Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing the complexities of neurodegenerative disease drug development, particularly the challenges in identifying and validating novel therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's Disease (AD)? Creative Biolabs' Complement Therapeutic solutions help you accelerate drug discovery and develop highly specific modulators by leveraging advanced antibody engineering and high-throughput screening platforms.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement cascade, a fundamental element of innate immunity, operates with complex and frequently contradictory effects in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) pathogenesis. Traditionally recognized for its role in host defense against pathogens and clearance of cellular debris, dysregulation of the complement system has emerged as a significant contributor to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in AD.
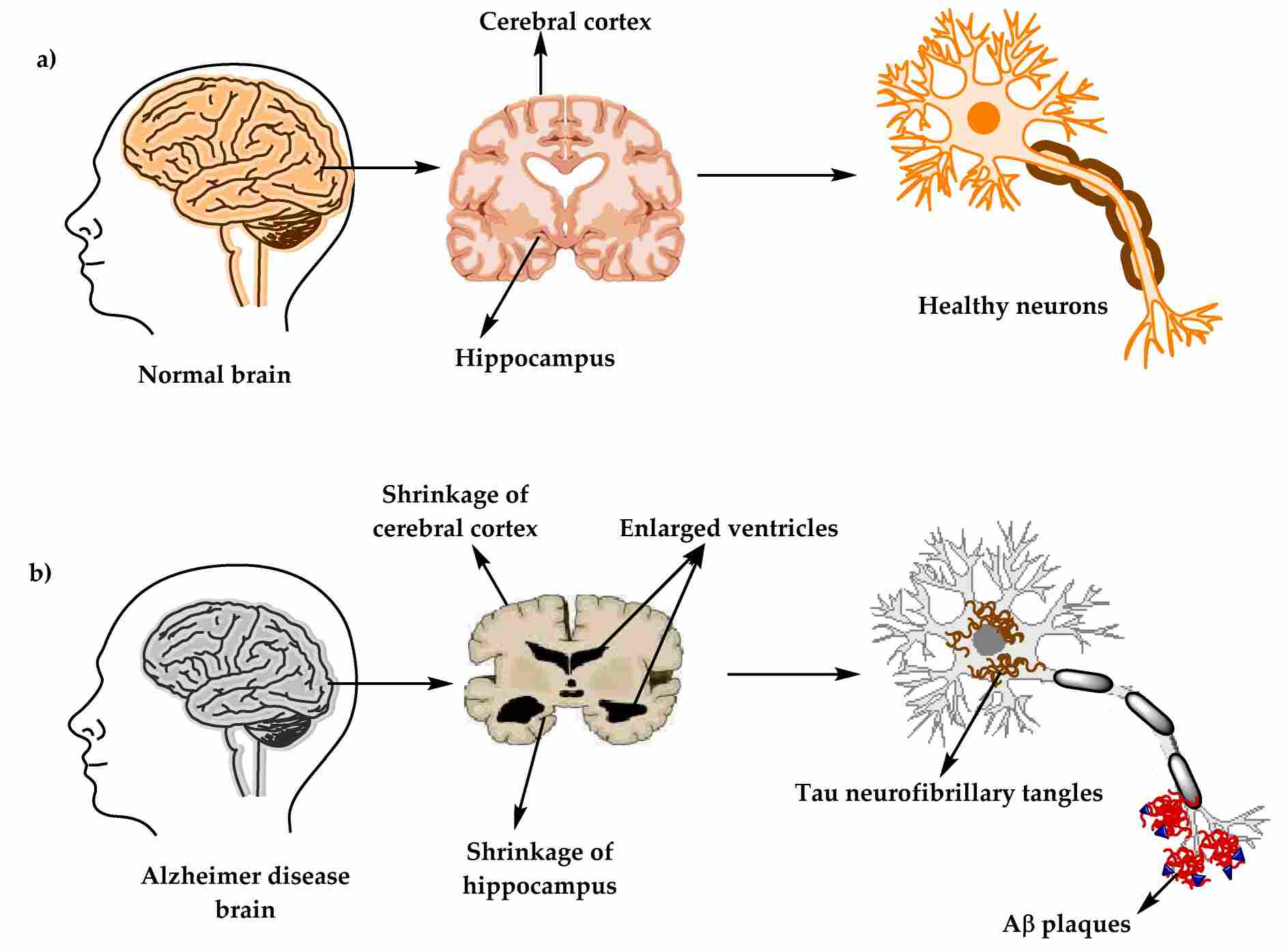 Fig.1 The physiological structure of the brain and neurons in (a) a healthy brain and (b) an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain.1,3
Fig.1 The physiological structure of the brain and neurons in (a) a healthy brain and (b) an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain.1,3
Consisting of over 30 proteins, it activates via three primary routes: classical (CP), alternative (AP), and lectin (LP) pathways. All culminate at complement component 3 (C3) activation, generating C3 convertases that split C3 into C3a and C3b. C3b, in turn, facilitates the formation of C5 convertases, cleaving C5 into C5a and C5b. C3a and C5a are potent anaphylatoxins, mediating inflammation and immune cell recruitment, while C5b initiates the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC, C5b-9), which can induce cell lysis.
In the context of AD, evidence suggests that complement activation is an early event, often preceding overt clinical symptoms. Key findings from published literature highlight its involvement in several pathological hallmarks:
Amyloid-beta (Aβ) Pathology
Complement component 1q (C1q), the initiating molecule of the classical pathway, has been shown to bind directly to Aβ aggregates and plaques. This binding can trigger classical pathway activation, leading to opsonization of Aβ by C3b, which, while potentially aiding in Aβ clearance by microglia, can also contribute to chronic inflammatory responses surrounding plaques.
Tau Pathology
While less extensively studied than Aβ, complement components have also been implicated in the progression of tauopathy. Abnormally phosphorylated tau clusters can trigger complement pathways, promoting neural impairment and degeneration.
Synaptic Loss
One of the most critical and early events in AD is synaptic dysfunction and loss, strongly correlating with cognitive decline. The complement components C1q and C3 have been found to tag synapses for removal by microglia, a process known as synaptic pruning. While essential for healthy brain development, this process becomes dysregulated in AD, leading to excessive and inappropriate synaptic elimination, contributing significantly to neurodegeneration.
Neuroinflammation
The anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a, generated during complement activation, act on their respective receptors (C3aR and C5aR1) expressed on microglia, astrocytes, and neurons. This interaction promotes a pro-inflammatory environment, exacerbating microglial activation, cytokine release, and neuronal damage. Furthermore, MAC formation can directly injure neurons.
The dual nature of the complement system—beneficial in acute clearance but detrimental in chronic activation—underscores the need for precise therapeutic modulation. Understanding these intricate signaling pathways and their contributions to AD progression is paramount for developing effective interventions.
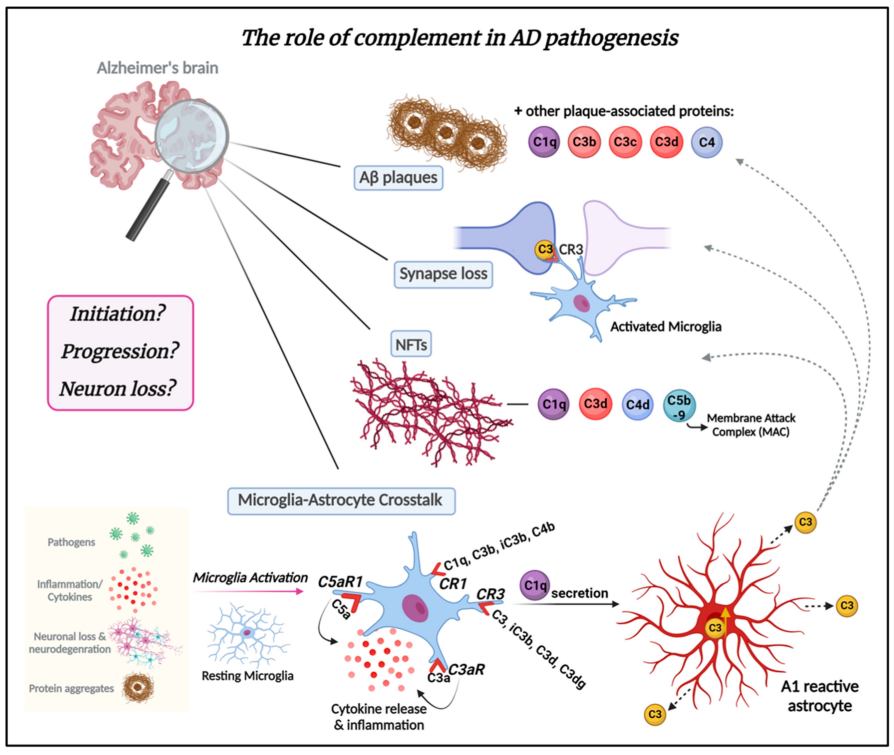 Fig.2 The role of the complement system in AD pathogenesis.2,3
Fig.2 The role of the complement system in AD pathogenesis.2,3
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of products and services to empower your research and therapeutic development targeting the complement system in Alzheimer's Disease, supporting every project stage from fundamental research to preclinical validation.
-
Recombinant Complement Proteins: Highly purified human and animal recombinant complement proteins (e.g., C1q, C3, C4, C5, Factor B, Factor D, MASP-2) for mechanistic studies and assay development.
-
Anti-Complement Antibodies: Validated anti-complement antibodies (e.g., anti-C1q, anti-C3, anti-C5, anti-C5aR1) for Western Blot, ELISA, IHC, and functional studies.
-
Complement Assay Kits: Ready-to-use kits for measuring complement activation, inhibition, and specific component levels (e.g., C3a, C5a, SC5b-9) in biological samples.
-
Complement Regulatory Proteins: Recombinant complement regulatory proteins (e.g., CD55, CD59, Factor H) for modulating complement activity.
-
Custom Complement Protein Expression and Purification: Tailored services for expressing and purifying specific complement proteins or fragments.
-
Custom Anti-Complement Antibody Development: Comprehensive services for generating monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against novel complement targets, including hybridoma and phage display.
Why Choose Us?
Choosing Creative Biolabs for your Complement System Therapeutic research offers unparalleled advantages, rooted in our deep expertise, advanced technological platforms, and unwavering commitment to scientific excellence. We understand the complexities of neurodegenerative diseases and the critical role of the complement system, positioning us as your ideal partner.
Here are the key advantages of partnering with Creative Biolabs:
-
Unrivaled Expertise in Complement Biology: Our team of seasoned scientists provides cutting-edge insights and strategic guidance, leveraging extensive experience in complement system research and its implications in diseases like AD.
-
Comprehensive Service Portfolio: We offer an end-to-end suite of services, from target identification and validation to custom antibody development, functional assays, and preclinical evaluation, streamlining your research pipeline.
-
State-of-the-Art Technology Platforms: Creative Biolabs invests in advanced technologies, including high-throughput screening systems and sophisticated protein engineering, enabling rapid, accurate, and scalable solutions for therapeutic discovery.
-
Commitment to Quality and Reproducibility: We adhere to stringent quality control, meticulously validating our recombinant proteins, antibodies, and assay services for high purity, activity, and reproducibility, ensuring reliable data.
-
Tailored Solutions for Unique Challenges: Recognizing that each project is unique, our flexible and collaborative approach customizes services to your specific requirements, perfectly aligning with your research goals.
Secure the Creative Biolabs Benefit – Solicit Pricing Now
FAQs
Here are some common questions from researchers exploring the therapeutic potential of the complement system in neurodegenerative diseases:
Q: How can targeting the complement system offer a specific therapeutic advantage in complex neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's?
A: Targeting the complement system allows for a highly specific approach by modulating key inflammatory and synaptic pruning pathways implicated in disease progression. Unlike broad anti-inflammatory strategies, precise complement modulation can potentially mitigate detrimental effects while preserving beneficial immune functions, offering a more refined therapeutic window.
Q: Given the complement system's dual role, how do you ensure that therapeutic interventions avoid suppressing its beneficial functions?
A: The strategy involves careful selection of specific complement components or pathways to target, often focusing on those predominantly involved in chronic, pathological activation rather than acute, protective responses. This precise modulation aims to restore balance without compromising essential immune surveillance or debris clearance.
Q: At what stage of neurodegenerative disease progression is intervention via the complement system most effective?
A: Research suggests that complement activation is an early event in many neurodegenerative conditions, often preceding significant neuronal loss. Therefore, early intervention, potentially even in preclinical or prodromal stages, may be most effective in slowing or preventing disease progression by mitigating chronic inflammation and synaptic damage.
Q: Are there potential off-target effects or safety concerns associated with modulating the complement system?
A: As with any therapeutic intervention, potential off-target effects are a consideration. However, by designing highly specific modulators and conducting rigorous preclinical and clinical evaluations, the aim is to minimize unintended consequences. The focus is on targeted inhibition of specific components or receptors to maintain overall immune integrity.
Q: How do complement-targeted therapies compare to other emerging strategies for neurodegenerative diseases?
A: Complement-targeted therapies represent a distinct and promising avenue, often complementing other strategies by addressing the critical neuroinflammatory and synaptic pathology aspects. They offer a unique mechanism of action that can be synergistic with approaches focused on amyloid or tau clearance, potentially leading to more comprehensive therapeutic outcomes.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for advancing research and therapeutic development in the intricate field of Complement System Therapeutics, particularly concerning its critical role in Alzheimer's Disease. Our comprehensive suite of products and services, coupled with our deep scientific expertise, positions us to help you overcome the challenges of neurodegenerative drug discovery and bring innovative solutions to patients.
Featured Services
Feature Products
References
-
Breijyeh, Zeinab, and Rafik Karaman. "Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer's Disease: Causes and Treatment." Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 25,24 5789. 8 Dec. 2020, DOI:10.3390/molecules25245789.
-
Batista, André F et al. "The Importance of Complement-Mediated Immune Signaling in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 25,2 817. 9 Jan. 2024, DOI:10.3390/ijms25020817.
-
Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig.1 The physiological structure of the brain and neurons in (a) a healthy brain and (b) an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain.1,3
Fig.1 The physiological structure of the brain and neurons in (a) a healthy brain and (b) an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain.1,3
 Fig.2 The role of the complement system in AD pathogenesis.2,3
Fig.2 The role of the complement system in AD pathogenesis.2,3