Primary ADCP Assay
To ensure the efficacy and safety of novel and biosimilar antibody therapeutics, thorough functional analysis and characterization reflecting the drug's mechanism of action (MOA) are essential. Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive service portfolio, including functional cell-based assays like antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) evaluation, to support your antibody drug development needs.
Introduction to ADCP
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) is a crucial mechanism by which therapeutic antibodies targeting diseases like cancer can eliminate unwanted cells. In this process, antibodies bind to specific antigens on the surface of target cells, acting as a bridge to immune effector cells, such as macrophages, that express Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) on their surface. The interaction between the antibody's Fc region and these FcγRs on the effector cell triggers the effector cell to engulf and destroy the antibody-coated target cell through phagocytosis. This antibody-mediated activation of phagocytes is a significant pathway for achieving therapeutic efficacy.
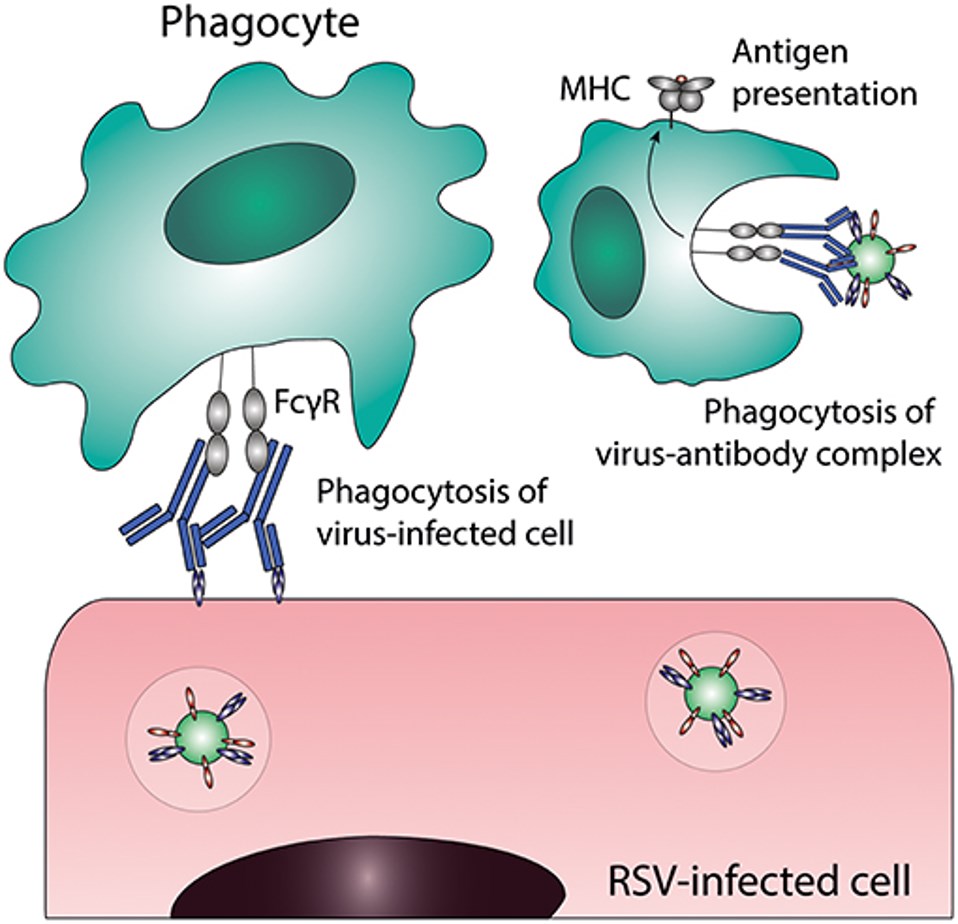 Fig.1 The process of antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis.1,3
Fig.1 The process of antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis.1,3
Primary ADCP Assay at Creative Biolabs
The conventional primary ADCP assay entails the isolation of monocytes from healthy donor peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using negative immunomagnetic selection, followed by in vitro differentiation into M2-polarized macrophages. This comprehensive methodology measures Fcγ receptor (CD32/CD64)-dependent phagocytic activity and integrates donor genotyping for FcγR polymorphisms, effectively accounting for genetic variability in antibody-FcγR interactions and the modulation of effector responses. We offer a reliable provision of human peripheral blood obtained from diverse donors, genotyping of effector cells for the FcγRIIIa 158 V/F polymorphism, and customizable assay design aligned with specific project needs.
Workflow: From Initiate to Results Delivery
The first stage is obtaining PBMC from healthy donors; next, monocytes are separated from the PBMCs usually using negative selection methods to ensure a high degree of purity.
To differentiate into macrophages, the separated monocytes go through prescribed conditions during culture. Usually, the treatment consists of the injection of growth factors and cytokines to generate the M2 macrophage phenotype, which is crucial for ADCP. Differentiating oneself might take many days, usually one week.
Target cells, such as tumor cells, are produced and often fluorescently tagged. This enables their exact identification and counting during the phagocytosis experiment.
We then incubate the target cells and test antibodies. This allows the antibody to bind to its target antigen on the target cell surface, a process called opsonization.
After that, we co-culture the antibody-opsonized target cells with the differentiated macrophages (effector cells). This allows the macrophages to interact with the antibody-bound target cells via Fc receptors (FcγRs).
The macrophages engulf the target cells, and this phagocytic activity is measured. Different methods can be used, including:
Flow cytometry: This is a common method where fluorescently labeled target cells within macrophages are quantified.
Live cell imaging: This allows for real-time monitoring of the phagocytosis process.
Reporter assays: While less direct, some assays use reporter genes to measure Fc receptor engagement, which correlates with phagocytosis.
Dose-response curves may be produced to evaluate the ADCP potency of the test antibody. The data produced by the selected measuring technique is examined to ascertain the degree of ADCP activity. Often this entails computing the proportion of macrophages that have consumed target cells.
Service Advantages
- Stable and sufficient human peripheral blood supply from multiple donors
- Effector cell genotyping regarding the FcγRIIIa 158 V/F polymorphism
- A large panel of target tumor cell lines to be used in ADCP assays
- The highest regulatory practice-compliant service upon request
- Flexible assay design that can be readily customized to fit your project
Case Study
Summary: This study examined the capacity of gp41-targeting antibodies to elicit ADCP responses. Experimental systems employing gp41-conjugated beads and primary HIV-1-infected cells as phagocytic targets, coupled with isolated monocytes and neutrophils, revealed that IgA antibody exhibited enhanced ADCP activity relative to IgG via FcαRI engagement, though effector cell types displayed distinct kinetic profiles. Notably, unlike antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), no cooperative phagocytic enhancement occurred between the two isotypes. These results highlight IgA-mediated ADCP as a potent mechanism for clearing HIV-1-infected cells, implying that vaccine-induced gp41-specific IgA responses could strengthen mucosal defense against viral entry.
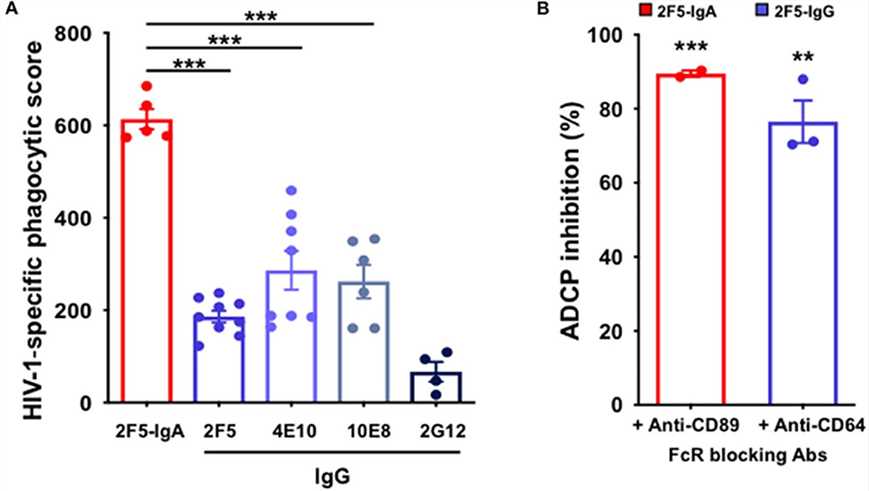 Fig.2 ADCP induced by anti-gp41 2F5-IgA and gp41-specific IgG.2,3
Fig.2 ADCP induced by anti-gp41 2F5-IgA and gp41-specific IgG.2,3
Associated Services
Complementing our primary ADCP assay, Creative Biolabs provides a robust ADCP reporter assay for comprehensive bioactivity assessment throughout therapeutic antibody development. Moreover, our expertise extends to a wide array of high-quality assays designed to quantify other crucial antibody Fc-mediated effector functions, including:
Q & A
-
Q1: What cell types are used as effector cells in primary ADCP assays?
A1: Primary human monocytes that have differentiated into macrophages are the most prevalent effector cells. Depending on the specific context and research question, other effector cells such as neutrophils or dendritic cells may also be utilized.
-
Q2: How is phagocytosis quantified in a primary ADCP assay?
A variety of approaches are employed, including:
Microscopy: A visual assessment of the quantity of target cells that have been phagocytosed by effector cells.
Flow Cytometry: Employing fluorescently labeled target and/or effector cells to measure engulfment events accurately.
Image Cytometry: Streamlined image analysis for enhanced precision in quantification.
-
Q3: What strategies can be implemented to reduce donor variability in primary ADCP assays?
A3: Implementing a reliable source of monocytes, standardizing differentiation protocols, and incorporating multiple donors can effectively reduce variability. Statistical analysis needs to consider the effects that are specific to each donor.
For specialized requirements in primary ADCP assays or to gain a deeper understanding of Creative Biolabs' ADCP assay services, please do not hesitate to contact us for further details.
References
- Van Erp, Elisabeth A., et al. "Fc-mediated antibody effector functions during respiratory syncytial virus infection and disease." Frontiers in Immunology 10 (2019): 548.
- Duchemin, Maxence, et al. "Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis of HIV-1-infected cells is efficiently triggered by IgA targeting HIV-1 envelope subunit gp41." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 1141.
- Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
