Complement is important for protection against infections. Dysregulation of complement activation can cause the onset and progression of numerous inflammatory diseases. Since C3 convertases mediate nearly all complement effector functions, they are ideal targets for therapeutic complement inhibition. At present, Creative Biolabs provides advanced complement therapeutic and drug discovery services targeting C3 convertases. We are confident to offer high-ranking technologies and cost-effective services to assist our clients’ projects.
Introduction of C3 Convertase
C3 convertase belongs to a family of serine proteases and is necessary for innate immunity as a part of the complement system which eventuates in opsonization of particles, release of inflammatory peptides, C5 convertase formation and cell lysis. There are three pathways of complement activation, the classical pathway, lectin pathway, and alternative pathway. All pathways converge at the level of the C3 molecule, where downstream events can be amplified by a mechanism of positive feedback supported by complement convertases, the classical/lectin pathway C3 convertase (C4b2a) or the alternative pathway C3 convertase (C3bBb). C3 convertases cleave C3 into C3a, a chemoattractant molecule, and C3b, which covalently binds to target surfaces and triggers phagocytosis.
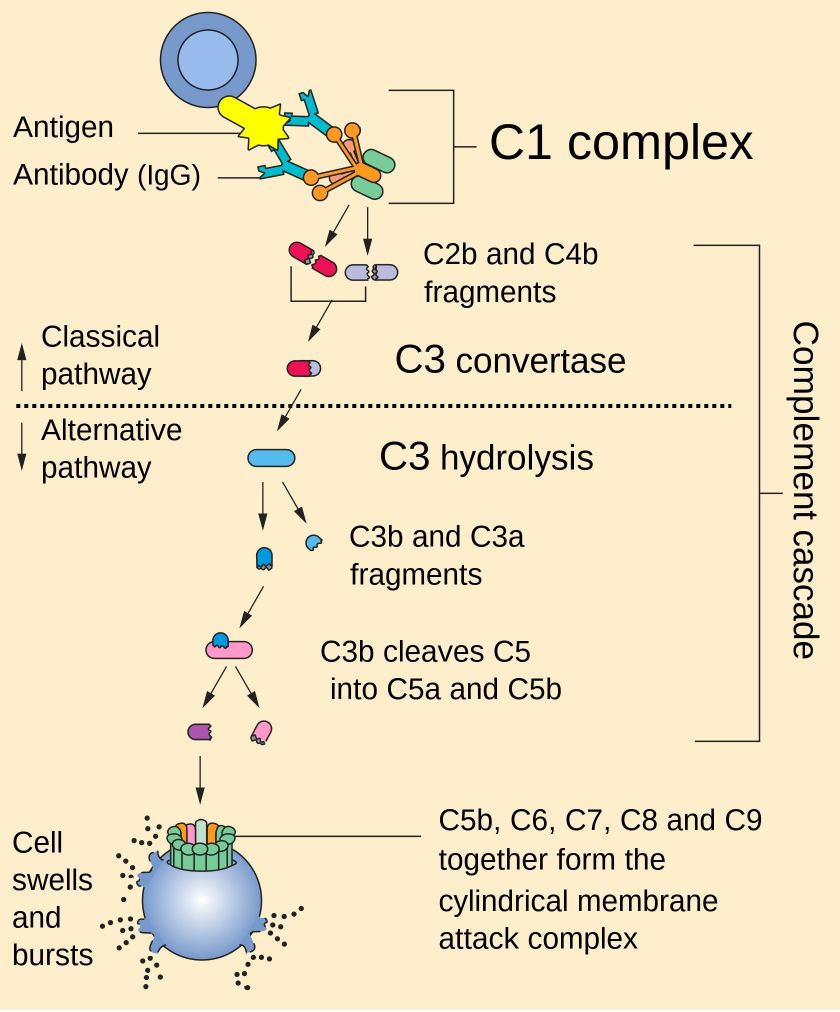
Fig. 1 The complement pathway.1
Disease and Related Therapeutics
C3 glomerulopathy (C3G), comprising C3 glomerulonephritis (C3GN) and dense-deposit disease (DDD), is a pathologic entity defined by dominant C3 accumulation with absent or scanty immunoglobulin (Ig) deposition. Genetic causes of C3 glomerulopathy include mutations in the genes coding for Factor H, C3, CFHR1, CFHR2, CFHR3, CFHR5, and Factor B. Autoimmune factors in C3G include autoantibodies in form of C3-Nephritic Factor, C4-Nephritic Factor or C5-Nephritic Factor. Most autoantibodies bind to neoepitopes exposed in these central complement enzymes. Some autoantibodies also bind to the single components, such as C3, C3b, Factor H or Factor B.
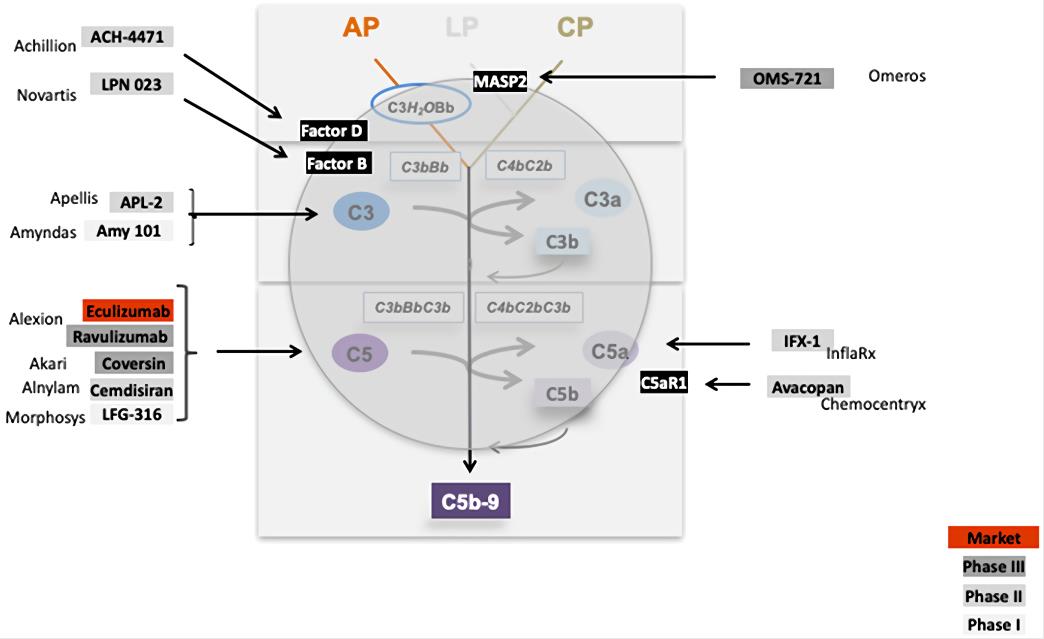
Fig. 2 Complement inhibitors in complement cascade.2, 3
-
Examples
ACH-4771 is a small Factor D inhibitor that blocks the catalytic side of Factor D. In presence of inactive Factor D, the alternative pathway convertase C3bBb is not formed and complement activation does not proceed. The other inhibitor LPN023, binds to the active site of Factor B and thus inhibits the alternative pathway C3 convertase and blocks C3 cleavage. Based on the different action sites of the inhibitor, it will be of interest to see which compound or which targeted pathway is most effective and which subform responds or benefits from which inhibitor. Besides, monoclonal antibody (mAb) was also designed by scientists to bind C3b, thereby preventing the formation of the C3 convertase.
What Can We Do for You?
Selective inhibition of C3 convertases is of great therapeutic interest for many researchers. Armed with advanced well-established drug discovery platform, antibody engineering platform as well as protein inhibitor platform, Creative Biolabs is fully equipped to reach out our hands to our clients who are doing or may have the desire to work on C3 convertase for drug discovery and validation. We have evaluated different mAbs and protein inhibitors targeting C3 convertase and its components. We will offer turn-key or ala carte services customized to our client’s needs. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more information.
References
-
By English text of 'Image:Complement pathway.png' by DO11.10German translation of 'Image:Complement pathway.png' by HdumanGalician translation MiguelferigCatalan translation LeptictidiumSpanish translation AsierogSVG by Perhelion - Own work based on: http://www.niaid.nih.gov/publications/immune/the_immune_system.pdf, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=45352985.
-
Zipfel, Peter F., et al. "Complement inhibitors in clinical trials for glomerular diseases." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 2166.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Rational drug design and structural analysis are employed to develop C3 convertase inhibitors that specifically target the active site or binding interfaces of the enzyme complex, minimizing off-target effects.
A: Formulation approaches, such as optimizing drug delivery systems or developing prodrugs, may improve the pharmacokinetic properties, bioavailability, and stability of C3 convertase inhibitors, enhancing their therapeutic potential.
A: Nanotechnology, drug conjugation strategies, and advanced drug delivery systems are being explored to enhance the stability, bioavailability, and targeted delivery of C3 convertase inhibitors.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


