Creative Biolabs is an innovative and ambitious company which delivers value-added services. We have established brilliant antibody engineering platform, protease inhibitor platform, and drug discovery platform and are fully equipped to partner with our clients who are working on complement systems for drug discovery and validation.
Complement Therapeutic Target C9
The role of the immune system is to protect the body from the pathogens. The immune system identifies a variety of pathogens including but not limited to bacteria, virus, and parasite. The complement system plays a crucial role in the innate defense against invading pathogens, of which the membrane attack complex (MAC) is the key effector that disrupts the pathogens.
The MAC comprises seven components. Complement component C9 is the major component of the MAC, a multi-protein complex that forms in the membrane of target pathogens. In contrast to perforin, a homologous protein of C9, which binds to the target‘s plasma membrane and oligomerizes in a Ca2+ dependent manner, C9 assembles directly onto the nascent MAC from solution.
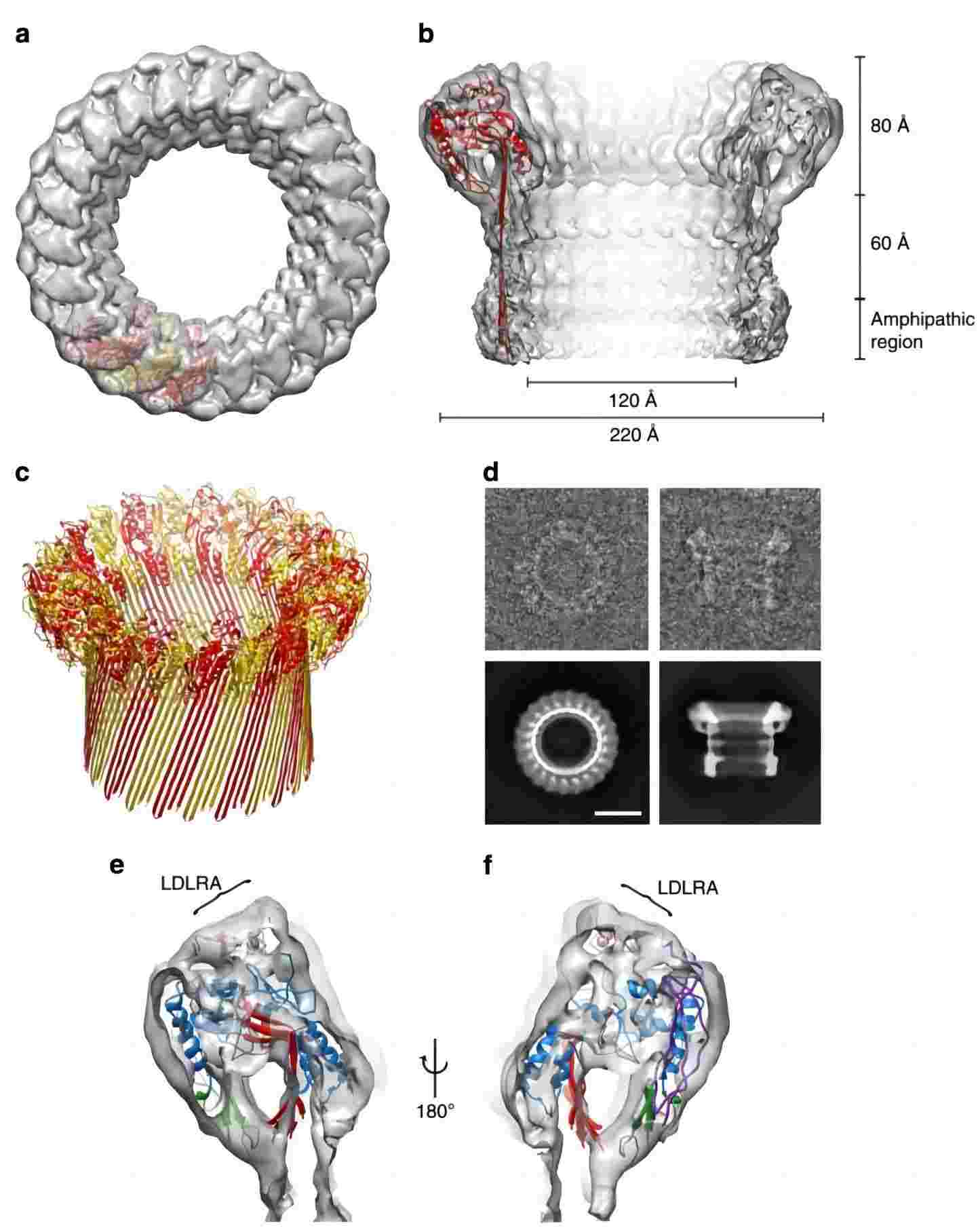
Fig.1 The structure of poly-C9.1, 3
Function
The MAC disrupts the pathogen by binding to its plasma membrane. When the pathogen attacks the body, it would be recognized as the “invader” by the immune system. Thus the complement system is triggered. The complement component C3, where all the pathways in the complement system converge on, is cleaved into C3a and C3b. After a serial cleavage by complement components, C5b is generated and binds to C6. The C5bC6 assembly then sequentially binds to C7, C8, and C9. The C5b-8 initiates the polymerization of C9 to construct a transmembrane tubule with an inner diameter of 100 Å.
C9- Related Disease
-
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) - Complement C9 is found to be involved in the Age-Related Macular Degeneration, which is the leading cause of irreversible vision loss for the elderly, accounting for approximately 9% of the worldwide blindness. It is a problem with the retina and occurs when part of the retina, called macula, is damaged.
-
Meningococcal Meningitis - Membrane Attack Complex is responsible for the cytolysis of the pathogens that are invading the body. As a component of the membrane attack complex, the deficiency of C9 increases the susceptibility of the body to the pathogen infections, particularly the infection of Neisseria meningitides.
Complement deficiency is associated with autoimmune disorders and increased susceptibility to certain infections. Creative Biolabs' outstanding research team are providing high-quality biotherapeutics development services on the complement-related drug discovery and validation. We offer turn-key or ala carte services customized to our client’s needs. If you are interested in our platform or you are calling for our services, please contact us for detailed information.
Published Data
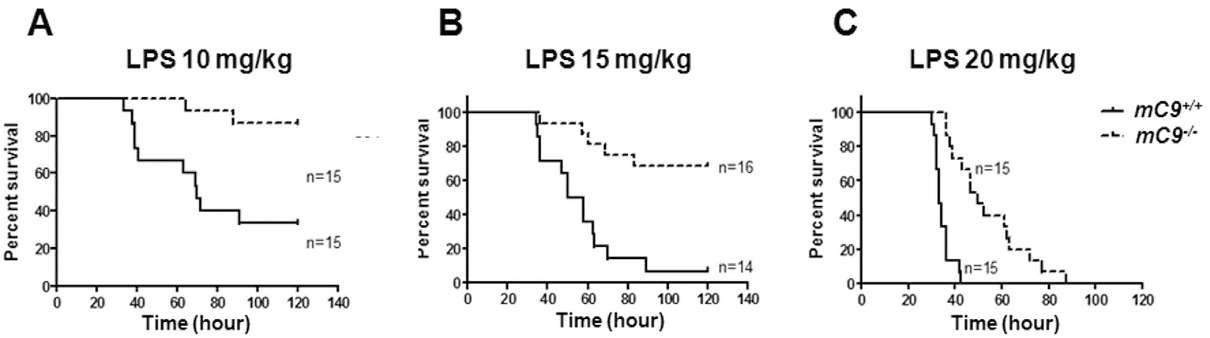 Fig.2 C9 deficiency shields mice from LPS-induced septic shock.2, 3
Fig.2 C9 deficiency shields mice from LPS-induced septic shock.2, 3
The initiation of terminal complement MAC formation begins with C5b, which sequentially attracts and binds C6, C7, and C8. The polymerization of C9 onto the C5b-8 complex culminates in the assembly of C5b-9, or MAC. This complex can form either lytic or non-lytic pores in cell membranes, compromising their integrity. In an effort to elucidate the function of terminal complement cascades, a successful generation of C9-deficient (mC9−/−) models was reported. Findings demonstrate that C9 deficiency reduces anti-erythrocyte antibody-driven hemolysis and diminishes LPS-provoked acute shock. This protective effect aligns with reduced IL-1β release and suppressed inflammasome activation in mC9−/− models, reinforcing C5b-9's pivotal role in both hemolysis and inflammasome activation.
References
-
Dudkina, Natalya V., et al. "Structure of the poly-C9 component of the complement membrane attack complex." Nature communications 7.1 (2016): 10588.
-
Fu, Xiaoyan, et al. "Target deletion of complement component 9 attenuates antibody-mediated hemolysis and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute shock in mice." Scientific Reports 6.1 (2016): 30239.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Researchers are constantly exploring innovative strategies, including gene therapy and RNA-based approaches, to modulate C9 expression or activity. These cutting-edge technologies hold promise for more precise and effective C9-targeted therapies.
A: Emerging trends in C9-targeted therapy research include the development of innovative drug delivery systems, combination therapies with other complement-targeted agents, and precision medicine approaches. Future directions may involve expanding therapeutic indications and exploring the long-term effects of these therapies.
A: Enhancing the selectivity and specificity of C9-targeted therapies is a priority in drug development. Strategies include using advanced drug delivery systems to target specific tissues or cells, designing monoclonal antibodies with high affinity for C9, and optimizing small molecules for their binding properties.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 C9 deficiency shields mice from LPS-induced septic shock.2, 3
Fig.2 C9 deficiency shields mice from LPS-induced septic shock.2, 3