Proteins
Creative Biolabs can generate a variety of complement system-related proteins, which could be qualified tools
for the early discovery process in life science research and groundbreaking development of specific clinical
applications.
Complement Components Complement Proteins Portfolio Complement Protein Products Quality and Customization Protein Assays FAQs Popular in Collection Related Products & Services
Complement Proteins
Creative Biolabs is committed to advancing immunology research with a comprehensive suite of complement proteins
that support specific research needs across the classical, lectin, alternative, and terminal pathways. Our
high-quality proteins empower researchers to uncover critical insights into immune responses, inflammation, and
infection mechanisms, driving innovations in therapeutic development and immunology.
Whether your work involves studying pathogen recognition, immune complex clearance, or complement-mediated cell
lysis, Creative Biolabs offers a robust and customizable solution to meet your research needs.
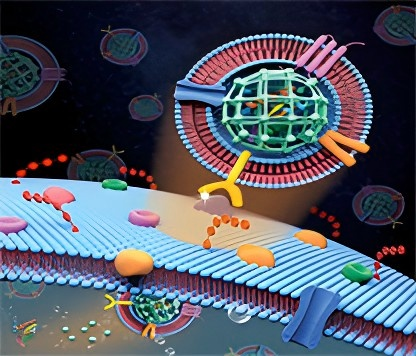
Components of the Complement System
Initially discovered in the 1890s as a heat-labile component of plasma that "complemented" antibodies in
bacterial lysis, our understanding of this system has evolved dramatically. The evolutionary conservation of
complement components across species underscores its fundamental importance in immune defense. The complement
cascade comprises over 30 plasma proteins and membrane-bound regulators that interact in a precisely
orchestrated manner. These proteins typically circulate in inactive zymogen forms, requiring specific
proteolytic cleavage for activation. This sophisticated activation mechanism prevents unnecessary inflammation
and tissue damage while maintaining a rapid response capability.
|
Activation Pathway
|
Description
|
Key Components
|
|
Classical Pathway
|
The classical pathway represents the antibody-dependent activation route of the complement system.
The pathway initiates when C1q recognizes antibody-antigen complexes or other activation surfaces,
leading to conformational changes that trigger the cascade.
|
-
C1 Complex: Consists of C1q, C1r,
and C1s molecules
-
C4: Cleaves into C4a and C4b fragments
-
C2: Forms C3 convertase when combined with
C4b
|
|
Lectin Pathway
|
The lectin pathway provides antibody-independent activation through pattern recognition. This
pathway recognizes carbohydrate patterns on microbial surfaces, providing an immediate response to
pathogen invasion.
|
|
|
Alternative Pathway
|
The alternative pathway maintains constant low-level activation through spontaneous C3 hydrolysis.
This pathway serves as an amplification loop for all complement activation routes.
|
|
Complement Proteins Portfolio
Creative Biolabs is a leader in providing high-quality, research-grade complement proteins that support advanced
studies in immunology, inflammation, and infection. Our complement protein portfolio is designed to facilitate
groundbreaking research, with each product optimized for specific experimental needs.
C1q
-
Role: C1q binds to the Fc region of IgG or IgM in immune complexes, initiating the classical
pathway.
-
Research Applications: Studies on autoimmune disorders, antibody responses, and immune
complex
clearance.
-
Product Variants: Recombinant human and animal-derived C1q proteins for in vitro research.
C1r and C1s
-
Role: C1r and C1s are serine proteases activated upon C1q binding, cleaving downstream
complement
proteins (C2 and C4) to amplify the complement cascade.
-
Research Applications: Investigations of antibody-antigen interactions, complement
deficiencies, and
inherited complement disorders.
-
Product Variants: Highly purified forms suitable for functional assays and structural
studies.
Lectin Pathway Proteins
Our portfolio provides comprehensive tools for probing the lectin pathway, allowing insights into innate
immunity and inflammation research.
MBL
-
Role: MBL recognizes and binds to carbohydrate patterns on pathogen surfaces, recruiting MASPs to
activate
downstream complement components.
-
Research Applications: Studies on host-pathogen interactions, inflammation, and innate immune
deficiency
disorders.
-
Product Variants: Recombinant and native MBL suitable for binding and complement activation studies.
MASP-1, MASP-2, and MASP-3
-
Role: MASPs are serine proteases that cleave C4 and C2, forming C3 convertase, a crucial enzyme for
the
Lectin Pathway.
-
Research Applications: Investigation of pathogen recognition, lectin pathway activation, and
MASP-related
genetic disorders.
-
Product Variants: Recombinant MASP proteins in various isoforms for biochemical and functional
studies.
Alternative Pathway Proteins
Our alternative pathway proteins support innovative research into non-antibody immune responses, crucial for
understanding immune surveillance mechanisms.
C3
-
Role: C3 undergoes spontaneous hydrolysis, which enables the formation of C3 convertase, essential
for
opsonization and immune cell recruitment.
-
Research Applications: Studies on pathogen opsonization, immune complex clearance, and C3-associated
diseases.
-
Product Variants: Recombinant and purified C3 proteins, including active and inactive forms for
mechanistic
studies.
C5
-
Role: Cleaved by C5 convertase into C5a and C5b, with C5a acting as a potent inflammatory mediator
and C5b
initiating MAC formation.
-
Research Applications: Research on inflammation, chemotaxis, and complement-associated autoimmune
diseases.
-
Product Variants: C5 and its active fragments, tailored for inflammation and chemotaxis studies.
Properdin
-
Role: Properdin stabilizes the C3 convertase complex on pathogen surfaces, enhancing the pathway's
amplification loop.
-
Research Applications: Studies focused on the stabilization and amplification of the alternative
pathway and
properdin deficiencies.
-
Product Variants: Native and recombinant properdin, suitable for in-depth studies of complement
stability
and amplification.
Terminal Pathway and Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) Components
Our portfolio includes each of these MAC components, supporting research on cell lysis, apoptosis, and
complement-mediated cytotoxicity. These products facilitate in-depth exploration of the terminal pathway,
enabling studies on immune cytotoxicity and the potential therapeutic targeting of MAC formation.
C5b
-
Role: C5b initiates MAC formation by sequentially recruiting C6, C7, C8, and C9 to form a pore on
the target membrane.
-
Research Applications: Studies on complement-mediated cell lysis, apoptosis, and membrane repair
mechanisms.
-
Product Variants: Purified C5b for MAC reconstitution and functional assays.
C6, C7, C8,
and C9
-
Role: These proteins sequentially assemble with C5b, creating the transmembrane pore that leads to
cell lysis.
-
Research Applications: Complement-mediated apoptosis, cancer cell lysis studies, and drug testing
for MAC inhibitors.
-
Product Variants: Recombinant C6, C7, C8, and C9, optimized
Complement Protein Products in Research
Complement proteins play essential roles in the immune system by enhancing immune responses through a complex
cascade. This cascade not only amplifies the immune response but also aids in immune cell recruitment, pathogen
lysis, and inflammation mediation. Over recent years, complement proteins have become a focal point of study
across various research fields.
|
Research Areas
|
Diseases/Mechanisms
|
Role of Complement Protein
|
|
Immunology and Autoimmune Disease Research
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
|
C1q is essential for studying apoptotic cell
clearance defects, a hallmark of lupus pathogenesis, and helps understand the autoantibody
production and immune complex deposition seen in SLE.
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
|
C5a and MAC are often upregulated in RA.
Researchers use these complement pathways to mimic the synovial inflammation and tissue destruction
that characterize RA.
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
|
Complement activation products like C3b and C5a are detected in demyelinating lesions.
|
|
Infectious Disease Research
|
Bacterial Pathogens
|
Many bacterial pathogens produce proteins that bind to host complement regulators (e.g., Factor H) to prevent complement activation on
their surfaces.
|
|
Viral Pathogens
|
Viruses modulate complement activation to evade immune detection.
|
|
Fungal Pathogens
|
Fungi also employ complement evasion strategies.
|
|
Cancer Research
|
Immune Modulation and Evasion
|
Tumors may upregulate complement inhibitors like CD55 or CD59 to prevent complement-mediated lysis.
|
|
Tumor-associated Inflammation
|
Studies show that blocking C5a receptors can
prevent inflammation-driven tumor growth in models of lung cancer.
|
|
Neuroinflammation Research
|
Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
|
Studies on C1q and C3 reveal how excessive complement activation promotes
microglial phagocytosis of neurons, which accelerates cognitive decline.
|
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
|
Models using complement inhibitors (e.g., anti-C5 monoclonal
antibodies) show that reducing complement activation reduces inflammation and
lesion formation.
|
|
Vaccine Development
|
Adjuvant Efficacy Enhancement
|
For example, vaccines that include adjuvants activating the C5a pathway show enhanced T-cell activation
|
|
Targeted Immunomodulation
|
Researchers use complement-activated peptides or proteins to promote stronger and longer-lasting
immune responses.
|
Product Quality and Customization Options
Creative Biolabs, with over two decades of experience in the biotechnology industry, offers an extensive suite
of complement protein products and customization options tailored to meet the precise needs of research labs
worldwide.
-
1
Product purity and activity
We use rigorous purification methods to produce complement proteins of the highest purity.
Each batch is meticulously analyzed for activity levels.
-
2
Lot-to-lot consistency
We use standardized procedures and advanced analyses to confirm that each batch meets the
required specifications, providing researchers with a reliable tool for their work.
-
3
Meeting industry standards
Our manufacturing facilities follow Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines and other
relevant industry certifications.
Our advanced recombinant protein technology allows Creative Biolabs to produce stable, active complement
proteins with unparalleled precision. We use state-of-the-art expression systems and optimization techniques to
ensure protein functionality and stability even under demanding research conditions.
High-yield expression systems
Creative Biolabs utilizes high-yield expression systems (e.g., mammalian, bacterial, yeast,
and insect cell
lines) that can be tuned to the specific needs of each protein.
Request a Quote
Proprietary stabilization technologies
Our proprietary stabilization technologies are designed to improve the durability and
activity of complement
proteins under a variety of storage and handling conditions.
Request a Quote