Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Wharton’s Jelly MSC Source
Introduction Advantages Applications Services FAQs
Why Develop Exosomes from Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells (WJMSCs-Exos)?
Wharton's jelly, the gelatinous connective tissue surrounding blood vessels within the umbilical cord, represents a uniquely rich and underutilized reservoir of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Among various MSC sources, Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (WJMSCs) are notable for their accessibility, abundance, and non-invasive harvesting process. These features, coupled with a favorable ethical profile—given that umbilical cords are typically discarded postpartum—position WJMSCs as an attractive alternative to other MSC sources, such as bone marrow or adipose tissue.
In recent years, a growing body of evidence has underscored the therapeutic promise of exosomes derived from WJMSCs (WJMSCs-Exos). These nanoscale vesicles, typically ranging from 30 to 150 nm in diameter, carry a diverse cargo of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that mirror the regenerative and immunomodulatory functions of their parent cells. Importantly, WJMSCs-Exos offer a potential solution to several limitations associated with traditional cell-based therapies, including concerns over immune rejection, cell engraftment efficiency, and the risks of aberrant differentiation. Their inherent stability and ability to cross biological barriers, such as the blood-brain barrier, further highlight their potential as next-generation therapeutic tools.
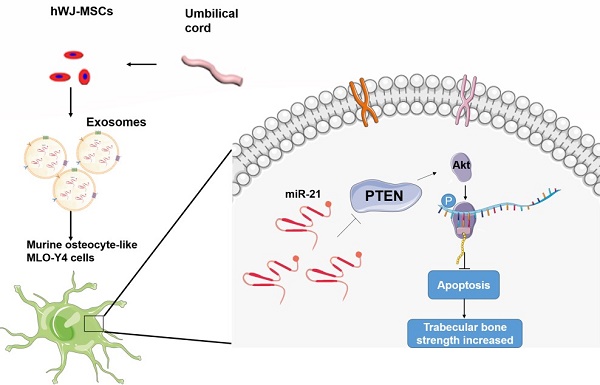 Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis.1
Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis.1
Creative Biolabs summarized the characteristics and promising applications of exosomes derived from WJMSCs (WJMSCs-Exos), and offers a range of services that support the isolation and development of WJMSCs-Exos. In addition, services like exosome modification and cargo loading allow for the engineering of WJMSCs-Exos to enhance their properties for specific treatments, such as lung-targeted exosome modification and cancer-targeted exosome modification.
Key Characteristics of WJMSCs-Exos
Several distinct features make Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (WJMSCs-Exos) a particularly attractive class of therapeutic agents:
-
Abundant Source. Wharton's jelly serves as a plentiful and easily accessible reservoir of MSCs, enabling the consistent production of large quantities of WJMSCs-Exos. This scalability highlights the value of exosome manufacturing services in meeting research and clinical demands.
-
Non-invasive collection. Unlike MSCs sourced from bone marrow or adipose tissue, which typically require invasive procedures, WJMSCs can be obtained from discarded umbilical cords, making the process ethically favorable and minimally invasive.
-
Low immunogenicity. WJMSCs-Exos generally exhibit minimal immunogenic responses, an advantage preserved through refined exosome purification protocols. This property makes them well-suited for allogeneic therapies without eliciting significant immune rejection.
-
Broad Biological Activity. WJMSCs-Exos reflect the inherent plasticity of their parental cells, exhibiting pleiotropic effects that influence a wide range of biological processes. Advanced exosome proteomic and RNA profiling techniques help elucidate these diverse functional roles, including their impact on inflammation, tissue regeneration, and cellular communication.
-
Regenerative potential. WJMSCs-Exos promote tissue repair and regeneration in various diseases. Their regenerative capabilities can be further clarified and optimized through services such as exosomal protein profiling services, exosomal RNA sequencing services, and functional assays to pinpoint specific bioactive cargo.
-
Easily modified. WJMSCs-Exos can be engineered to deliver specific therapeutic payloads—whether small RNAs, proteins, or small molecules—through parental cell modification or direct exosome loading. This versatility makes them promising candidates for targeted drug delivery applications.
-
Favorable Handling Properties. Thanks to their lipid bilayer structure, WJMSCs-Exos are remarkably stable under standard storage and transport conditions. This robustness facilitates long-term storage and simplifies logistics for clinical and research use.
Together, these characteristics position WJMSCs-Exos as a highly promising tool in regenerative medicine and therapeutic development.
How WJMSCs-Exos Exert Therapeutic Potential?
Intranasal delivery of WJMSCs-Exos has been shown to suppress neuroinflammation in rats by dampening proinflammatory cytokine production and inhibiting the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway in glial cells. This approach also reduces neuronal apoptosis, supporting recovery after brain injuries. Additionally, WJMSCs-Exos, when pretreated with ginkgolide A, can inhibit the aggregation of α-synuclein and restore neural function. Exosomal miRNA sequencing services are instrumental in pinpointing key regulatory RNAs underlying these neuroprotective effects.
WJMSCs-Exos exhibit strong regenerative potential by promoting chondrocyte proliferation, driving macrophage polarization, and suppressing inflammation—critical steps for cartilage repair. In osteonecrosis models, they protect osteocytes via the miR-21-PTEN-AKT axis. Furthermore, the abundant α-2-macroglobulin content in WJMSCs-Exos enhances skin wound healing in mice. Exosomal RNA isolation and qPCR services can help validate these mechanisms, while exosome engineering services offer opportunities to tailor WJMSCs-Exos for targeted tissue regeneration.
WJMSCs-Exos serve as promising drug delivery vehicles. For instance, paclitaxel-loaded WJMSCs-Exos have been shown to suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition and induce apoptosis in cervical cancer cells in vitro. Similarly, WJMSCs-Exos carrying miR-124 inhibit the proliferation and migration of glioblastoma cells. Exosome modification services can further enhance the targeting capabilities of these vesicles, including tumor-specific modifications for improved delivery.
WJMSCs-Exos can potentiate antimicrobial therapies. When co-administered with certain antimicrobial drug, they amplify the anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic responses against E. coli infection. Likewise, combining WJMSCs-Exos with aloe-emodin enhances the killing of Leishmania parasites and promotes wound healing. Exosomal protein profiling services can elucidate the immunomodulatory roles of these exosomes in infectious disease contexts.
WJMSCs-Exos modulate immune responses by enhancing neutrophil survival and boosting their phagocytic capacity—an effect that may benefit patients with immunodeficiencies. As neutrophils are frontline defenders in pathogen clearance, these findings open the door for exosome-based immunotherapy. Exosome functional assays in vitro provide critical insights into the mechanisms underlying these immune-enhancing properties.
-
Graft-versus-host Disease
The immunosuppressive potential of WJMSCs-Exos, particularly those enriched in PD-L1, offers a novel strategy for managing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). By attenuating T-cell activation, PD-L1-enriched exosomes could mitigate GVHD severity. Exosome engineering services focused on PD-L1 modification could facilitate the development of targeted therapies for this challenging condition.
WJMSCs-Exos support lymphatic regeneration by delivering angiopoietin-2 to lymphatic endothelial cells, activating the PROX1/Akt pathway, and promoting lymphangiogenesis. These actions have been shown to improve lymphatic function and reduce swelling in lymphedema models, highlighting the potential of WJMSCs-Exos as a therapeutic option for this condition.
Preconditioning bone marrow-derived myeloid cells with WJMSCs-Exos facilitates their differentiation into an immunosuppressive phenotype, which aids in restoring alveolar architecture, enhancing angiogenesis, and suppressing inflammation—culminating in improved lung function. Exosome modification services can optimize these effects, while disease models serve to validate therapeutic efficacy in lung injury scenarios.
Creative Biolabs: Your Partner in WJMSCs-Exos Research and Development
While the therapeutic promise of WJMSCs-Exos is clear, translating these vesicles into clinically viable products requires overcoming significant challenges in isolation, characterization, engineering, and large-scale production. That's where Creative Biolabs comes in. We provide a comprehensive suite of exosome services tailored to your research and development needs—from isolation and profiling to functional validation and therapeutic engineering. Whether you're looking to load specific cargo into exosomes, optimize their targeting capabilities, or scale up production for preclinical and clinical studies, our team is ready to support your goals. Interested in unlocking the potential of WJMSCs-Exos for your next therapeutic project? Contact us today and let's explore the possibilities together.
FAQs
Q: What makes Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived exosomes (WJMSCs-Exos) unique compared to exosomes from other MSC sources?
A: WJMSCs-Exos stand out for several reasons. Wharton's jelly provides a rich, non-invasive, and ethically favorable source of MSCs, allowing for large-scale exosome production. These exosomes exhibit low immunogenicity, carry a broad range of bioactive molecules, and demonstrate potent regenerative and immunomodulatory effects across various disease models. Their cargo profile and stability make them particularly suitable for clinical translation.
Q: How can WJMSCs-Exos be used in research and therapy?
A: WJMSCs-Exos have demonstrated promise in neurological diseases, tissue regeneration, cancer therapy, immunomodulation, and infectious disease management. They can serve as therapeutic agents themselves—modulating inflammation, promoting repair, or delivering specific cargo—and as vehicles for engineered therapies, such as miRNA or small-molecule drugs. At Creative Biolabs, we support researchers in both natural and engineered exosome applications through our comprehensive exosome services.
Q: What are the main challenges in working with WJMSCs-Exos?
A: Challenges include comprehensive characterization of their cargo, ensuring reproducibility in bioactivity, and scaling up production for clinical use. Creative Biolabs offers tailored solutions for these challenges, including optimized exosome isolation kits, exosomal RNA/protein profiling services, and scalable production platforms to support your R&D efforts.
Q: Can WJMSCs-Exos be customized for specific therapeutic targets?
A: Absolutely. WJMSCs-Exos can be engineered to carry specific therapeutic molecules—such as miRNAs, small interfering RNAs, proteins, or drugs—via advanced techniques like electroporation, chemical conjugation, or parental cell modification. Creative Biolabs' exosome engineering services allow you to design exosomes with precise targeting and delivery capabilities to meet your unique research or therapeutic goals.
Reference
-
Kuang, Ming-jie, et al. "Exosomes derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via the miR-21-PTEN-AKT signalling pathway." International journal of biological sciences 15.9 (2019): 1861. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis.1
Fig.1 Exosomes derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis.1









