In Situ Hybridization Detection Service for Circular RNAs
With established specific platforms and reliable strategies for circRNAs, Creative Biolabs can design the probe and develop the in situ hybridization (ISH) detection assay for our clients.
Introduction of Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
To identify the RNAs of interest, ISH employs an oligonucleotide probe attached to various tags, including alkaline phosphatase, fluorescent dyes, or an antigen, such as digoxigenin. The method coupling a fluorescent dye called FISH, specific RNA targets including circRNAs may be identified, located, and visualized in fixed cells or tissues. FISH can characterize gene spatiotemporal expression patterns in these.
Experimental Procedures
The procedure of FISH for circRNA detection can divide into the following steps: probe design, sample preparation, hybridization, washing, and observation.
 Fig.1 The working flow of FISH.
Fig.1 The working flow of FISH.
- Probe design
The probe designed to target the region excluding the backsplice junction (BSJ) can bind to the circRNA and its linear counterpart, whereas the one spanning BSJ can only detect the circRNA since BSJ is the unique region owned by circRNA during the looping. Based on this, a BSJ-spanning probe with a fluorescent dye is usually designed to specifically detect the circRNA.
- Sample preparation
The tissue or cells at the appropriate stage according to your experimental purpose will be chosen to fix. 4% formaldehyde or paraformaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline is commonly used. After fixation, samples are permeabilized to hybridization reagent penetration, the addition of detergents such as Tween-20 can further enhance it. FISH also successfully fits with unfixed cells.
- Hybridization
Hybridization is the most critical step during the FISH. Temperature, salt concentration, pH, and incubation of the hybridization reaction will influence the results. After confirmation of the reaction conditions, the target-specific probe will be used to hybridize the target RNA. Signal amplification is required when the fluorescence signal is weak.
- Washing & Observation
To decrease background signals, the washing process seeks to eliminate unwanted hybrids and unbound probe molecules from the samples. At this step, autofluorescence in tissues or cells is normally reduced by the use of ethanol. The specimen is examined under a fluorescent microscope at the final of the test.
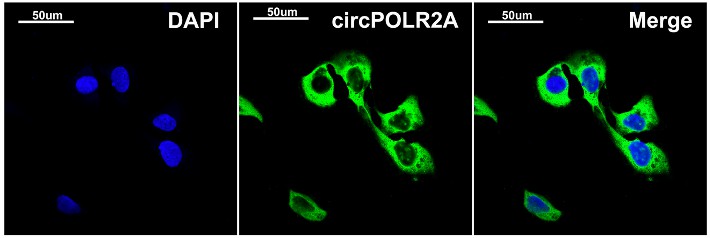 Fig.2 CircPOLR2A is located in cell cytoplasm verified by FISH.1
Fig.2 CircPOLR2A is located in cell cytoplasm verified by FISH.1
Key Features
- Fast and efficient.
- Extensive molecular information is available.
- Can be applied to genome-wide screening.
- Suitable for a variety of tissues and cell cultures.
In order to satisfy all of your circRNAs analysis needs, Creative Biolabs, a respected biotech firm, specializes in circRNAs, builds a knowledgeable team of skilled experts, and establishes a clear methodology in this field. Please feel free to contact us for more details about your project involving circRNAs analysis.
Reference
- Xu, Zhipeng, et al. "Circular RNA circPOLR2A promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by facilitating the UBE3C-induced ubiquitination of PEBP1 and, thereby, activating the ERK signaling pathway." Molecular Cancer 21.1 (2022): 146.
