In Situ MicroRNA Detection Service
Overview of microRNA
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNAs (18–22 nucleotides) that influence genes by modifying mRNA stability or translation. MiRNA levels have been shown to be closely related to the development of cancer, cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, and a variety of other illnesses. Therefore, miRNAs can be considered as diagnostic and prognostic markers of diseases. However, in situ analysis of miRNA expression remains challenging due to their short length and low expression levels. There is an urgent need to establish an in situ microRNA detection platform to assist in cancer therapy and other pathologies.
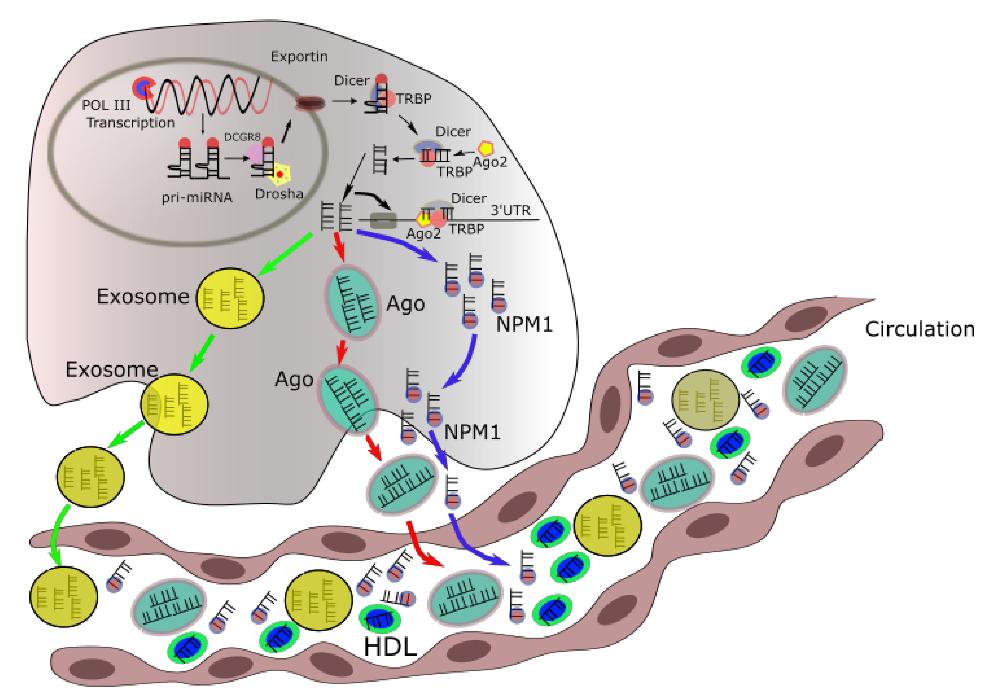 Fig.1 Mechanism of microRNA synthesis. 1
Fig.1 Mechanism of microRNA synthesis. 1
Our In Situ MicroRNA Detection Service
Creative Biolabs succeeded in providing in situ microRNA detection services by using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). We combine an array of fluorescent pre-labeled probes with corresponding microRNA targets to produce a powerful fluorescent signal, while the unbound ones will not produce a strong signal. Throughout the process, factors such as incubation time, temperature, and washing conditions need to be optimized according to the project to obtain better results. Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive customized optimized services to ensure the desired results for each customer.
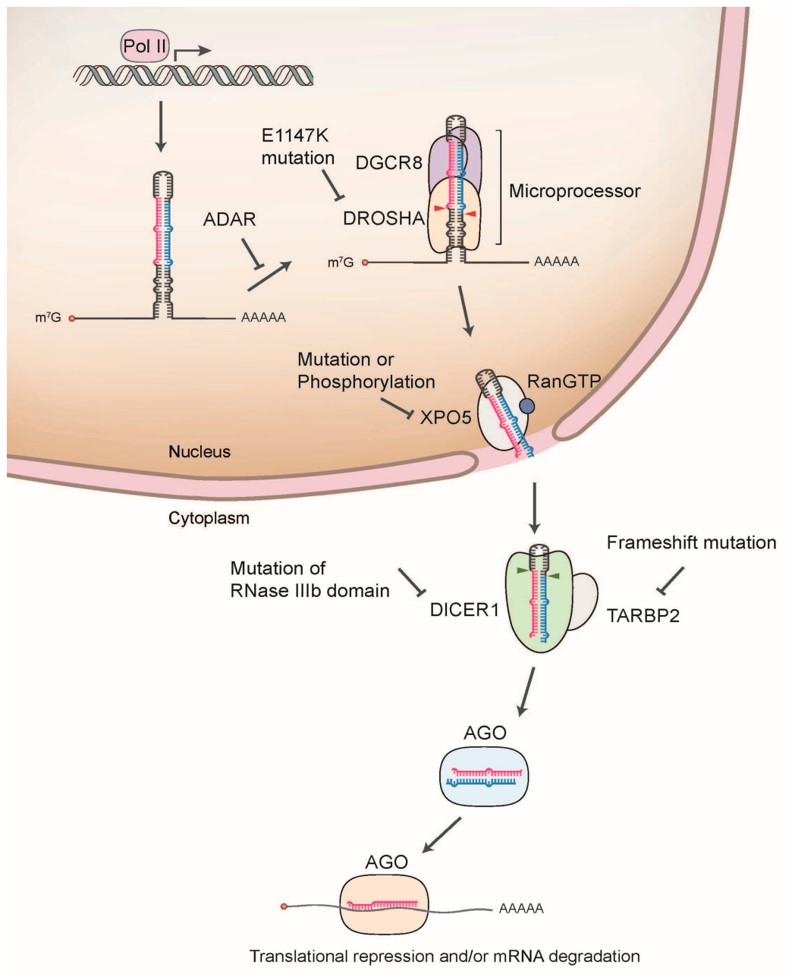 Fig.2 Schematic illustration of miRNA biogenesis dysregulation in cancer.2
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of miRNA biogenesis dysregulation in cancer.2
Workflow of Our In Situ MicroRNA Detection Service
Creative Biolabs provides a one-stop customized in situ microRNA detection service with long-term practical experience and novel technologies to ensure the ideal results for each customer.
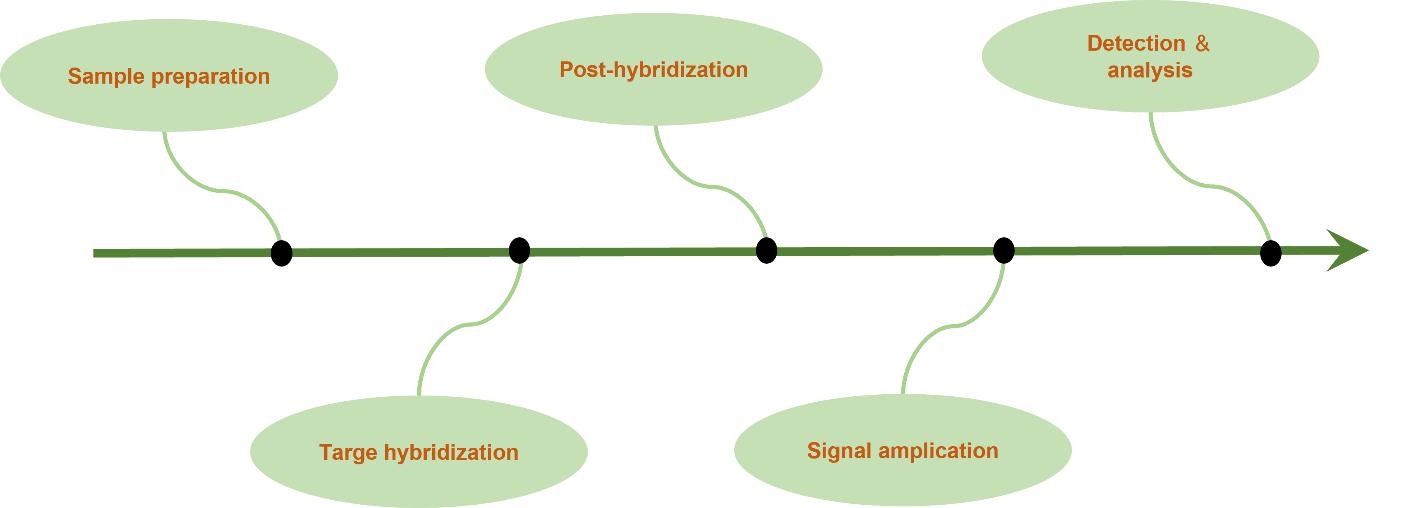 Fig.3 Our in situ microRNA detection service workflow. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.3 Our in situ microRNA detection service workflow. (Creative Biolabs)
Our Highlight Features
|
Excellent efficacy and specificity for detecting low-abundance miRNAs Our probes optimized with Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) and others can realize excellent sequence specificity, low secondary structure, and minimum self-annealing, which leads to higher binding affinity along with extremely precise and sensitive detection of miRNA. |

|

|
Multiple available microRNA target probes enable multiplexing and co-localization We have a wide range of available microRNA target probes to choose from, including but not limited to: microRNA-122a, microRNA-124a, microRNA-138, microRNA-375, microRNA-377, microRNA-168a..... |
|
Highly experienced scientists guarantee each customer's project executes smoothly Our professionals have years of expertise in detecting microRNA in situ and stick to the high-quality standards utilized in RNA research to satisfy global customers. |

|

|
Comprehensive customized services to empower our in situ microRNA detection services We provide customized in situ microRNA detection services covering probe designing to results analysis with state-of-the-art technologies. |
Published Data
Here are some representative published data displays.
The study found that HmiRR (Heat-induced microRNA Retrieval) utilizing TRS pH 9 (Target retrieval solution pH 9) pH 9 with or without pepsin digestion presents solid results, with the highest microRNA hybridization efficiency after lengthy formalin fixation (range 100-144 h).
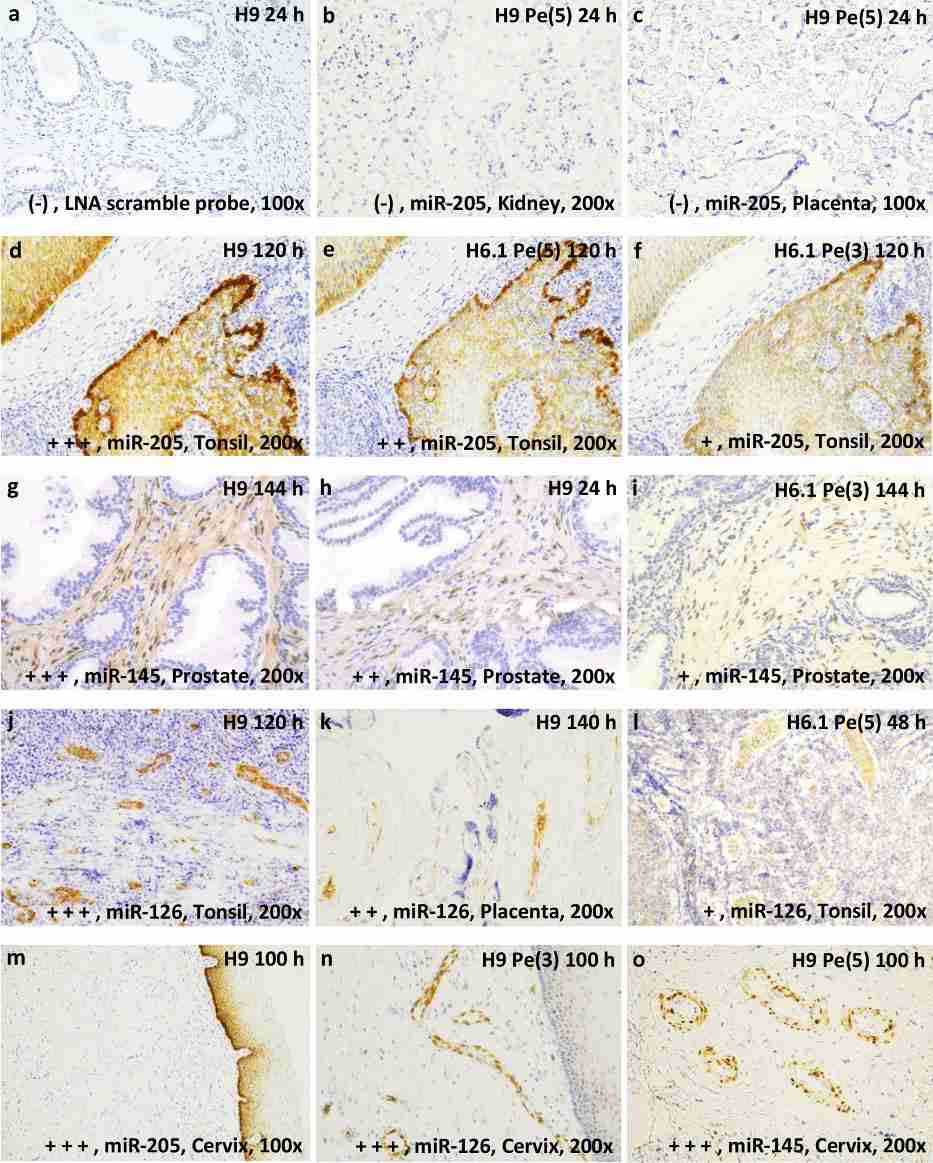 Fig.4 miRNAs hybridization images of the scoring scale. 3
Fig.4 miRNAs hybridization images of the scoring scale. 3
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is in situ microRNA hybridization detection?
A1: In situ hybridization is an excellent approach to determine the cellular location of mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs. This method is a visualization method that can simultaneously detect, localize, and quantify individual miRNA molecules at the cellular level.
Q2: What benefits do numerous pairs of probes offer over only one pair, as is required for a gene?
A2: The length of the RNA sequence to be detected is often taken into account while designing the number of probes. A minimum of three pairs of probes will typically be designed for short sequences. Multiple probes' targeting advantages can be compatible with fragmented or partially degraded RNA, and they can also lessen the poor gene detection caused by insufficient steric hindrance exposure of some target segments, increasing the detection efficiency and sensitivity.
If you are interested in our in situ microRNA detection service, please contact us with no hesitation.
References
-
Ho, Phuong TB, Ian M. Clark, and Linh TT Le. "MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy." International journal of molecular sciences 23.13 (2022): 7167.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. -
Ali Syeda, Zainab, et al. "Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in cancer." International journal of molecular sciences 21.5 (2020): 1723.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. -
Paulsen, Isabella W., et al. "A novel approach for microRNA in situ hybridization using locked nucleic acid probes." Scientific Reports 11.1 (2021): 4504.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
