ARID4A and Associated Diseases
AT-rich interaction domain containing 4A (ARID4A), also known as retinoblastoma-binding protein 1 (RBBP1), and its homologue RBBP1L1 (ARID4B) are two well-known leukemia and tumor suppressors. Both of them contain an AT-rich interacting domain and specifically interact with pRB. ARID4A modulates the methylation of lysines in histones H3 and H4 as well as other epigenetic marks in vivo. ARID4A also acts as a bridging molecule that recruits the histone deacetylase HDAC and exhibits HDAC-dependent/independent activity inhibition. Dysfunction of ARID4A may lead to a series of serious diseases.
ARID4A and Prader-Willi/Angelman Syndrome
Both PWS and AS result from the defective genomic imprinting on the parental chromosome 15q11–q13. Genomic imprinting in patients is infected by a bidirectional cis-acting imprinting center (IC) upstream of the SNRPN promoter. The rule of ARID4B and ARID4A act as Rb-binding proteins to regulate IC imprinting has been confirmed. Gene knockout experiments revealed that combined deficiencies of ARID4A and ARID4B altered the modification of PWS/AS-IC epigenetically, resulting in inhibited trimethylation of histones H3K9 and H4K20, respectively. These results suggest the ability of both to interact with the SNRPN and act as a protein complex to regulate PWS/AS genomic imprinting.
ARID4A and Leukemia
The evolution of leukemia is a long-term process with many steps from premalignant to malignant, which includes epigenetic changes and histone modifications. Previous experiments have demonstrated the roles of ARID4B and ARID4A in the genesis of leukemia. Young mice deficient in ARID4A were unable to produce efficient blood cells, which resulted in mononucleosis, decreased platelets, bone marrow function impairment and fibrosis, and anemia. The study confirmed that ARID4A deficiency can lead to induced hematopoiesis in mice, and then transform into chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and eventually AML, which is very similar to the evolution of human leukemia.
ARID4A and other Diseases
ARID4A is an important epigenetic marker regulatory gene. In addition to PWS/AS and leukemia, related studies have also confirmed the role of ARID4A in male fertility. Mice lacking ARID4A completely lose male reproductive ability and gonadal function, meaning that ARID4A supports spermatogenesis, establishment of the blood-testis barrier, and plays an integral role in the AR/RB regulatory pathway that supports the regulation of cell function and male fertility.
The sequencing study of ARID4A found that its function is realized through several unique structural domains. Five important domains have been identified, including the ARID domain, the chromo barrel domain, the Tudor domain, the PWWP structure and the R2 domain. These domains fold independently and do not interact directly. Among them, the chromo barrel domain can recognize methylated lysine and histone, and the R1 domain located in the ARID region is responsible for its gene repression ability, and the direct interaction between the R1 domain and DNA will lead to non-HDAC-dependent repression. Furthermore, the R2 domain located c-terminal to ARID4A can interact with SAP30 and produce HDAC-dependent inhibition.
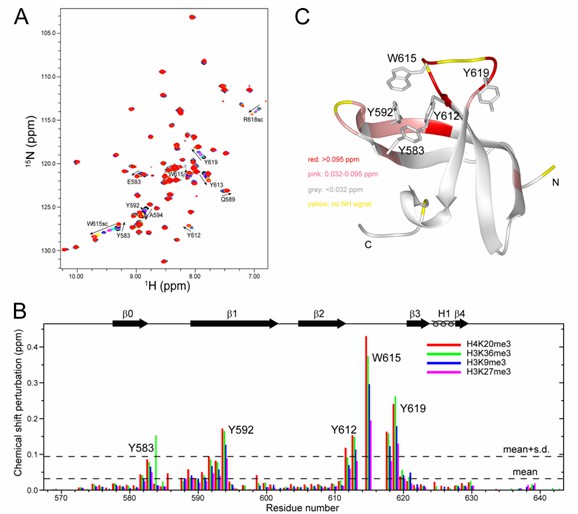 Fig.1 Recognition of the RBBP1 CD by methylated histone tails. (Gong, 2012)
Fig.1 Recognition of the RBBP1 CD by methylated histone tails. (Gong, 2012)
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing the best service to our clients. With our support, you can fully explore the infinite possibilities between ARID4A and associated diseases. With the help of our well-trained staff, you are free to choose a variety of standardized molecular biology experiments, or develop new protocols that suit your project. Please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Gong, W.; et al. Structural insight into recognition of methylated histone tails by retinoblastoma-binding protein 1. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2012, 287(11): 8531-8540. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
