MYO9B and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs, with excellent scientists and advanced platforms, can provide one-stop and detailed customer service and the most optimal strategies to solve all your questions in the field of gene therapy.
Overview of MYO9B
In humans, myosin-IXb (MYO9B, also known as CELIAC4 or MYR5) is a protein encoded by MYO9B. MYO9B is a member of the myosin family, which is molecular motor heavy chain proteins based on actin. In the neck domain of MYO9B, calmodulin can bind to four IQ motifs as a light chain. This protein complex contains a single-headed structure and can move on the actin filaments toward the minus end. MYO9B also has rho-GTPase activity. Differing from the conventional non-muscle myosin-9, MYO9B is an unconventional myosin.
MYO9B in Disease
Diseases associated with MYO9B include celiac disease, inflammatory bowel diseases, osteoporosis, and type 1 diabetes.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases
Single nucleotide polymorphisms of MYO9B are associated with the risk of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). IBD is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes relapse and remission of the intestinal tract. IBD can classify into two clinical syndromes of ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD). According to the meta-analysis of ten studies, five MY09B gene polymorphisms are evaluated. The rs1545620 polymorphism is related to a decreased risk of IBD. So does rs2305767. The rs962917, rs1457092, and rs2305764 are linked to the increased risk of IBD. To sum up, SNPs in MY09B are significantly associated with the risk of IBD with contradictory results.
- Osteoclasts and osteoporosis
The RhoGAP activity of MYO9B plays a key role in the regulation of osteoclasts. Osteoclasts, derived from the monocyte-macrophage lineage, are large multinucleated cells, which degrade or resorb bone in response to various external signals such as small GTPase Rho. MYO9B contains a RhoGAP domain and regulates osteoclast function as an inhibitor of Rho signaling in osteoclasts. The siRNA-based knockdown of MYO9B results in increased activity of Rho and decreased bone resorptive capacity. The decreased resorption can be reversed with the addition of a Rho inhibitor. Excessive bone resorption results in osteopenia and osteoporosis. Taken together, MYO9B acts as a critical regulator of osteoclast function.
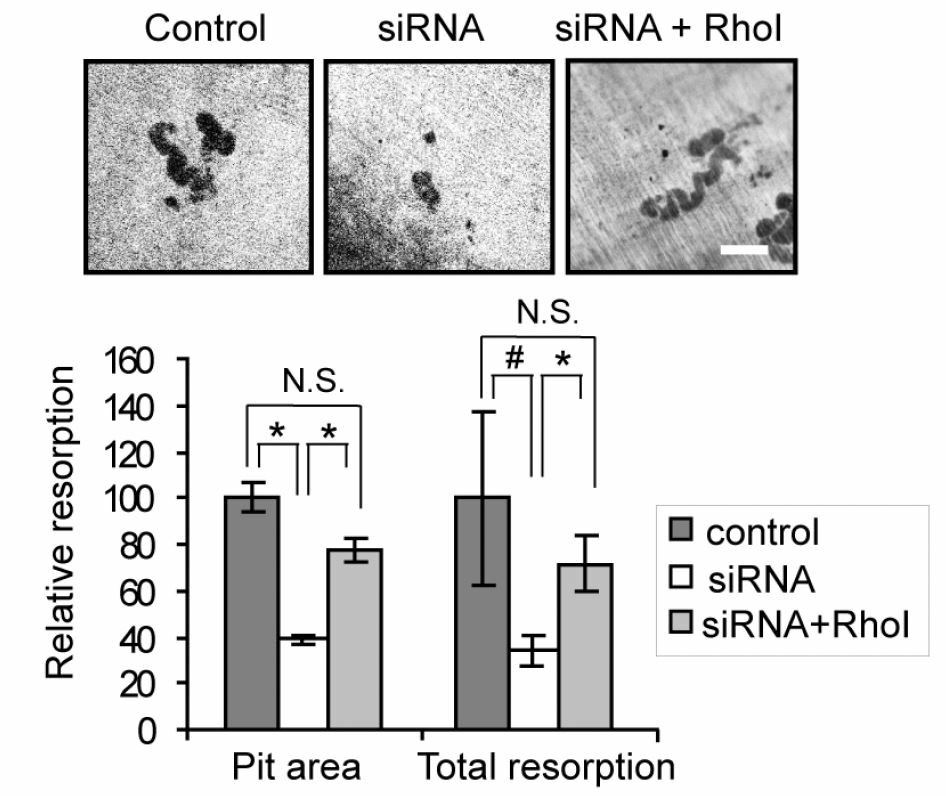 Fig.1 Knockdown of MYO9B causes the loss of bone resorptive capacity in a Rho-dependent way. (McMichael, 2014)
Fig.1 Knockdown of MYO9B causes the loss of bone resorptive capacity in a Rho-dependent way. (McMichael, 2014)
As a leader in biotechnology service providers, Creative Biolabs can provide end-to-end services of gene therapy for our clients. Each of the magnificent strategies is conducted by our well-trained technicians with years of experience in gene therapy. Please feel free to contact us for more details about your MYO9B project.
Reference
- McMichael, B. K.; et al. The RhoGAP Activity of Myosin IXB Is Critical for Osteoclast Podosome Patterning, Motility, and Resorptive Capacity. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9: e87402. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
