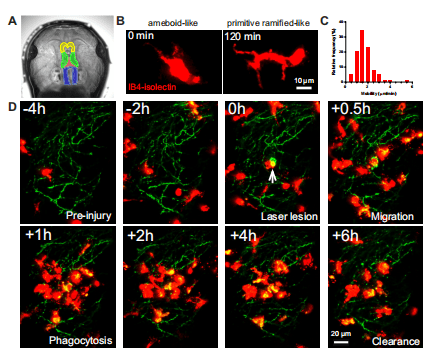
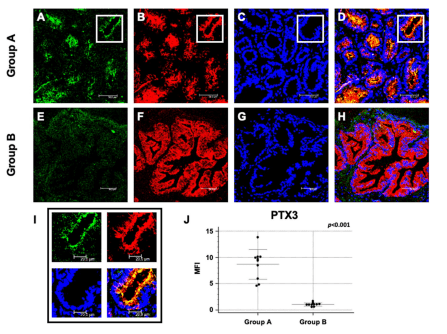
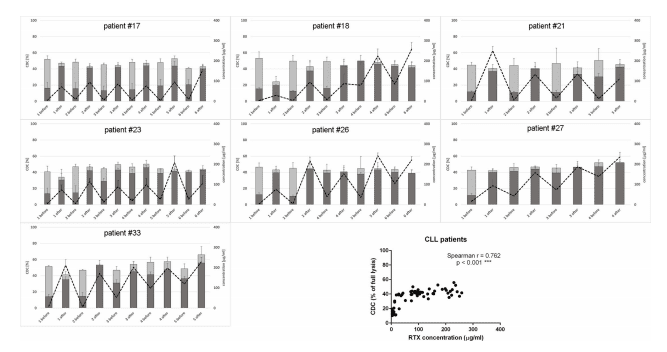
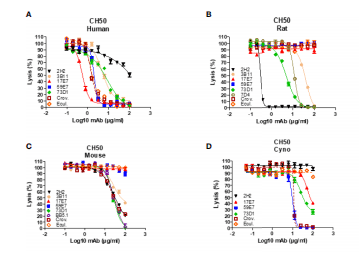
Introduction: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system
with an underlying immune-mediated and inflammatory pathogenesis. Innate immunity, in addition
to the adaptive immune system, plays a relevant role in MS pathogenesis. It represents the
immediate non-specific defense against infections through the intrinsic effector mechanism
“immunothrombosis” linking inflammation and coagulation. Moreover, decreased cerebral blood
volume (CBV), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and prolonged mean transit time (MTT) have been widely
demonstrated by MRI in MS patients. We hypothesized that coagulation/complement and platelet
activation during MS relapse, likely during viral infections, could be related to CBF decrease.
Our specific aims are to evaluate whether there are differences in serum/plasma levels of
coagulation/complement factors between relapsing-remitting (RR) MS patients (RRMS) in relapse
and those in remission and healthy controls as well as to assess whether brain hemodynamic
changes detected by MRI occur in relapse compared with remission. This will allow us to
correlate coagulation status with perfusion and demographic/clinical features in MS patients.
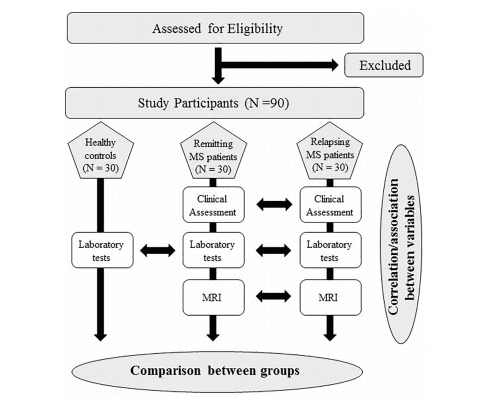
Materials and Methods: This is a multi-center, prospective, controlled study. RRMS patients (1°
group: 30 patients in relapse; 2° group: 30 patients in remission) and age/sex-matched controls
(3° group: 30 subjects) will be enrolled in the study. Patients and controls will be tested for
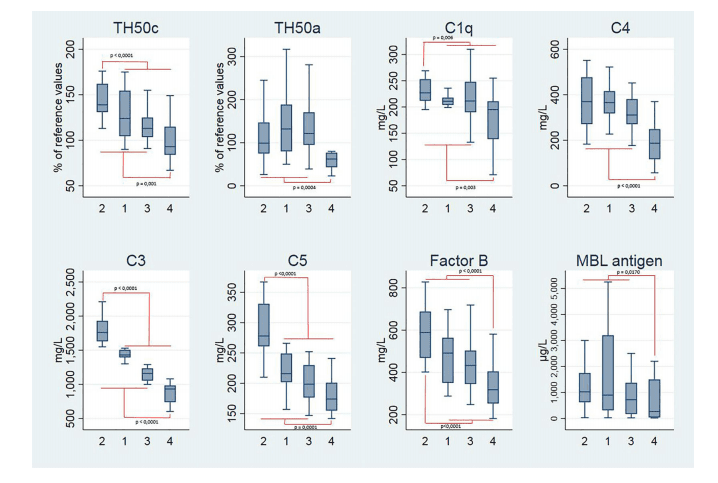
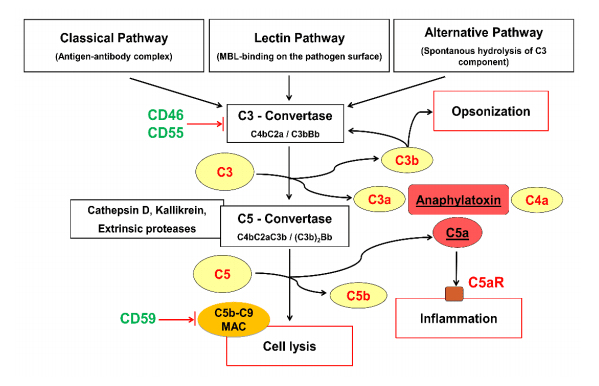
either coagulation/complement (C3, C4, C4a, C9, PT, aPTT, fibrinogen, factor II, VIII, and X,
D-dimer, antithrombin, protein C, protein S, von-Willebrand factor), soluble markers of
endothelial damage (thrombomodulin, Endothelial Protein C Receptor), antiphospholipid
antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, complete blood count, viral serological assays, or microRNA
microarray. Patients will undergo dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI using a 3.0-T
scanner to evaluate CBF, CBV, MTT, lesion number, and volume.
Statistical Analysis: ANOVA and unpaired t-tests will be used. The level of significance was set
at p ≤ 0.05.
Discussion: Identifying a link between activation of coagulation/complement system and cerebral
hypoperfusion could improve the identification of novel molecular and/or imaging biomarkers and
targets, leading to the development of new effective therapeutic strategies in MS.
Clinical Trial Registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, identifier NCT04380220.
Keywords: multiple sclerosis, coagulation, complement, platelets, relapse, infection, cerebral
hypoperfusion