Creative Biolabs has established excellent platforms, including (but not limited to) antibody engineering platform, protease inhibitor platform, and drug discovery platform, to support the drug discovery and validation. These platforms significantly accelerate the discovery process and overcome the challenges associated with time-consuming and labor-intensive assays.
Complement Component C7
The macrophage and neutrophils derived from the innate immune system provide the first defense when the common microorganisms attack the body. The innate immune system is essential for the control of common bacterial infections. As part of the innate immune system, the complement system is made up of a large number of distinct proteins that react to opsonize pathogens and elicit a series of inflammatory responses. A number of the components in complement system are serine proteases and they are activated stepwise by proteolytic cleavage. Physiologically, the effect of almost all the serine proteases comes into one key point: complement component C3 which is cleaved by C3 convertase into C3a and C3b. C3b binds to C3 convertase to generate C5 convertase which in turn cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b. C5b forms a complex called Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) or terminal complement complex (TCC) together with C6, C7, C8, C9, and other components.
Fig.1 NMR-derived structure of C7 and its factor I-like modules.1, 3
Function
The MAC deployed by the immune system targets Gram-negative bacteria and certain parasites. It is initiated when C5 is cleaved into C5a and C5b. C7 serves as a membrane anchor. The C5bC6 assembly binds to C7 and the resulting complex alters the configuration of the protein exposing a hydrophobic site on C7, enabling C7 to insert into the lipid bilayers of the target cells.
The novel role of C7 was recently discovered by a group of researchers. The finding revealed that C7 expression displayed a gradual downward trend in normal, benign, borderline and malignant ovarian tissues and decreased expression of C7 was correlative to poor differentiation in patients with ovarian cancer, indicating that C7 is a potential tumor suppressor in ovarian cancer.
C7-Related Disease
One major end point of complement activation is the formation of the MAC which is responsible for the cytolytic function of the complement system and contributes to the innate defense against pathogens. C7 acts as the part of the anchor to the bilayer of the pathogens. The deficiency of C7 leads to the dysfunction of MAC, which causes enhanced susceptibility to fatal pyoderma gangrenosum.
Creative Biolabs provides high-quality biotherapeutics development services based on the complement system. We offer turn-key or ala carte services customized to our client's needs. If you are interested in our platform, please contact us for detailed information.
Published Data
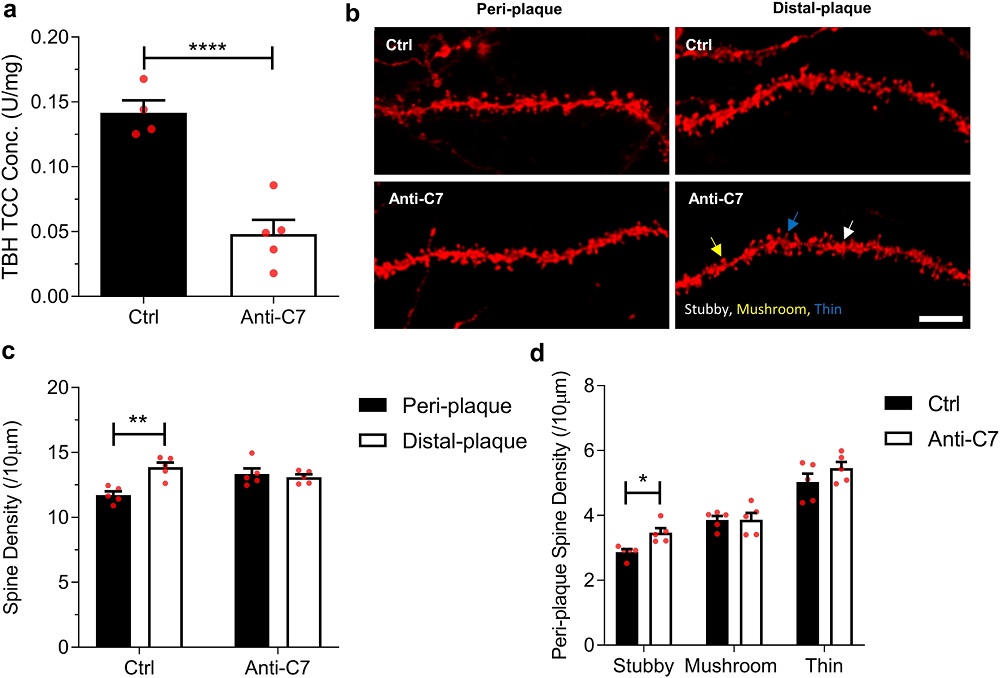 Fig.2 AppNL-G-F mice received treatment with a C7-blocking monoclonal antibody, effectively inhibiting systemic complement activity throughout the study duration.2, 3
Fig.2 AppNL-G-F mice received treatment with a C7-blocking monoclonal antibody, effectively inhibiting systemic complement activity throughout the study duration.2, 3
Complement plays a role in both synaptic pruning during development and synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer's disease (AD). New methodologies were established to measure levels of C1q, C3 fragments, and the MAC in whole brain homogenates and synaptoneurosomes from wild-type and AppNL-G-F AD model mice across different ages. The effects of systemic treatment with a MAC-blocking antibody and gene knockout of MAC components were examined regarding synapse loss. AppNL-G-F mice showed elevated levels of C1q, C3 fragments, and MAC compared to controls, correlating with age and disease severity. Administration of an anti-C7 antibody moderated synapse loss, as shown by dendritic spine density near plaques. Blocking or eradicating MAC formation reduced synapse loss in AD mouse models, indicating MAC's pivotal role in driving synaptic degeneration and C7 might be a potential therapeutic target.
References
-
Phelan, Marie M., et al. "Solution structure of factor I-like modules from complement C7 reveals a pair of follistatin domains in compact pseudosymmetric arrangement." Journal of Biological Chemistry 284.29 (2009): 19637-19649.
-
Carpanini, Sarah M., et al. "Terminal complement pathway activation drives synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease models." Acta Neuropathologica Communications 10.1 (2022): 99.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Researchers modulate complement C7 activity using various approaches, including monoclonal antibodies, small molecules, and gene therapies. Monoclonal antibodies can specifically target C7, while small molecules may inhibit its function. Gene therapies can be used to regulate C7 expression.
A: Delivering targeted therapies to specific tissues or cells while minimizing off-target effects is a significant challenge in the development of C7-targeted therapies. Strategies such as nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems and antibody-drug conjugates are being explored to enhance the specificity of C7-targeted treatments.
A: Complement activation, including the involvement of C7, has been implicated in neuroinflammatory diseases like MS. In MS, complement proteins contribute to inflammation and demyelination of nerve cells. Understanding the specific roles of C7 in these processes may provide insights into potential therapeutic strategies to mitigate neuroinflammation in MS and related disorders.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 AppNL-G-F mice received treatment with a C7-blocking monoclonal antibody, effectively inhibiting systemic complement activity throughout the study duration.2, 3
Fig.2 AppNL-G-F mice received treatment with a C7-blocking monoclonal antibody, effectively inhibiting systemic complement activity throughout the study duration.2, 3