Overview Workflows & Case Study Applications Related Products Featured Services Protocols Q&A Resources
The complement receptor-ligand binding assays are valuable in understanding the molecular interactions between
complement receptors and their ligands. With advanced platforms and standard procedures, Creative
Biolabs provides rapid and customized complement receptor-ligand binding assays to customers worldwide.
Overview of Complement Receptors Ligand
Complement receptors are a group of proteins found on the surface of various immune cells, including leukocytes
(such as neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells) and some non-immune cells. These receptors are involved in
the recognition and binding of complement components, particularly the activated fragments of the complement system.
These complement receptors have diverse functions and contribute to various immune processes, including
phagocytosis, clearance of immune complexes, modulation of immune responses, and cell-cell interactions.
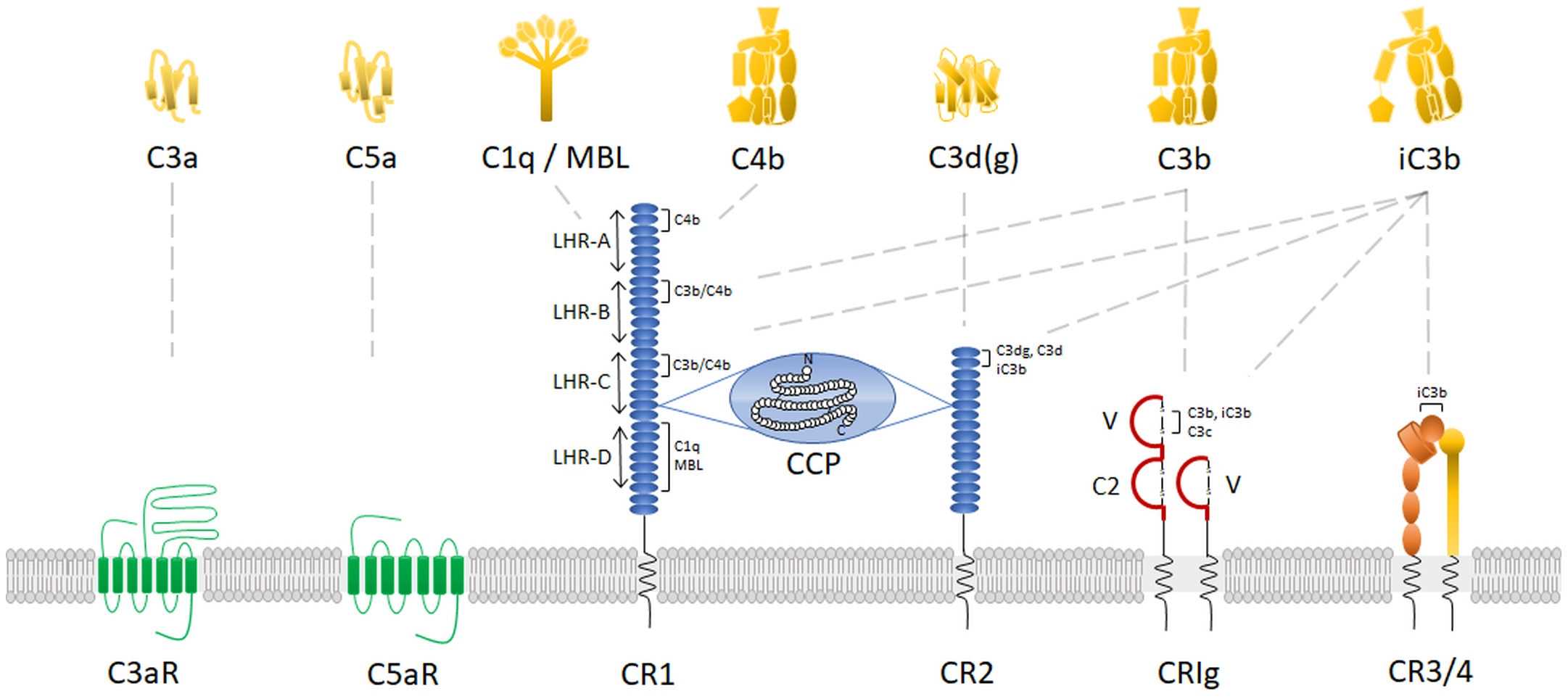 Fig. 1 Diagram of complement receptors and ligands.1, 2
Fig. 1 Diagram of complement receptors and ligands.1, 2
Introduction of Receptor Ligand Binding Assay
Method
The complement receptor ligand binding assay is a laboratory test used to assess the interaction between complement
receptors and their ligands, which can be performed by radioisotope labeling, receptor-ligand enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Immunoprecipitation, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
Analysis
The results provide information about the strength of the interaction between the complement receptor and its
ligand, including the binding affinity and kinetics, and aid in characterizing the roles and functions of complement
receptors in immune processes.
Workflow of Receptor Ligand Binding Assay & Case Study
Radioisotope labeling
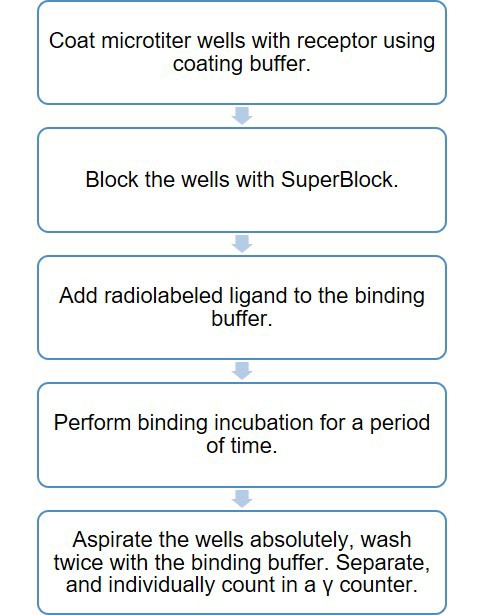
Receptor-ligand ELISA
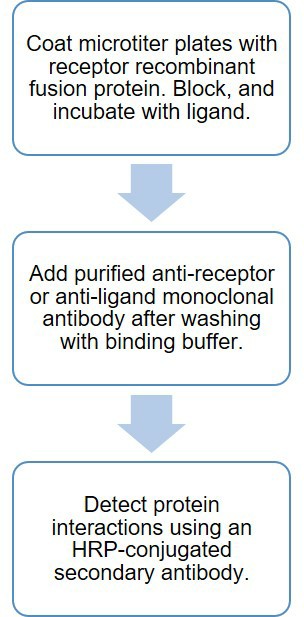
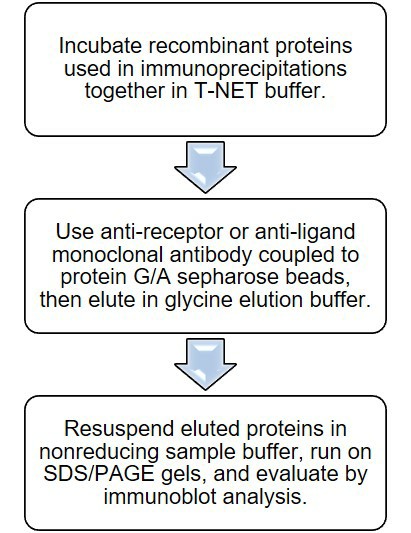
Immunoprecipitation
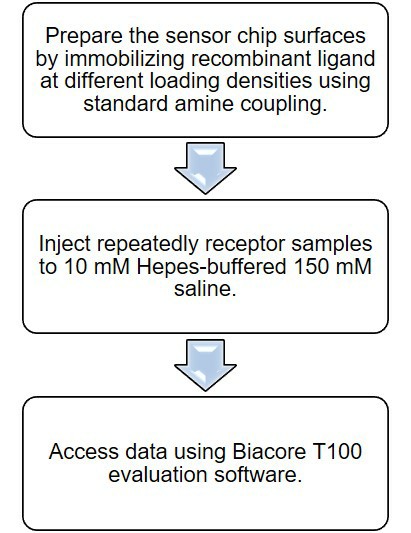
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
Applications
Characterizing receptor-ligand interactions
The assay is commonly used to study and characterize the binding interactions between receptors and
their specific ligands to help researchers understand the molecular mechanisms underlying cellular
signaling, immune responses, and disease processes.
Drug discovery and development
Screening potential therapeutic compounds or small molecules against specific receptors and their
ligands, helps the development of targeted drugs that modulate receptor-ligand interactions and
potentially treat various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, cancers, and infectious diseases.
Assessing receptor expression and function
The assay can be used to determine the expression levels and functional activity of specific receptors
in different cell types or tissues to understand the roles of receptors in cellular processes and
provide valuable information about receptor abnormalities or dysregulation in disease conditions.
Biomarker discovery and validation
The assay can aid in the discovery and validation of biomarkers-specific molecules or patterns
associated with particular diseases or disease stages. Identifying reliable biomarkers can contribute to
early diagnosis, disease prognosis, and monitoring of treatment response.
Related Products
Featured Services
|
|
|
Total Complement Activity Test
|
C1q-Binding Assays
|
|
Creative Biolabs offers total complement activity test services for our clients. Total complement
activity tests include CH50, AH50, and LP50.
|
Creative Biolabs offers high-quality C1q-binding assays for the characterization of therapeutic
mAbs.
|
|
Learn more
|
Learn more
|
Overall, the receptor ligand binding assay provides a valuable tool for understanding receptor-ligand interactions,
drug discovery, biomarker identification, and diagnostic research. Creative Biolabs is always
committed to providing the highest-quality and most appropriate complement receptor-ligand binding assays for the
various needs of clients. Please directly contact us for more
details.
Protocols
Resources
References
-
Vandendriessche, Sofie, et al. "Complement receptors and their role in leukocyte recruitment and phagocytosis." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 9 (2021): 624025.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Questions & Answer
A: The assay involves immobilizing the complement receptor on a solid surface and then incubating it with the ligand of interest. The binding between the receptor and the ligand is quantified using various detection methods, such as fluorescence, radioactivity, or enzyme-linked assays. The purpose of this assay is to measure and characterize the binding affinity and kinetics of complement receptors and their ligands, providing insights into their molecular interactions.
A: These assays can be used to study the role of complement receptors in immune responses, inflammation, and diseases such as autoimmune disorders. They can also help in the development of therapeutic agents targeting complement receptors. And with appropriate assay miniaturization and automation, complement receptor-ligand binding assays can be adapted for high-throughput screening of large compound libraries to identify potential modulators or inhibitors.
A: Some challenges include the availability and purity of recombinant complement receptors and ligands, optimization of assay conditions, and potential interference from non-specific binding or other factors that may influence the results.
A: A variety of sample types can be appropriate for the complement receptor-ligand binding assay, these may include cellular extracts, tissue lysates, or purified proteins. Our assay platform can accommodate a wide range of complement receptors and their corresponding ligands, including but not limited to CR1, CR2, CR3, CR4, C3aR, C5aR, and more. It is highly recommended to contact our technical support team to discuss your specific requirements and the right sample types for your specific research project.
A: Yes, it certainly can. One of the strengths of our assay is its capacity to test the binding affinity of multiple ligands to a complement receptor in parallel. This can prove invaluable when studying the competitive dynamics of receptor-ligand interactions.
A: Certainly! We understand that research goals and parameters can vary greatly between projects. We are flexible enough to offer customized solutions suited to unique research needs. You just need to discuss it with our specialists and provide us with your specific requirements.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Diagram of complement receptors and ligands.1, 2
Fig. 1 Diagram of complement receptors and ligands.1, 2