Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Gingival MSC Source
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes (GMSC-Exos)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have long been recognized for their regenerative and immunomodulatory capacities, yet the inherent risks associated with direct stem cell transplantation—including tumorigenicity, ectopic differentiation, and immune incompatibility—have driven interest toward cell-free alternatives. Among these, exosomes, the nanoscale vesicles secreted by MSCs, are emerging as potent mediators of intercellular communication and tissue repair. Gingival mesenchymal stem cells (GMSCs), a neural crest-derived MSC subpopulation isolated from gingival connective tissue, exhibit unique advantages over traditional MSC sources such as bone marrow and adipose tissue. They are easily accessible, minimally invasive to harvest, and possess a highly proliferative and immunomodulatory phenotype.
GMSC-derived exosomes (GMSC-Exos) encapsulate the molecular hallmarks of their parent cells, including RNAs, proteins, and lipids, offering a cell-free strategy that maintains therapeutic efficacy while circumventing many of the safety concerns associated with whole-cell therapies. Recent evidence suggests that GMSC-Exos can reproduce—and in some instances surpass—the regenerative and immunosuppressive effects of GMSCs in models of inflammatory disease and tissue damage.
Recognizing the clinical and research potential of these vesicles, Creative Biolabs has developed a comprehensive exosome service platform. We provide a full suite of GMSC-Exo based services, ranging from high-purity exosome isolation and characterization to advanced profiling and functional evaluation, ensuring clients receive reliable, reproducible results for their translational research or therapeutic pipelines.
Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes (GMSC-Exos) with Periodontal Protective Property
Among the most promising indications for GMSC-Exos is periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by alveolar bone loss and degradation of the periodontal ligament. Unlike other MSC populations, GMSCs are innately specialized for periodontal homeostasis due to their tissue origin. Their secreted exosomes exhibit a distinct capacity to regulate inflammatory and osteogenic pathways within periodontal microenvironments.
-
In vitro, GMSC-Exos have demonstrated the ability to simultaneously enhance the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) and suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt5a signaling. This dual function is particularly valuable in inflammatory bone loss conditions where bone regeneration and immune suppression must occur concurrently.
-
In vivo models support these findings. In a ligature-induced mouse model of periodontitis, exosomes derived from TNF-α-preconditioned GMSCs significantly mitigated alveolar bone resorption. Mechanistic investigations revealed that this effect was partly mediated by the delivery of miR-1260b, which attenuates osteoclast activity by modulating the Wnt5a/RANKL axis and promoting anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization.
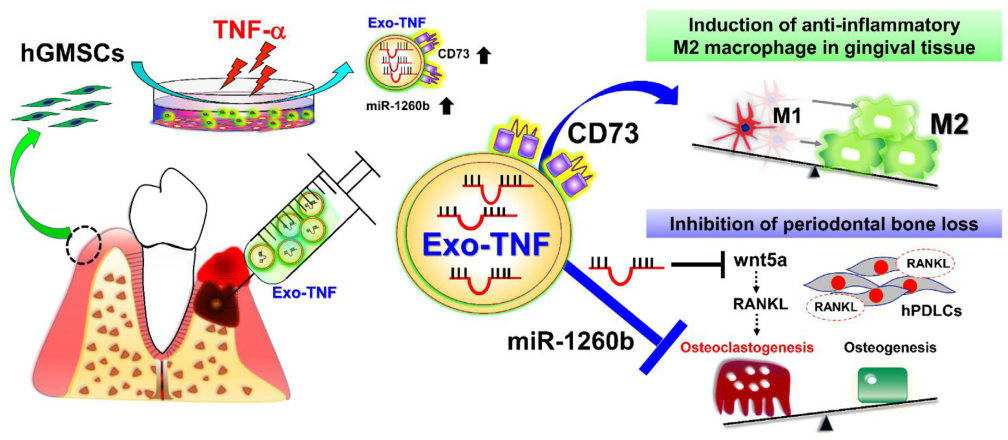 Fig.1 Proposed therapeutic strategy for periodontal disease using exosomes derived from TNF-α-treated GMSCs.1
Fig.1 Proposed therapeutic strategy for periodontal disease using exosomes derived from TNF-α-treated GMSCs.1
To facilitate such research, Creative Biolabs offers end-to-end exosome characterization services tailored for periodontal studies. Our portfolio includes nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and expression detection for canonical surface markers (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81). These tools are essential for confirming the identity and functional potential of GMSC-Exos in regenerative dental research.
Potential Applications of GMSC-Exos in Other Fields
While their periodontal applications are well-documented, GMSC-Exos are increasingly being recognized for their broader therapeutic potential in fields such as autoimmune disease management, wound healing, and neural regeneration.
-
Autoimmune Disease Modulation
GMSC-Exos have been shown to suppress T-cell proliferation and cytokine release, contributing to amelioration of autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Notably, in collagen-induced arthritis models, GMSC-Exos outperformed their parental cells in mitigating joint inflammation, underscoring their potential as a cell-free immunotherapeutic alternative. Their mechanism of action involves the delivery of anti-inflammatory miRNAs and immune-regulatory proteins that modulate effector T cell responses and antigen-presenting cell activity.
In the context of chronic wound healing, particularly in diabetic models, GMSC-Exos incorporated into hydrogel delivery systems have markedly accelerated re-epithelialization. These vesicles promote extracellular matrix remodeling by enhancing collagen synthesis, stimulate angiogenesis, and support peripheral nerve repair, thereby fostering a holistic tissue regeneration environment. Such results open avenues for applying GMSC-Exos in skin grafting, burn therapy, and diabetic ulcer treatment.
Neuroprotective applications of GMSC-Exos are gaining momentum. In retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury, exosomes from TNF-α-preconditioned GMSCs reduced neuronal apoptosis and inflammation by transferring miR-21-5p, which targets pro-apoptotic regulators such as PDCD4 in microglia. Similarly, in peripheral nerve injury models, the combination of GMSC-Exos with biomaterials such as chitin conduits or small intestinal submucosa has demonstrated synergistic effects—promoting axonal outgrowth, Schwann cell activation, myelination, and taste bud regeneration.
To support these applications, Creative Biolabs offers exosome engineering services, including exosome labeling services and disease-targeted exosome modification services, to tailor exosomes for specific therapeutic needs. Additionally, our exosome profiling services, such as exosomal RNA isolation and qPCR analysis services and exosomal protein isolation and profiling service, ensure precise measurement and analysis of exosomal components.
Advanced Exosome Profiling and Validation Services at Creative Biolabs
As a trusted partner in exosome research, Creative Biolabs is committed to advancing GMSC-Exo based applications from bench to bedside. Our services go beyond routine isolation—we offer:
Whether you are exploring the regenerative promise of GMSC-Exos in dentistry, dermatology, or neurology, we 're here to support your innovation every step of the way. Our scientists work closely with each client to design tailored study protocols, interpret complex data, and ensure regulatory-compliant documentation for preclinical pipelines. Contact us today to learn how our cutting-edge technologies and expert team can accelerate your research or therapeutic development.
FAQs
Q: What are GMSC-derived exosomes and how are they different from other MSC-Exos?
A: Gingival mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (GMSC-Exos) are small extracellular vesicles secreted by GMSCs. Unlike exosomes from other mesenchymal stem cell sources, GMSC-Exos have a unique affinity for periodontal tissues and show enhanced anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects, making them particularly well-suited for applications in oral and periodontal regenerative therapies.
Q: What therapeutic advantages do GMSC-Exos offer over GMSC-based cell therapies?
A: GMSC-Exos retain the therapeutic benefits of GMSCs—such as immunomodulation and tissue repair—while avoiding risks associated with direct cell transplantation, including tumorigenicity, uncontrolled proliferation, and immune rejection.
Q: How can Creative Biolabs support research on GMSC-Exos?
A: We offer end-to-end exosome solutions tailored for GMSC-Exo research, including high-quality exosome isolation, purification, characterization (e.g., NTA, TEM, surface markers), and profiling (e.g., RNA, protein, lipid, metabolite). For clients focused on therapeutic translation, we also provide engineering services for exosome labeling and targeted delivery design.
Reference
-
Nakao, Yuki et al. "Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss." Acta biomaterialia vol. 122 (2021): 306-324. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.046. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Proposed therapeutic strategy for periodontal disease using exosomes derived from TNF-α-treated GMSCs.1
Fig.1 Proposed therapeutic strategy for periodontal disease using exosomes derived from TNF-α-treated GMSCs.1









