Creative Biolabs provides advanced complement therapeutic and drug discovery services of C3-target of complement system for our customs based on the years of research in this field. We are confident to offer high-ranking technologies and cost-effective service to assist our clients’ project.
Complement System
The complement system is considered an ancient and evolutionary conserved component of the innate immune mechanism. It comprises more than 30 element proteins, regulators and receptors which collaborate to form the complement cascade defending against infections as well as clearing invaders. There is an increasing appreciation that the complement system involves numerous physiological and pathological processes in the body.
C3
Three major pathways of complement which are the classical, alternative and lectin pathways converge on complement C3. As the central component among the intricate protein network of the complement system, C3 is associated with diverse immunomodulatory system and biological process that affect human physiology and pathophysiology, thereby representing a ‘hot-spot’ for current complement-targeted therapeutic intervention. It is the most abundant complement protein which mediates numerous protective effects or pathological effects of complement. C3 plays roles in complement cascade by active fragments or complexes, which are achieved through a panel of enzyme processing procedure.
C4b2a is C3 convertase (C3-cleaving enzyme) that triggers the activation in classical (antibody) or lectin (sugar) pathways, whereas in the alternative pathway that is C3bBb. Active fragments or complexes of complement proteins are produced for corresponding activities through the effect of C3 convertases. C3 fragments like C3b, C3dg, and iC3b can covalently bind to their targets recruiting phagocytes to the targets and performing phagocytosis. In addition, they facilitate the activation of B cells for enhancing humoral immunity. The smaller fragment C3a can strengthen the antigen presenting cells (APCs) to present antigens and stimulate T cell proliferation. Downstream of C3, the membrane attack complex (MAC) forms ultimately with the help of C5 convertase and other important factors to lyse the target bacteria and activating cells.
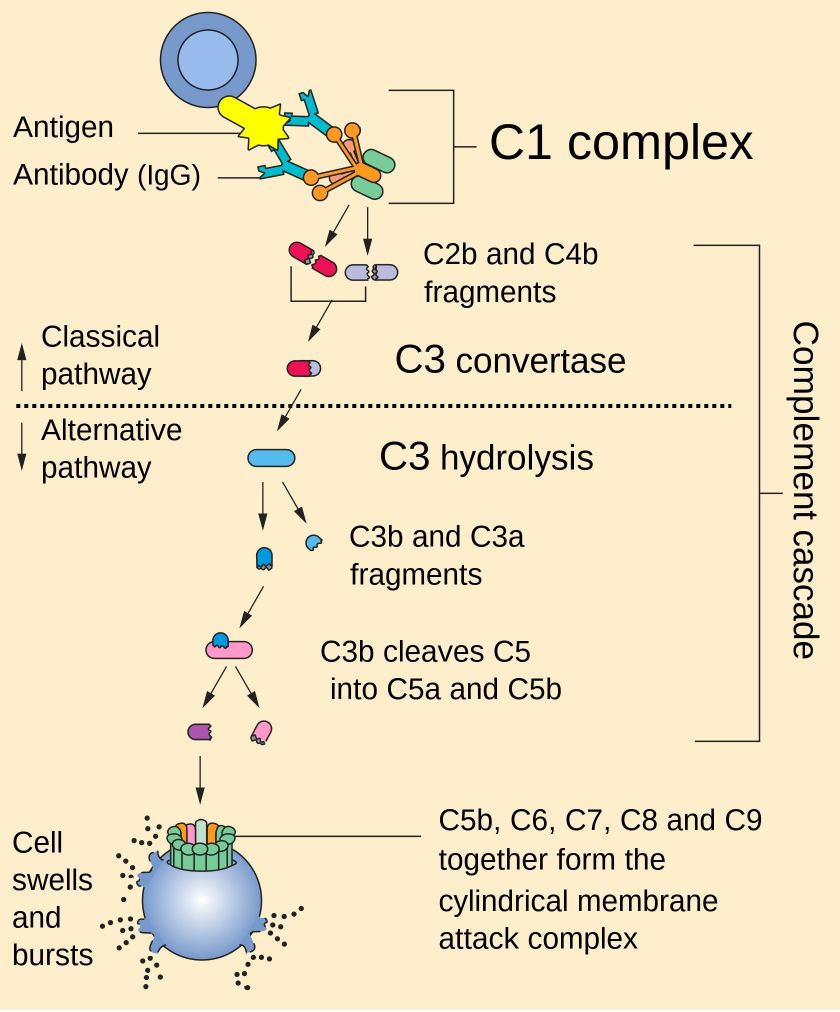 Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki,
without modification.
Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki,
without modification.
Fig.1 The complement pathway
C3 Related Disease
As we all know, the complement cascade would never be an isolated system but critically intertwined with other systems such as immune, inflammatory system, and related to other significant developmental or metabolic processes. While the underlying processes within the cascade during complement activation are highly complex and diverse, this level of complexity is not only essential for an adequate response to distinct triggers but also offers a wide panel of potential targets for therapeutic intervention. In addition, with the fact that the mechanisms of numerous complement-related disorders are revealed in recent years, the role of complement is undergoing a profound paradigm shift and therapeutic intervention is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Based on a thorough understanding of the complement system as well as abundant research experience of complement therapeutic, Creative Biolabs has developed the C3-target complement therapeutic services for various conditions which including but not limited to:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
-
Endotoxin shock
-
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
It is of great honor for us to share these experiences with our clients and give a hand in the research of therapeutic intervention. If you are interested in our service, please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Published Data
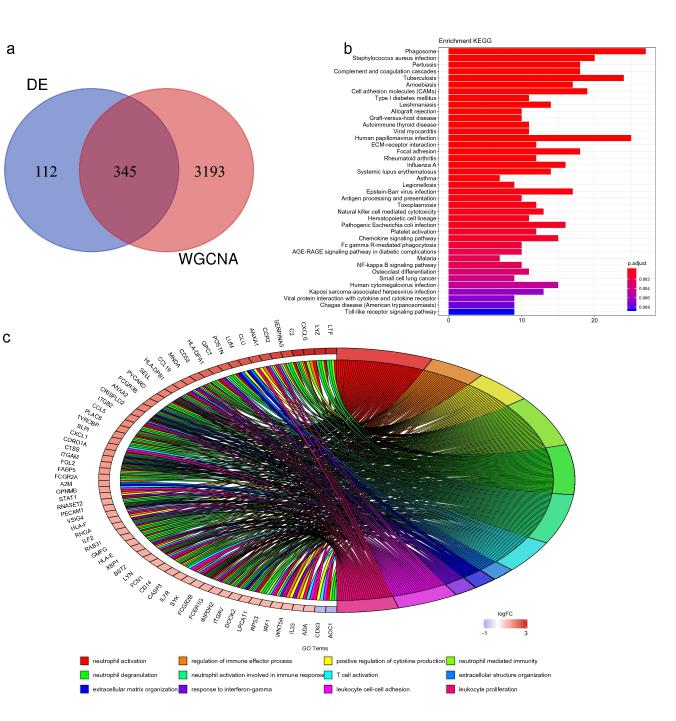 Fig.2 Functional enrichment profiling of genes implicated in diabetic kidney disease.1
Fig.2 Functional enrichment profiling of genes implicated in diabetic kidney disease.1
The intricate mechanisms underlying diabetic nephropathy remain elusive, while current therapeutic interventions offer limited success. Numerous public databases harbor vast data sets poised for advanced bioinformatics scrutiny. Differential expression analysis and WGCNA spotlighted C3 as a gene of interest, implicating the complement and coagulation pathway within KEGG. Furthermore, C3's pivotal role was substantiated through central positioning in the PPI network. This research highlights the promise of targeting complement C3 for therapeutic intervention in diabetic nephropathy. Beyond innate immune defense via PRRs, the complement system emerges as a significant pro-inflammatory mediator implicated in diabetic nephropathy's pathogenesis, warranting further investigation.
Reference
-
Tang, ShuMei, et al. "Identification of C3 as a therapeutic target for diabetic nephropathy by bioinformatics analysis." Scientific Reports 10.1 (2020): 13468. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Emerging strategies include the development of monoclonal antibodies that selectively inhibit C3 activation, small molecule inhibitors targeting key enzymatic steps in the complement cascade, and innovative gene therapies aimed at modulating C3 expression or activity.
A: C3-targeted therapies offer a more upstream approach compared to inhibitors targeting downstream components like C5. By intervening at the C3 level, these therapies have the potential to impact multiple pathways and effector functions of the complement cascade, making them attractive candidates for broader modulation of immune responses.
A: Our researchers are exploring innovative drug design and delivery strategies to enhance the specificity of C3-targeted therapies. By precisely targeting C3 activation or function, these approaches aim to minimize off-target effects and reduce the risk of compromising host defense mechanisms.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 Functional enrichment profiling of genes implicated in diabetic kidney disease.1
Fig.2 Functional enrichment profiling of genes implicated in diabetic kidney disease.1