gene that is located on chromosome 12 of the human. The protein encoded by this gene also is a member of the SNF2/RAD54 helicase family and plays a significant role in epigenetic transcriptional repression. Meanwhile, CHD4 is also of vital importance in multiple nuclear processes, such as lymphocyte development and differentiation, genome stability maintenance, chromatin assembly, DNA damage repair (DDR), cell cycle transition, and the proceeding of malignancy. Recently, increasing studies have focused on its relationship with the progression and drug resistance of tumors.
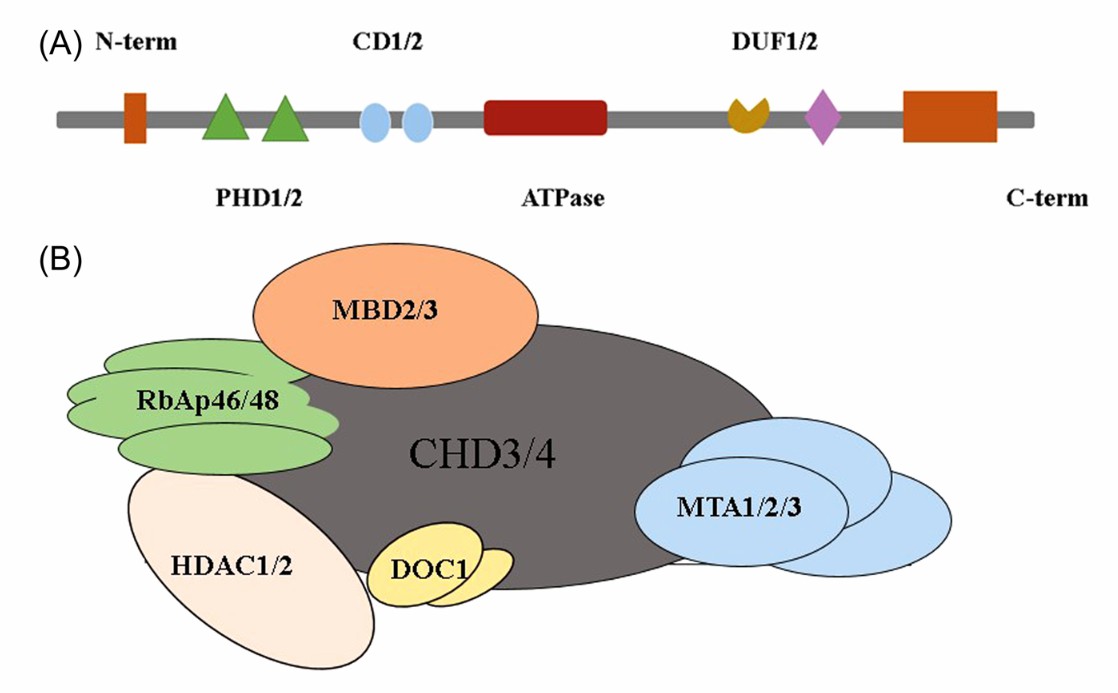 Fig.1. Structure of CHD4 NuRD complex. (Jia, 2022)
Fig.1. Structure of CHD4 NuRD complex. (Jia, 2022)
CHD4 and Associated Diseases
- Cancers
Being an important component of NuRD, CHD4 is involved in the epigenetic regulation of chromatin structure and gene expression. A large number of recent investigations have demonstrated that CHD4 could silence many tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) with the cooperation of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). Additionally, CHD4 suppression cumulatively increases DNA damage. These studies suggest that CHD4 may affect cancer behavior and treatment responses to various cancers, such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and lung cancer. Noteworthy, as mentioned in Li’s study (Li, 2017), CDH4 was identified as a proto-oncogene in some cancer, while acting as an anti-oncogene in some other cancers. The expression level of CHD4 may be an effective biomarker for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors.
- Autoimmune Diseases
Previous studies have found that CHD4 is of vital importance in the self-antigen expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells. It can organize the promoter regions of Fezf2-dependent genes and participate in the Aire-mediated induction of self-antigens via super-enhancers to eliminate autoreactive T cells. Moreover, CHD4 was recently shown to be essential for the process of lymphocyte development and differentiation by interacting with corresponding transcriptional programs. CHD4 lacking causes autoreactive T cells infiltration in the peripheral organs and B cells arresting during the B cell development stage. Seelig et al. (Seelig, 1995) first proposed CHD4 as an autoantigen in the autoimmune disease dermatomyositis (DM). Later on, many scholars have also focused on the relationship between CHD4 and autoimmune diseases. Based on the above studies, CHD4 has become a potential biomarker for autoimmune disease diagnosis in recent years.
CHD4 has become a potential biomarker candidate for human disease diagnosis. Creative Biolabs is a professional biotechnology company with a distinguished scientific team and rich experience in related research. If you have any questions about the CHD4 gene and associated diseases, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Jia, M., et al. CHD4 orchestrates the symphony of T and B lymphocyte development and a good mediator in preventing from autoimmune disease. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022, 10:e644. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
