PKN2 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is one of the well-recognized experts who are professional in applying advanced one-stop drug discovery platforms for a broad range of project objectives. Here we describe the PKN2 gene and associated diseases for our clients. We are able to provide technical support services at all stages of your drug development.
Introduction of PKN2
Encoded by the PKN2 gene, Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 are the enzyme expressed in both humans and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. As a member of the Protein Kinase N (PKN) family, the expression of PKN2 can be detected in tissues throughout the body. First described in 1994, PKN2 plays important roles in multiple cellular pathways, such as cell cycle progression, cell adhesion, cell migration, and transcription activation signaling processes.
PKN2 and Cancers
Studies have shown that PKN2 is involved in tumor cell migration, invasion, and apoptosis. In experiments with HeLa cells, PKN2 regulates mitotic entry and cytokinesis. Furthermore, PKN2 can regulate the velocity and direct motility of urothelial cells during cell migration and tumor cell invasion. Thus, PKN2 may affect differentiation during prostate cancer progression. In addition, high expression of PKN2 has been detected in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Recent studies have shown that the expression of PKN2 can inhibit the growth of colon cancer cells by inhibiting the polarization of TAMs into M2.
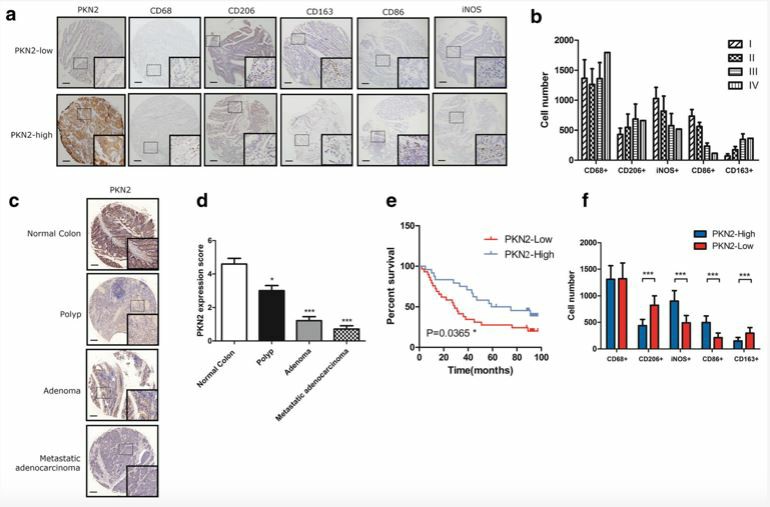 Fig.1 Overexpression of PKN2 is associated with better clinical outcome and high M1 content in human colon cancer. (Cheng, 2018)
Fig.1 Overexpression of PKN2 is associated with better clinical outcome and high M1 content in human colon cancer. (Cheng, 2018)
PKN2 and Heart Diseases
In humans, PKN2 is necessary for embryonic development. As a potential effector of the Rho signaling pathway, PKN2 binds to tyrosine phosphatases via a PDZ domain. In mouse models, knockout of PKN2 causes mesoderm expansion, failure of heart development and neural tube closure, and ultimately death. Furthermore, loss of PKN2 in cardiomyocytes severely affects ventricular myocardium development, and abnormalities in PKN2 signaling may lead to congenital heart disease/cardiomyopathy. In this case, PKN2 has been served as the potential therapeutic target against heart diseases.
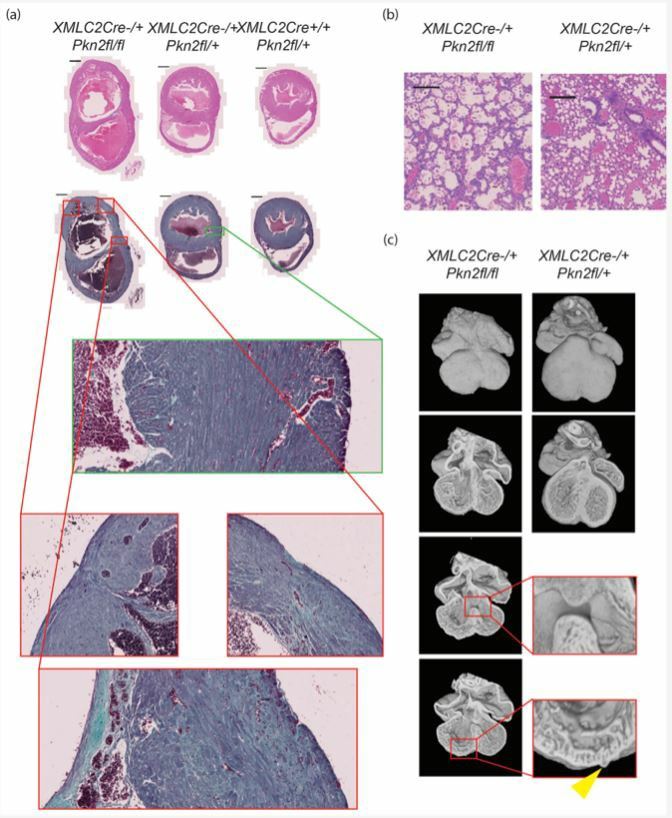 Fig.2 PKN2 knockout in cardiomyocytes causes defective embryonic heart development leading to failure prior to adulthood. (Marshall, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 PKN2 knockout in cardiomyocytes causes defective embryonic heart development leading to failure prior to adulthood. (Marshall, et al., 2022)
Related Services
- Viral Vector Design and Construction
- mRNA Therapeutics
- siRNA In Vitro Screening Service
- ASO In Vitro Screening Service
Equipped with world-leading technology platforms and professional scientific staff, Creative Biolabs can provide one-stop drug discovery services from target identification to the final IND-enabling. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
References
- Marshall, JJ.; et al. PKN2 deficiency leads both to prenatal congenital cardiomyopathy and defective angiotensin II stress responses. bioRxiv. 2022 Jan 1. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Cheng, Y.; et al. PKN2 in colon cancer cells inhibits M2 phenotype polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via regulating DUSP6-Erk1/2 pathway. Molecular cancer. 2018 Dec;17(1):1-6. Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
