Background Services Overview Protocols Related Products Published Data Q&A Resources
Creative Biolabs is a cutting-edge complement testing service supplier with state-of-the-art
facilities. Our dedicated scientists and technical experts have abundant experience in complement activity
testing, which enables us to provide our clients with quality and professional individual components activity test
services.
Overview of Individual Components Activity Test
Individual complement components can be quantitatively tested by immunoprecipitation assays, such
as immunoprecipitation tests (radial immunodiffusion or nephelometer techniques), ELISA, and the like, without
regard to functional activity. In routine testing, C3, C4, and B factors are most frequently measured, followed by
C1 inhibitors and other components, to determine the diagnosis of complement-associated diseases. In most
cases, total hemolytic activity (CH50 and AH50) indicates complement deficiency, and quantitative tests can be
performed as an alternative to functional assays for individual components. If a defect is verified by this test,
further functional tests are not required. On the other hand, if the quantitative test does not reveal any
defects, a functional test is required to verify the diagnosis. The simplest method of detecting the functional
activity of individual complement components is to test the ability of the sample to reconstitute the hemolytic
activity of serum which is deficient for the protein. To finally demonstrate the lack of only one single component,
the purified functionally active component can be added to the serum to restore the hemolytic activity of the
corresponding pathway.
-
Quantitative Tests for Individual Components
Quantitative tests of complement components are the second most common complement test after CH50 and AH50.
Quantification of most individual complement components can be performed by immunochemical assays including
nephelometry, turbidometry and RID, ELISA and other methods. These measurements utilize the formation
of antibody-antigen immune complexes to determine protein concentration. When the antigens, such as C1
inhibitor, C1q, C3, C4, and C5, FB, and FH, are in equilibrium with the antibodies to the complement components,
immune complexes are formed and can then be subsequently measured.
-
Nephelometry: nephelometry is quantified based on the light scatter from immune complexes. The
intensity of light scatter produced by an immune complex is proportional to the number of complexes present
in the sample. This test method is usually used for the quantification of C3, FB, and C4.
-
Turbidimetry: in contrast to nephelometry which relies on light scatter, turbidimetry allows quantitation of
antigens based on changes in the transmission of light. The same equilibrium is formed between the
complement antigen and the antibody to form an immune complex, which in turn alters the transmission of
light through the specimen in a manner that depends on the concentration of the complement factor of
interest.
-
RID: RID is a versatile method allowing for measurement of complement component concentration
(particularly for C2) or complement function. RID uses an agarose gel containing either antiserum to
complement factor for component levels or heterologous red blood cells from sheep, rabbit, or chicken for
functional assays. If it is an antiserum-type RID, a precipitin ring will be observed. If it is an
erythrocyte agarose gel, hemolysis will be observed around the well. In both cases, the diameter around the
well is proportional to either the antigen concentration or the complement activity.
-
ELISA and other tests: other complement components, such as C1 inhibitor, MASP-1/2, and
regulators, are tested by ELISA or time-resolved immunofluorometric assay (TRIFMA).
-
Functional Activity Test for Individual Components
Normal concentrations of single components do not exclude functional defects. Thus, if a functional defect is
suspected or needs to be ruled out, the functional activity of individual complement proteins needs to be
tested. A simple way to detect the functional activity of individual complement components is to test for the
sample's capability to reconstitute the total complement activity of a serum deficient for a known component.
This can be done by using serum that depletes the actual component and adding fresh serum from the patient to
see whether the activity can be restored.
Our Services of Individual Components Activity Test
Creative Biolabs has a robust standardized complement test platform and a variety of test technologies,
such as nephelometry, ELISA, RID, and TRIFMA assays, to deliver fast, reliable & objective, easy
to interpret results within 3 hours. We provide our customers with routine quantitative tests and functional
activity test for individual components as well as a full range of complement components testing
services, including but not limited to:
Creative Biolabs works closely with each customer, from researchers to diagnosticians, to provide
their results in the most cost-effective and rapid way while maintaining customers’ confidentiality. If you
have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Protocols
Hemolytic Assay Protocols for Individual Component
Hot Complement Serum Products
Published Data
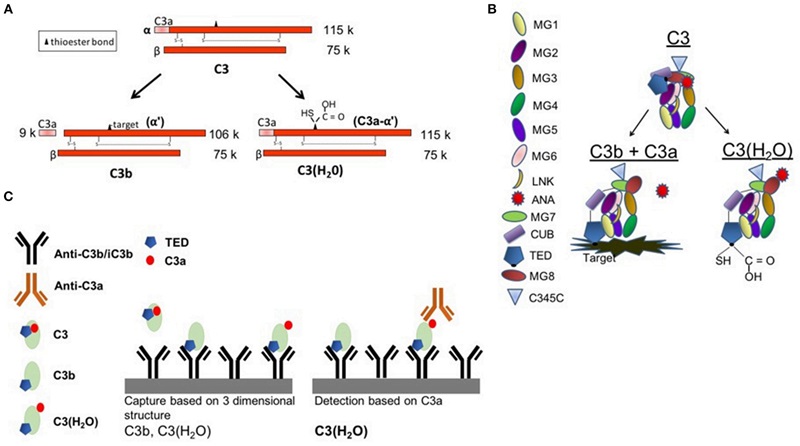 Fig.1 ELISA assay of C3(H2O).1
Fig.1 ELISA assay of C3(H2O).1
The identification of a C3(H2O) uptake mechanism has sparked renewed interest in this variant of the alternative pathway activator in human biospecimens. Until recently, no quantitative method existed to measure C3(H2O) without interference from other complement activation products. Researchers have now developed an ELISA assay to quantify C3(H2O), positioning it as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human diseases. Initial applications of this assay allowed for the establishment of baseline C3(H2O) levels in fluids from healthy individuals, as well as the optimization of sample storage and handling protocols. They observed approximately 500 ng/ml of C3(H2O) in freshly collected serum and plasma—significantly lower than previous estimates derived from purified C3 samples.
Resources
Reference
-
Elvington, Michelle, et al. "Development and optimization of an ELISA to quantitate C3 (H2O) as a marker of human disease." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 703. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Questions & Answer
A: Individual complement components can be isolated from human or animal plasma using various purification techniques, such as chromatography, ultracentrifugation, or immunoaffinity methods. And they can be measured through various techniques, including ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay), hemolytic assays, and functional complement activation assays.
A: Some commonly tested individual complement components include C1q, C3, C4, C5, CFH, CFB and CFI. These components play crucial roles in the complement cascade and immune system functioning. Individual complement components activity testing is conducted to assess the functional activity of specific complement proteins in a controlled experimental setting. Studying the activity of individual complement components helps researchers understand the specific roles of these proteins in the immune response, inflammation, and various disease processes.
A: Future research may focus on developing more specific and sensitive assays for individual complement component activity testing, exploring the functional consequences of genetic variants or mutations, and investigating the role of complement components in various disease pathologies.
A: The individual components activity test measures the functional activity of specific components within a system. The type of measurements can vary depending on the context of the experiment. For example, in a biological context, it could measure enzyme activities, protein interactions, or gene expression levels.
A: We understand that not all research needs are the same. Therefore, yes, we do offer customization in our testing services based on your project's unique requirements. We will work closely with you to understand the specifics of your project and tailor our approach accordingly.
A: Absolutely, the individual components activity test is designed to analyze how distinct components behave or interact under various conditions. It provides quantitative outcomes that can help you comprehend how changes in the environment affect the activity and performance of specific components.
A: The turnaround time for these tests can vary significantly based on the complexity and scope of the experiment, as well as the specific activity to be measured. On average, you can anticipate a turnaround time of two to four weeks.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.1 ELISA assay of C3(H2O).1
Fig.1 ELISA assay of C3(H2O).1