AP2A1 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating the development of gene therapy. Based on our understanding of gene therapy and potential target genes, we now describe the AP2A1 gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Overview of AP2A1
Adaptin proteins (APs), also known as clathrin adaptor proteins, are membrane-bound heterotetrameric complexes located in cell buds and vesicles. APs are ubiquitously expressed in eukaryotes and are highly conserved. APs can be divided into five types, AP1, AP2, AP3, AP4, and AP5. They complete the post-TGN trafficking together. Among them, AP1, AP2, and AP3 are the most abundant APs that have been identified in various organisms. Compared with AP1 and AP3, the AP2 complex has relatively few isoforms, including AP2A1, AP2A2, AP2B1, AP2M1, and AP2S2. The AP2 complex is a heterotetramer with a small adaptin (sigma), a medium adaptin (mu), and two large adaptins (alpha or beta). Encoded by the AP2A1 gene that is located on chromosome 19q13.3 and consisting of 24 coding exons and 23 intervening introns., AP2 complex subunit alpha-1 can be observed in clathrin-coated vesicles.
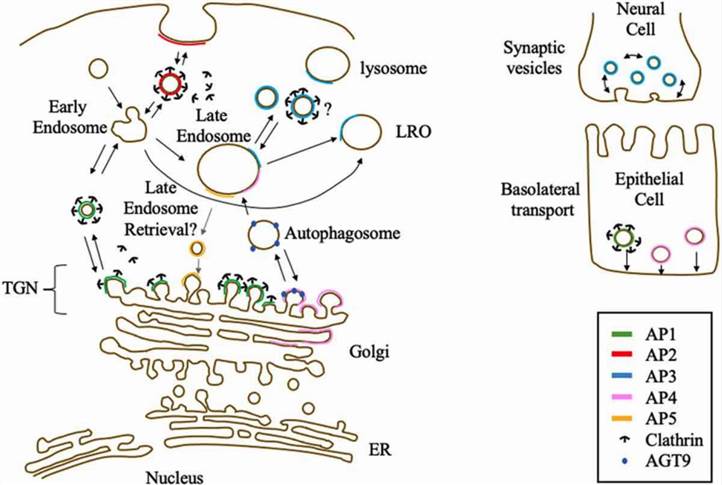 Fig.1 APs known or suggested locations and functions. (Shin, 2021)
Fig.1 APs known or suggested locations and functions. (Shin, 2021)
Functions of AP2A1
The ability of AP2A1 to recognize and bind cargo proteins, clathrin, and accessory proteins makes it critical for clathrin-dependent endocytosis. As part of the protein coating on the vesicle cytoplasm, it links clathrin to receptors in the vesicle. Furthermore, it has been proposed that AP2A1 mediates binding to the plasma membrane and acts as a scaffold for endocytosis accessory proteins. Furthermore, due to its unique peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha responsive domain, AP2A1 has a partially non-redundant function to increase fatty acid oxidation in adipose tissue by interacting with syndecan-2.
AP2A1 Associated Diseases
Studies have shown that AP2A1 is involved in a variety of cellular processes, including synaptic vesicle recycling pathways, neural cell development, differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells, cellular defense, and related neurodegenerative diseases. Aberrant expression of AP2A1 has been implicated in the pathology of various cancers and serves as an important candidate biomarker gene, such as ovarian cancer, pediatric medulloblastoma, and Alzheimer's disease. Further research on AP2A1 may help to better understand and target specific diseases.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Shin, J.; et al. Role of adaptin protein complexes in intracellular trafficking and their impact on diseases. Bioengineered. 2021, 12(1): 8259-8278. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
