CSE1L and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating the development of gene therapy. Based on our understanding of gene therapy and potential target genes, we now describe the CSE1L gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Overview of CSE1L
Chromosomal segregation 1 like (CSE1L), also known as cellular apoptosis susceptibility (CAS) and exportin-2, is a cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein that is highly expressed in a variety of cancers. It is first identified as the gene that confers resistance to immunotoxins in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Homologous to the yeast CSE1 gene, CSE1L encodes a protein with 971 amino acids distributed in the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells.
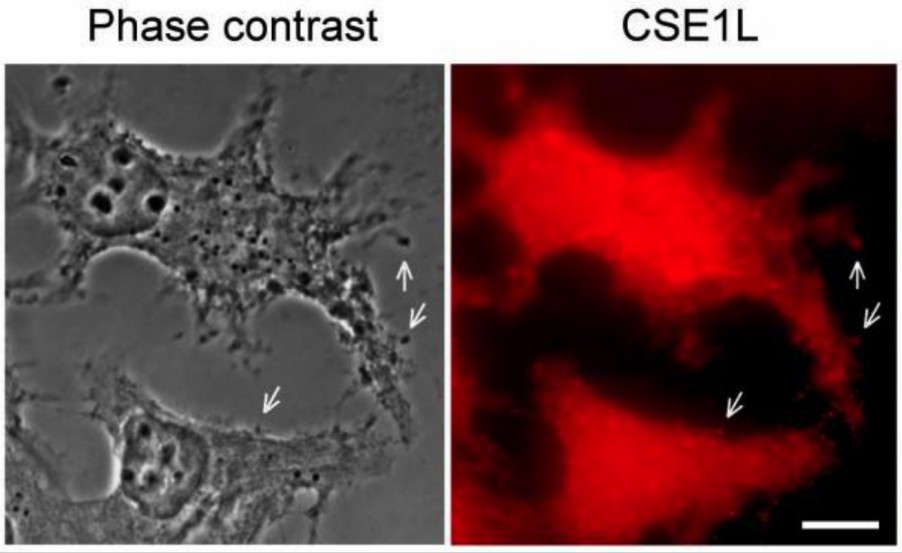 Fig.1 CSE1L staining in vesicles surrounding the outside of the cell membrane. (Tai, 2010)
Fig.1 CSE1L staining in vesicles surrounding the outside of the cell membrane. (Tai, 2010)
Functions of CSE1L
CSE1L is essential for cell survival, and serious consumption of CSE1L can lead to cell death. As one of the central apoptosis executive molecules, the CPP32 apoptosis pathway is involved in CSE1L-mediated cancer cell apoptosis. Through a vector of antisense CSE1L cDNA, it has been demonstrated that CSE1L mediates apoptosis restricted to selected apoptotic stimuli, such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribosylating toxin and tumor necrosis factor. In addition, recent studies suggest that CSE1L may be associated with p53 target promoters, and reduced CSE1L expression inhibits p53-mediated transcription, thereby reducing apoptosis.
Paclitaxel treatment blocks or prolongs cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle during apoptosis induction and induces microtubule aster formation in apoptotic cells. Microtubules are the target of paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in cancer cells, and CSE1L is a microtubule-associated protein. Increased CSE1L expression inhibited paclitaxel-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest and intracellular microtubule aster formation thereby inhibiting paclitaxel-induced apoptosis.
CSE1L Expression in Cancer
High-level expression of CSE1L can be observed in a series of different cancer types, and the expression level of CSE1L is positively correlated with high tumor stage, high tumor grade, and poor prognosis in cancer patients. For example, strong expression of CSE1L can be detected in hepatocellular carcinoma but not in normal hepatocytes.
It is worth noting that increased CSE1L expression can not enhance the proliferation of cancer cells but may play an important role in regulating cancer metastasis and progression. CSE1L regulates most chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Recent studies showed that CSE1L plays an important role in regulating the chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis of cancer cells. In this case, CSE1L is a promising target to screen more effective anticancer agents and to develop strategies with improved cancer chemotherapy efficacy.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Tai, C.J.; et al. Cellular apoptosis susceptibility (CSE1L/CAS) protein in cancer metastasis and chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2010, 29(1): 1-9. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
