Complement is an important effector system of host defense. However, erroneous activation or insufficient regulation of the complement cascade may turn its destructive actions against the host’s cells, resulting in diseases characterized by serious tissue injury. As a consequence, inhibition or modulation of complement activity has been recognized as a promising therapeutic strategy for many years. Creative Biolabs has established a comprehensive drug discovery platform and is proud to provide complement-based drug development services for the treatment of a range of diseases involved in the complement therapeutic target -MBL-associated serine proteases 1 (MASP-1).
Serine Proteases as Drug Targets
Serine proteases are key components of the complement system. Eight serine proteases constitute the complement cascade, including C1r, C1s, C2a, MASP-1, MASP-2, factor D, factor B, and factor I. During complement activation, these proteases activate each other in a cascade-like manner, thereby mediating various physiological processes. Among which, complement serine proteases are responsible for the generation of the biologically active products that directly or indirectly cause tissue damage, as well as represent amplification points of complement activation, therefore, they are logical targets of pharmacological control. To date, a number of promising approaches for the clinical substitution, inhibition or modulation of complement have been developed and great efforts have been focused on the development of protease inhibitors, due to the suitability of serine proteases to be the drug targets, which is also called “druggability”.
The Role of MASP-1 in Diseases
MASP-1 is a serine protease that functions as a component of the lectin pathway of complement activation. The lectin pathway is initiated when mannan-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins, in complex with the MBL-associated serine proteases (MASP-1, MASP-2, MASP-3) and MBL-associated proteins (MAp44 and MAp19), binds to appropriate targets. Moreover, it is also involved in other proteolytic cascades like coagulation and tends to be a major link between the complement system and coagulation.
Particularly, increased MASP-1 plasma levels in patients in the subacute phase of myocardial infarction (MI) and decreased levels of MASP-1 in patients with acute ischemic stroke have been observed, suggesting that MASP-1 may play a vital role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, a recent study has demonstrated that MASP-1 could be a driver of disease progression in HCV infection via direct activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Besides, investigators suggest that the possibility of monospecific inhibition of MASP-1 activity which may, in due course, have therapeutic potential.
The development of therapies for different disease indications in which complement has an important role and it is a difficult but promising area of drug discovery. Therefore, many potential drug candidates and therapeutic strategies are currently in the pipeline of various biotechnology and biopharmaceutical companies. Creative Biolabs offers a full range of complement therapeutic development services for the MASP-1 related disease to contribute to your project success, including
-
Recurrent Diseases
-
Subacute Myocardial Infarction
-
Acute Ischemic Stroke
As a first-class company in the biopharmaceutical field, Creative Biolabs is a trusted partner and expert in the complement-targeted drug discovery and development. Moreover, we are capable of providing development services with the flexibility and experience to tailor solutions to each project. If you’re interested in our services, please free feel to contact us for more information.
Published Data
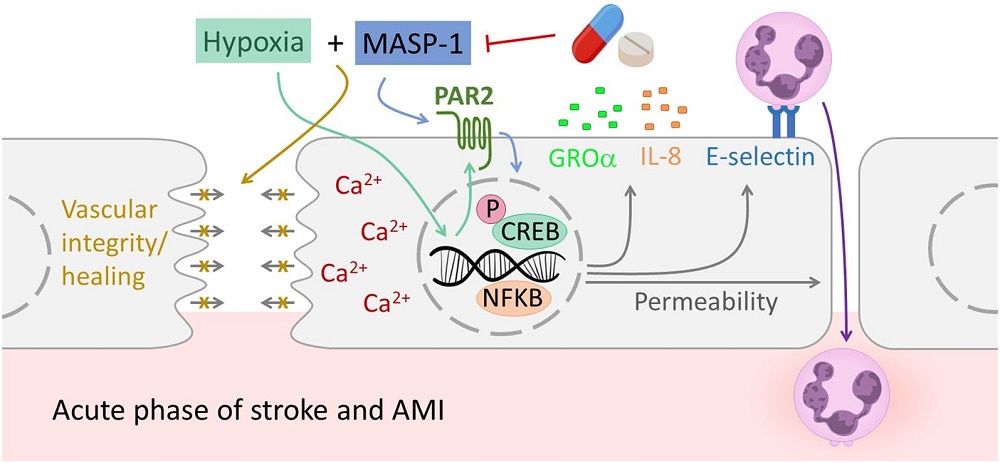 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the interplay between hypoxic conditions and MASP-1 influence on endothelial cell function.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the interplay between hypoxic conditions and MASP-1 influence on endothelial cell function.1
Low oxygen levels and the complement lectin pathway play a role in the development of atherosclerosis and associated cardiovascular incidents. MASP-1, a key complement lectin pathway enzyme, promotes inflammation in ECs by activating protease-activated receptors (PARs). This study explores the interaction between hypoxia and MASP-1 in ECs, aiming to elucidate their impact on atherosclerosis. Hypoxia impaired EC wound healing, altered ICAM expression, and increased PAR2. Both hypoxia and MASP-1 elevated GROα, IL-8, and endothelial permeability, disrupting vascular integrity and signaling pathways. Despite their individual effects, they cooperatively activated key pathways and adhesion molecules. This suggests MASP-1 as a potential therapeutic target in acute atherosclerotic conditions.
Reference
-
Demeter, Flóra, et al. "Detrimental interactions of hypoxia and complement MASP-1 in endothelial cells as a model for atherosclerosis-related diseases." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 14882. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: MASP-1 is unique in its role as an initiator of the lectin pathway. While other complement components like C3 and C5 have been extensively studied as therapeutic targets, MASP-1 represents a relatively newer avenue of research with potential therapeutic applications.
A: While autoimmune diseases and sepsis have been the primary focus of MASP-1-related research, there is growing interest in its role in other conditions, such as ischemia-reperfusion injury, inflammatory bowel diseases, and neurological disorders. Targeting MASP-1 could have broader therapeutic implications in these areas, although further research is needed to establish its effectiveness.
A: Recent advances in MASP-1 research include the identification of novel inhibitors and the elucidation of their role in various disease pathways. Researchers have been exploring the potential of small molecules or monoclonal antibodies to selectively inhibit MASP-1 activity in diseases where complement dysregulation is implicated. Additionally, a better understanding of MASP-1's role in inflammatory conditions has opened up new avenues for targeted therapies.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the interplay between hypoxic conditions and MASP-1 influence on endothelial cell function.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the interplay between hypoxic conditions and MASP-1 influence on endothelial cell function.1