Immunopathology Complement Activation Complement Molecular Mechanisms Related Products Hot Services Q&A Resources
Are you currently facing challenges in developing effective therapies for rare diseases like Hereditary Angioedema (HAE), including difficulties in targeting the complement system and navigating complex regulatory landscapes? Creative Biolabs’ comprehensive suite of products and services helps you accelerate your drug discovery and development process for HAE therapeutics through advanced complement pathway analysis, custom assay development, and high-quality recombinant proteins.
Immunopathology Features
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare and potentially life-threatening genetic disorder due to C1 inhibitor deficiency. These episodes occur in over one-half of the patients with HAE during their lifetimes. It is characterized by recurrent angioedema attacks which affect the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and airway. Minor trauma or stress may trigger an attack, but swelling often occurs without a known trigger. The prevalence of HAE is approximately one in 80,000 people. Symptoms of HAE typically begin in childhood and get worse around twelve years of age. On average, untreated individuals have a chance of an attack every 1 to 2 weeks, and most episodes last for about 3 to 4 days. The frequency and duration of attacks vary greatly between individuals, even among people in the same family.
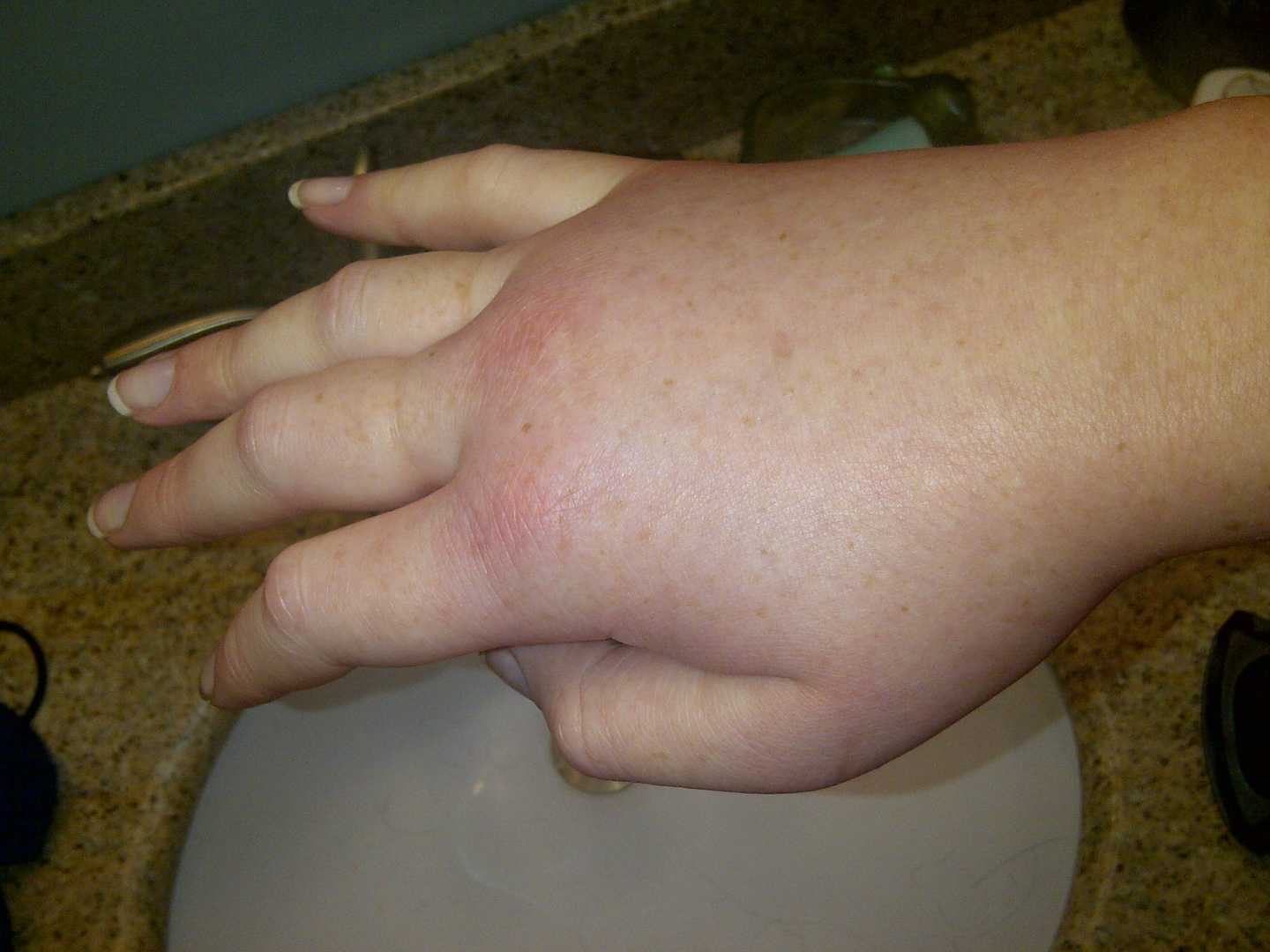
Fig. 1 Hereditary angioedema.1
Classification
HAE is classified into three distinct types: type I, type II, and type III.
-
Types I and II result from mutations in the SERPING1 gene, which encodes the C1 protease inhibitor; they account for 80-85% and 15-20% of cases, respectively, and are characterized by low C4 levels with type I showing reduced C1-inhibitor and type II exhibiting dysfunctional C1-inhibitor, all following an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern without sex predominance.
-
Type III does not involve C1-inhibitor but is often linked to mutations in the factor XII gene, causing increased bradykinin levels and promoting swelling.
Cause of HAE
HAE is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait and results from mutations in the gene responsible for the synthesis of C1 inhibitor. However, 20-25% of the cases are estimated to be the result of spontaneous mutations. More than 200 mutations within this gene have been reported. Type I HAE is caused by the mutations that lead to a low level of C1-inhibitor. Type II HAE results from the mutations of genes which make the truncated or misfolded Ci-inhibitors. These mutations lead to the dysfunction of the protease inhibitor.
Treatment of HAE
Currently, the treatment options for HAE including but not limited to attenuated androgens, fresh frozen plasma, and antifibrinolytics. These treatments have shown undesired effects or limited efficacy. C1 inhibitor replacement therapy has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HAE. The recombinant C1-inhibitor is underway.
Complement Activation Pathways and HAE Pathogenesis
The primary pathogenesis of HAE is not directly driven by the dysregulation of the alternative or lectin pathways of the complement system. Instead, the deficiency or dysfunction of C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) primarily impacts the classical pathway and the contact system, leading to the characteristic bradykinin-mediated angioedema.
Table 1 HAE-related complement activation pathways.
|
Complement Activation Pathways
|
HAE Pathogenesis
|
|
Classical Pathway
|
-
C1-INH serves as a crucial regulator of the classical complement pathway. It inhibits the serine proteases C1r and C1s within the C1 complex. In HAE with C1-INH deficiency (Type I) or dysfunction (Type II), this inhibitory control is lost.
-
Uncontrolled activation of C1r and C1s leads to excessive cleavage of C4 and C2, components of the classical pathway.
-
While the over-activation of the early classical pathway contributes to the consumption of C4 (a diagnostic marker for HAE), it is not the direct cause of angioedema.
-
The primary link to angioedema via the classical pathway is indirect: the lack of functional C1-INH also leads to the dysregulation of the contact system.
|
|
Alternative Pathway
|
-
The alternative pathway maintains a low level of continuous activity, which becomes amplified on microbial surfaces.
-
C1-INH does have some regulatory effects on components of the alternative pathway, but its deficiency in HAE is not considered the primary driver of pathogenesis through this pathway.
|
|
Lectin Pathway
|
-
C1-INH also modulates the lectin pathway by inhibiting MASP-1 and MASP-2.
-
It is not the central mechanism causing angioedema in HAE.
|
Molecular Mechanisms of Complement-Mediated
Table 2 Molecular mechanisms of complement-mediated.
|
Key Complement Components
|
Functions
|
|
C1-INH
|
-
HAE is most commonly caused by a quantitative deficiency (Type I HAE) or a functional defect (Type II HAE) of C1-INH. C1-INH is a serine protease inhibitor (serpin) that controls several critical enzymes within the complement and contact activation systems.
-
The underlying cause is usually a mutation in the SERPING1 gene, which encodes C1-INH.
|
|
C1 Complex
|
C1-INH normally inhibits the activation of C1r and C1s, which are serine proteases within the C1 complex (C1q, C1r, C1s). In HAE, the lack of functional C1-INH results in uncontrolled activation of C1.
|
|
C4 and C2 Cleavage
|
-
Activated C1r and C1s cleave complement components C4 and C2. This cleavage in HAE occurs excessively.
-
The excessive cleavage of C4 leads to its depletion, which is a characteristic laboratory finding in HAE (low C4 levels). This consumption is a strong indicator of classical pathway activation.
|
Creative Biolabs has been focusing on drug discovery and complement therapeutics for quite a few years. With our comprehensive Complement Therapeutics Platform, Creative Biolabs is equipped to provide excellent services to the global clients. Please contact us for detailed information.
Related Hot Products
Our comprehensive complement platform offers a broad and cost-effective selection of complement-related products. We welcome you to contact us.
Table 3 Featured products.
Related Hot Services
Table 4 Complement test services for SS-related complement studies.
Resources
Reference
-
By LucyHAE - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=22728152
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: