FLT4 and Associated Diseases
Fms-related tyrosine kinase 4 encoded by the FLT4 gene is a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor, which is mainly distributed on the surface of lymphatic endothelial cells and is responsible for regulating the formation of lymphatic vessels. At present, a large number of studies have shown that the FLT4 gene plays an important role in human health and is closely related to the occurrence of various diseases. As a comprehensive solution provider, Creative Biolabs has established an all-in-one gene therapy-related research platform, which can provide more efficient gene function analysis and overall solutions for researchers engaged in gene therapy.
Function of FLT4
FLT4 is located on chromosome 5 (5q35) and contains 31 exons. Fms-related tyrosine kinase 4 encoded by the FLT4 gene is a tyrosine kinase receptor for vascular endothelial growth factors C and D. It is a single-chain transmembrane protein consisting of 1298 amino acids and forms a highly glycosylated structure. FLT4 protein, also known as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3), belongs to the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) family. The intracellular region of the FLT4 protein is a tyrosine-protein kinase region with multiple autophosphorylation sites. Phosphorylated FLT4 protein can expose its own kinase domain, thereby triggering the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathway. In addition, during embryonic development, FLT4 protein is expressed in all endothelial cells and plays an important role in cardiovascular development. However, in adulthood, FLT4 is predominantly expressed in lymphocytes and is involved in lymphangiogenesis.
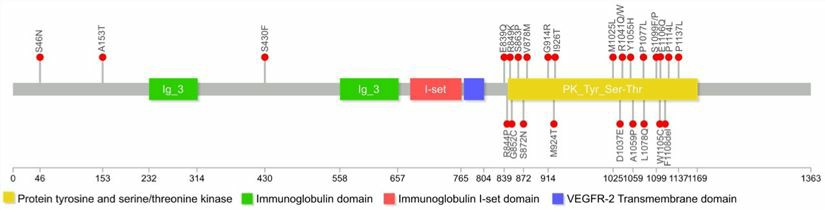 Fig.1 Schematic representation of FLT4 gene. (Liu, 2021)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of FLT4 gene. (Liu, 2021)
FLT4-related Diseases
Mutations in the FLT4 gene can cause hereditary lymphedema type IA (also known as Milroy disease). Milroy disease (MD) is characterized by swelling of the legs and feet, and fibrotic thickening of the skin on the toes. Lymphatic vessels are inconspicuous in most lymphatic images of MD patients. Current studies have shown that lymphatic dysfunction in MD patients is related to mutations in the immunoglobulin domain and protein kinase domain of FLT4 protein. In addition, FLT4 mutations were found to be associated with two lymphoid defects. One is lymphatic collector dysfunction and the other is primary lymphoid hypoplasia of the skin.
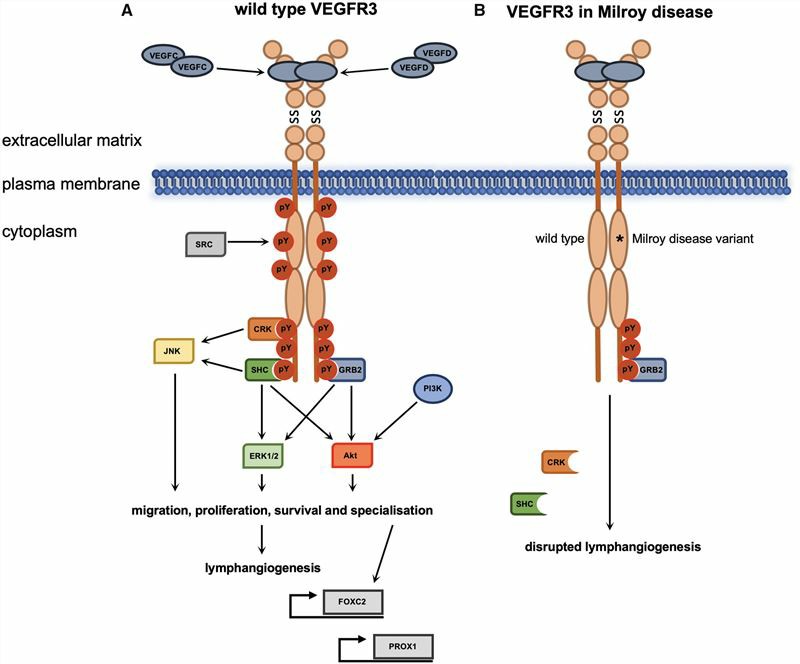 Fig.2 VEGFR3 signaling during lymphangiogenesis and Milroy disease. (Monaghan, 2021)
Fig.2 VEGFR3 signaling during lymphangiogenesis and Milroy disease. (Monaghan, 2021)
FLT4 protein also plays an important role in the formation and development of tumor lymphatic vessels. A large number of studies have shown that FLT4 protein is expressed in a variety of malignant tumors such as colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and liver cancer. When FLT4 protein is combined with its ligand VEGF-C, FLT4 protein can promote tumor growth and metastasis, tumor lymphangiogenesis, and tumor lymph node metastasis. Therefore, FLT4 is a new target for the treatment of tumors.
Creative Biolabs continues to strengthen itself and continues to invest in many aspects such as hardware facilities, technology platforms, talent teams, and innovation exploration. With an advanced nucleic acid-targeting research platform, we are willing to help with gene research projects. If you have an idea for disease treatment research on FLT4 or other genes, please contact us to further discuss your proposal to help you accelerate your progress.
References
- Liu, N.; Gao, M. FLT4 Mutations are associated with segmental lymphatic dysfunction and initial lymphatic aplasia in patients with milroy disease. Genes. 2021. 12(10). Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Monaghan, RM.; Page, DJ.; et al. The physiological and pathological functions of VEGFR3 in cardiac and lymphatic development and related diseases. Cardiovascular Research. 2021. 117(8):1877-1890. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
