Creative Biolabs is an innovative and ambitious company which delivers value-added services. We own brilliant antibody engineering platform, protease inhibitor platform, and drug discovery platform. We are fully equipped to partner with our clients who are doing or may have the desire to work on complement systems for drug discovery and validation.
Introduction of Complement System and Complement Factor B
The human complement system acts as a primitive component of the first humoral immune system designed to eliminate the infecting pathogens. It is comprised of approximately 30 serum and cellular components, including activating serine protease, receptors as well as positive and negative regulators. The complement system involves in opsonization for phagocytosis and anaphylatoxin activities, and is responsible for binding and lysing the plasma membrane of the pathogens. The complement system consists of three pathways, the classical pathway, the lectin pathway, and the alternative pathway.
Complement factor B is a single-chain molecule of 764 amino acids (MW of 90 kD), which can circulate in the blood to maintain homeostasis. Factor B contributes to the formation of C3/C5 convertases of the alternative complement pathway. The gene encoding factor B localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6p21.
 Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Fig.1 Complement factor B.
Function of Complement Factor B
Factor B is part of the alternative pathway of the complement system. It can be cleaved by complement factor D yielding the noncatalytic chain Ba (~33 kD) and the catalytic subunit Bb (~60 kD). The Ba region localizes at the N-terminus of the molecule and contains residues 1-259. This region comprises three complement control protein (CCP) domains, which are important for the initial binding of factor B to C3b. The catalytic subunit Bb (residues 260-764) combines with C3b to form the alternative pathway C3 convertase (C3bBb), which is stabilized by the binding of properdin. After cleavage of C3, the C5 convertase [(C3b)2Bb] is subsequently formed. Moreover, it is documented that Bb is involved in the proliferation and differentiation of preactivated B lymphocytes, while Ba inhibits their proliferation. Bb is also associated with the rapid spreading of peripheral blood monocytes, stimulation of lymphocyte blastogenesis, immunosuppression, apoptosis and lysis of erythrocytes.
Complement Factor B Deficiency
Complement factor B deficiency is an immunologic disorder characterized by increased susceptibility to bacterial infections, particularly Neisseria infections, due to a defect in the alternative complement pathway. Additionally, factor B deficiency is involved in various diseases, such as septic shock, stroke, systemic lupus erythematosus, Alzheimer’s disease, melioidosis, and multiple sclerosis. Interestingly, inactivation of factor B in mice prevents a number of autoimmune or inflammatory diseases, indicating an attractive target for therapy.
With professional knowledge and rich research experiences in drug discovery and complement therapeutic field, Creative Biolabs' outstanding research team are providing high-quality biotherapeutics development services based on the complement system. We offer turn-key or ala carte services customized to our client’s needs. We cut down on the time and effort you spend on setting up the assay. If you are interested in our platform or you are calling for our services, please contact us for detailed information.
Published Data
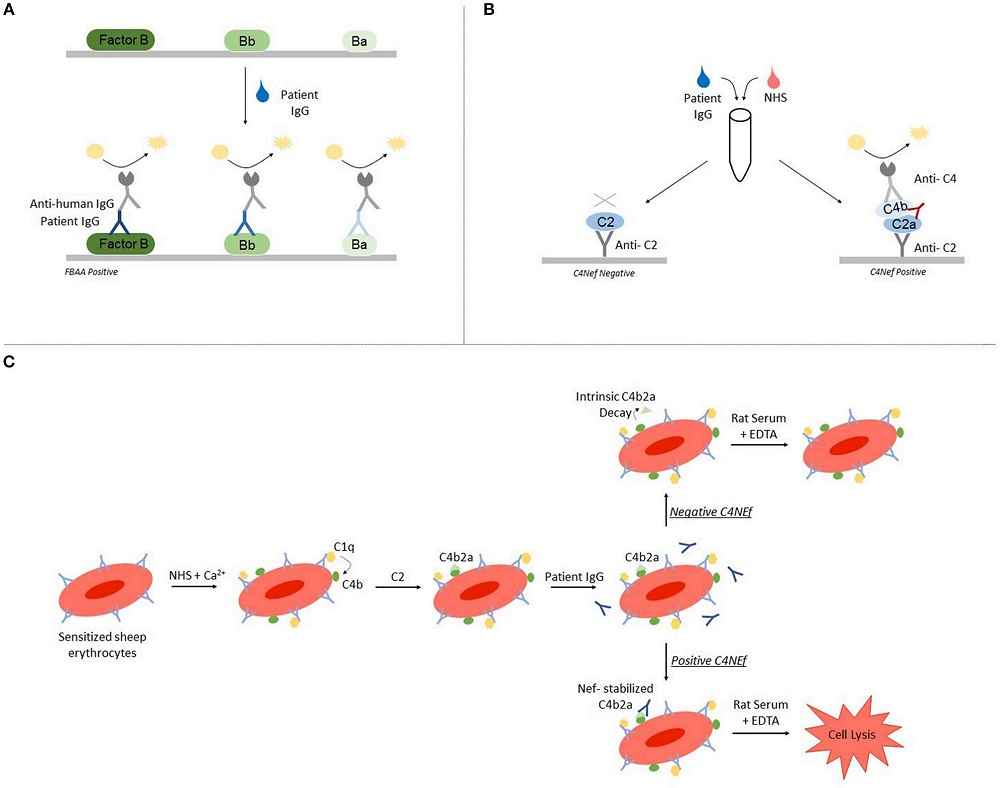 Fig.2 Detection of complement factor B autoantibodies using ELISA and hemolytic assays.1
Fig.2 Detection of complement factor B autoantibodies using ELISA and hemolytic assays.1
C3 Glomerulopathy (C3G) is a renal condition driven by disruptions in the alternative complement pathway, integral to innate immunity. In C3G, such disruptions lead to complement protein deposition in the kidney's glomerular basement membrane. Persistent complement activation in these patients arises from rare genetic mutations and autoantibodies that alter regular complement protein function. Factor B autoantibodies, found solely in C3G cases, uniquely stabilize the C3 convertase, affecting normal complement processes distinctively compared to C3 nephritic factors (C3Nefs). As testing for these antibodies becomes more commonplace, their precise role in disease progression will be elucidated.
Reference
-
Hauer, Jill J., et al. "Factor B and C4B2a autoantibodies in C3 glomerulopathy." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 668. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Yes, there are natural regulators of complement factor B activity. Factors such as factor H and factor I play critical roles in regulating the activity of complement factor B and other components of the alternative complement pathway. These regulators help prevent excessive complement activation and ensure that the immune response is appropriately controlled.
A: Developing drugs targeting complement factor B involves a multi-faceted approach. Researchers can explore small molecules, monoclonal antibodies, or other biologics that specifically inhibit complement factor B's enzymatic activity. Computer-aided drug design, high-throughput screening, and structural biology techniques can aid in identifying potential drug candidates. Preclinical studies involving animal models and in vitro assays are essential to assess efficacy and safety before advancing to clinical trials.
A: Future research and development could focus on designing highly specific inhibitors of complement factor B that effectively modulate its activity without disrupting other complement pathways. Additionally, investigating the role of complement factor B in various diseases, uncovering its interactions with other immune pathways, and exploring its potential as a diagnostic biomarker are all important directions. Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials will provide valuable insights into the efficacy and safety of therapies targeting complement factor B in different disease contexts.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 Detection of complement factor B autoantibodies using ELISA and hemolytic assays.1
Fig.2 Detection of complement factor B autoantibodies using ELISA and hemolytic assays.1