ROCK1 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs provides products and technical services used in a variety of research and preclinical applications, and our team of experts provides the flexibility needed for the project solutions at competitive prices and fast turnaround times, while still maintaining the quality our customers expect to meet their needs to the greatest degree.
Backgrounds of ROCK1
Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) is a member of the Ras protein family, it is located on chromosome 18 (18q11.1), encoding a 1354-amino acid protein. ROCK1 is a significant effector kinase of the small GTPase RhoA. It plays an important regulatory role in the growth and survival of cancer cells as well as the invasion and metastasis of tumors. ROCK1 is a downstream signaling effector of RhoA, which is widely expressed in various tissues of noncentral systems. It is mainly expressed in non-neuronal tissue and ROCK2 is expressed in the brain and the spinal cord abundantly and improves with age. In addition, it is highly expressed in various cancer tissues and regulates apoptosis in various types of cancer cells.
Functions of ROCK1
ROCK1 is a multifunctional protein that regulates many cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, contraction, migration, metabolism, apoptosis, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. ROCK1 activation is required for calcineurin activation. It is required for maintaining the cell proliferation of malignant osteoblasts. Additionally, ROCK1 could regulate insulin resistance, adiposity, and hepatic lipid accumulation. It also is a central player in the formation of stress fibers.
Different Expression of ROCK1 in Diseases
ROCK1-mediated oncogenic characteristics in various tumors have been demonstrated by a dominant active mutant of ROCK1, which enhanced the invasion of cancer cells and direct phosphorylation of myosin light chain, which leads to increased cell migration and invasion, activation of AKT/mTOR/eIF4E signaling pathway, up-regulation of M-CSF cytokines, and promotion of osteolysis and metastasis. The effect of ROCK1 knockout on the growth, proliferation, and apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells may be mediated by the regulation of cytoskeletal actin-myosin contraction. ROCK1 defects lead to delayed maturation of bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) stimulated by IL-3 and slowed the growth of stem cell factor (SCF) stimulated cells. The reduction in neuronal ROCK1 protein leads to reduced neuronal PTEN phosphorylation and subsequently causes impairment of neuronal tau dephosphorylation. ROCK1 knockdown decreased amyloid precursor protein (APP), and treatment with bafilomycin accumulated APP levels in neurons depleted of ROCK1. In the past, dysregulated ROCK1 level has been reported in many metabolism-related disorders, including obesity, diabetes, and NAFLD.
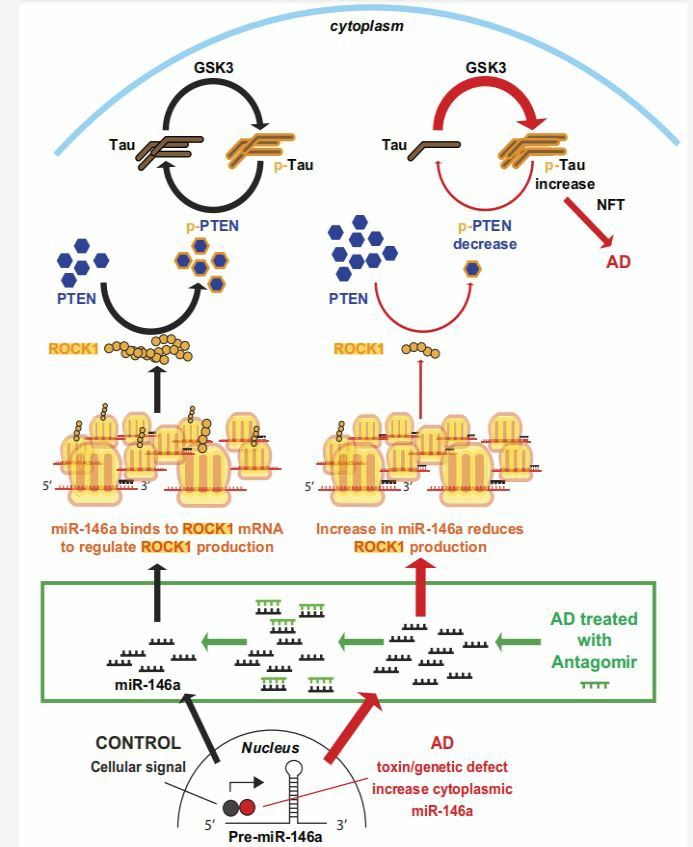 Fig.1 A model of the proposed inductive effects of microRNA-146a in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). (Wang, 2016)
Fig.1 A model of the proposed inductive effects of microRNA-146a in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). (Wang, 2016)
Creative Biolabs' mission is to help biomedical researchers save time and cost to accomplish their research goals. We have an experienced and highly skilled team of multi-professional scientists who can provide the best advice and solutions at any stage of the project without any concern for the quality of delivery. Contact us now to discuss your project, or just to learn about our gene therapy services.
Reference
- Wang, G.; et al. MicroRNA-146a suppresses ROCK1 allowing hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports. 2016, 6(1): 1-12. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
