Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Neural Stem Cell Source
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
Introduction of Neural Stem Cell-derived Exosomes (NSC-Exos)
Exosomes derived from neural stem cells (NSC-Exos) have emerged as a promising tool in the field of neuroscience and regenerative medicine. These nanoscale vesicles, typically ranging from 30 to 150 nm in diameter, are secreted by NSCs and serve as carriers of a rich assortment of bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, mRNAs, and microRNAs. What makes NSC-Exos particularly valuable is that they preserve many of the beneficial properties of their parent cells—such as promoting neurogenesis, neuroprotection, and neuronal plasticity—without the risks associated with cell transplantation, like tumorigenicity or immune rejection.
Unlike whole-cell therapies, exosomes can cross the blood-brain barrier, be stored long-term without loss of function, and be engineered to carry specific therapeutic payloads. These characteristics make NSC-Exos highly attractive candidates for treating a range of neurological disorders, from stroke and Alzheimer 's disease to glioma and spinal cord injury.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a full suite of services to support NSC-Exo research, including isolation from cell lines and detailed characterization using advanced methods like nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Whether you're looking to explore the natural cargo of NSC-Exos or engineer them for targeted delivery, our team offers the technical expertise and flexible solutions to help you advance your research from concept to application.
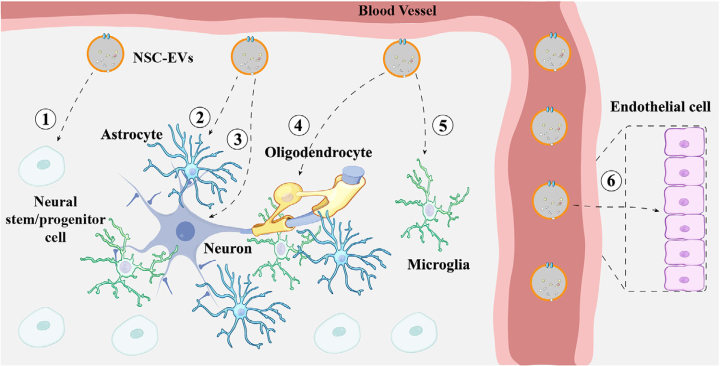 Fig.1 The functions of neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (NSC‐EVs) in the central nervous system microenvironment.1
Fig.1 The functions of neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (NSC‐EVs) in the central nervous system microenvironment.1
NSC-Exos with Neuroprotective Properties
NSC-Exos hold several practical and biological advantages over using NSCs directly:
-
Direct brain delivery: When administered intranasally, NSC-Exos can reach distinct brain regions with high efficiency.
-
Intercellular messaging: These exosomes are rapidly internalized by recipient cells, triggering key cellular processes by releasing their functional contents.
-
Low tumor risk: Unlike NSCs, exosome-based therapies pose minimal risk of tumorigenesis or unwanted cell proliferation.
-
BBB permeability: With a nanoscale diameter of 30–150 nm, NSC-Exos can cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB) with ease.
-
Long-term stability: They 're stable at -80°C, retain integrity at 4°C for short periods, and can even be lyophilized for extended storage and transport.
-
Enhanced brain targeting: Compared to exosomes from other stem cell types, NSC-Exos show stronger homing to neural tissue and more robust neurotrophic effects.
Feasibility Application of NSC-Exos in the Neurological Disease Treatment
With their multi-faceted neuroprotective capabilities, NSC-Exos have sparked growing interest in a variety of neurological applications. At Creative Biolabs, we support this research with a comprehensive suite of profiling services—including exosomal RNA isolation and qPCR, proteomics, and miRNA sequencing—to help dissect exosome cargo and optimize therapeutic strategies.
NSC-Exos can promote recovery after stroke by shifting microglia toward an anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, reducing inflammation and enhancing neuronal regeneration. They've also been shown to alleviate intracranial bleeding and cerebral edema. Through our exosome engineering platform, NSC-Exos can be loaded with neurotrophic factors like BDNF to further enhance endogenous NSC differentiation and brain repair.
In neurodegenerative settings, NSC-Exos can interfere with Aβ binding to neuronal receptors, reducing Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and plaque burden. This is largely driven by miRNAs such as miR-125-5p, miR-124-3p, and miR-125a-5p. Using exosomal miRNA sequencing and other profiling, Creative Biolabs provides technical support to help client to pinpoint these regulatory molecules for targeted interventions in diseases like Alzheimer 's.
Delivery of miR-124-3p via NSC-Exos has shown strong inhibitory effects on glioma cell proliferation and invasion, primarily through suppression of flotillin 2. Creative Biolabs offers exosomal proteomic detection services and exosomal miRNA sequencing to analyze and verify the molecular interactions between exosomal miRNAs and glioma cells, potentially providing novel therapeutic approaches for cancer treatment.
NSC-Exos help mitigate neuron apoptosis, inflammation, and microglial activation in spinal cord injury models by promoting autophagy via LC3B and beclin-1. They also stimulate vascular remodeling and the neurogenic differentiation of endogenous NSCs. For research in spinal cord and traumatic brain injury, our exosome quantification services and exosome cargo loading services help optimize the loading of therapeutic agents into NSC-Exos, making them suitable for nervous system disease model construction and research in spinal cord and brain injury recovery.
The Most Comprehensive Exo Research Services at Creative Biolabs
NSC-Exos represent a powerful and versatile tool for tackling neurological diseases. They not only support neurogenesis and anti-inflammatory responses but also facilitate drug delivery and tissue regeneration. To help researchers realize the full potential of these nanocarriers, Creative Biolabs offers an end-to-end exosome research services—from high-quality exosome manufacturing to functional validation. We also provide exosome labeling and surface modification services to support in vivo tracking and targeted delivery.
As the field continues to evolve, NSC-Exos are positioned to play an increasingly vital role in neuroscience and regenerative medicine. If you 're exploring stem cell-derived exosomes for brain-related applications, contact us. Our team is here to provide tailored solutions in exosome engineering, purification, and in vitro/in vivo functional testing to move your project forward with confidence.
FAQs
Q:What makes NSC-derived exosomes different from exosomes derived from other stem cells?
A: NSC-Exos are particularly enriched in neurotrophic factors, neural-specific miRNAs, and proteins that support brain development and repair. Compared to exosomes from other mesenchymal or pluripotent stem cells, NSC-Exos show a stronger tendency to home to neural tissue and exert more targeted neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects.
Q: Can NSC-Exos actually cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
A: Yes, and that 's one of their biggest advantages. Due to their nanoscale size (typically 30–150 nm) and biological membrane composition, NSC-Exos can cross the BBB more efficiently than many synthetic drug delivery systems. This makes them especially valuable for treating brain-related disorders through non-invasive routes like intranasal administration.
Q: Are NSC-Exos safe for therapeutic use?
A: So far, NSC-Exos have demonstrated a favorable safety profile in preclinical studies. Unlike whole-cell therapies, exosomes do not divide or differentiate, which significantly reduces the risk of tumorigenesis. Plus, their immunogenicity is relatively low. Still, rigorous quality control and functional testing are essential before any clinical application.
Q: Can NSC-Exos be customized for specific therapeutic applications?
A: At Creative Biolabs, we offer exosome engineering services that allow you to load NSC-Exos with specific RNAs, proteins, or small molecules. Whether you're interested in enhancing their targeting abilities or delivering therapeutic agents like BDNF or miRNAs, we can help tailor the exosomes to your needs.
Q: How stable are NSC-Exos during storage and transport?
A: NSC-Exos are relatively stable. They can be stored at -80°C long-term without significant degradation. For short-term use, 4°C storage is acceptable. Lyophilized (freeze-dried) exosomes also retain bioactivity and are much easier to ship globally, especially for collaborative research or commercial development.
Reference
-
Li, Xiangyu et al. "Neural stem/progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel therapy for neurological diseases and beyond." MedComm vol. 4,1 e214. 7 Feb. 2023, doi:10.1002/mco2.214. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The functions of neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (NSC‐EVs) in the central nervous system microenvironment.1
Fig.1 The functions of neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (NSC‐EVs) in the central nervous system microenvironment.1









