Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Menstrual Blood MSC Source
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
Introduction: A Novel and Ethical Source of MSCs
Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MBMSCs) represent a unique and ethically uncontroversial source of adult stem cells. Harvested non-invasively from menstrual effluent, MBMSCs circumvent many of the ethical and procedural barriers associated with bone marrow or adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). These cells possess classical MSC characteristics, including fibroblast-like morphology, plastic adherence, and multipotency, and are capable of differentiating into osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, hepatic, and even cardiomyogenic lineages under appropriate stimuli. Their high proliferation rate and non-invasive accessibility make them especially attractive for scalable therapeutic applications.
The Emergence of MBMSC-derived Exosomes (MBMSC-Exos)
As cell-free therapeutic strategies continue to gain traction, exosomes—nanoscale extracellular vesicles of endosomal origin—have emerged as potent mediators of paracrine signaling. MBMSCs, like other MSC populations, secrete exosomes enriched with a broad array of biologically active molecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which collectively recapitulate many of the regenerative properties of their parental cells. MBMSC-derived exosomes (MBMSC-Exos) have garnered increasing attention for their capacity to modulate diverse cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, and immune regulation. Once internalized by recipient cells, MBMSC-Exos trigger functional responses that mirror the reparative and immunomodulatory cues of MBMSCs themselves.
What distinguishes MBMSC-Exos is their unique molecular composition, partly reflective of the reproductive tissue origin of their parent cells. These vesicles are increasingly recognized for their therapeutic versatility across domains including tissue regeneration, oncology, and reproductive biology.
The Advantages of MBMSC-Exos as Therapeutic Agents
Several features distinguish MBMSC-Exos as promising agents in cell-free therapy:
-
Non-invasive collection: Unlike bone marrow or adipose tissue harvesting, menstrual blood collection is entirely non-invasive and repeatable.
-
Scalability: The high proliferative capacity of MBMSCs supports mass production of exosomes under GMP-compatible conditions.
-
Low immunogenicity: Like other MSC-derived exosomes, MBMSC-Exos exhibit minimal immunogenicity, enhancing their suitability for allogeneic applications.
-
Stability and delivery potential: The lipid bilayer of exosomes ensures cargo protection and supports systemic delivery, including crossing biological barriers like the BBB.
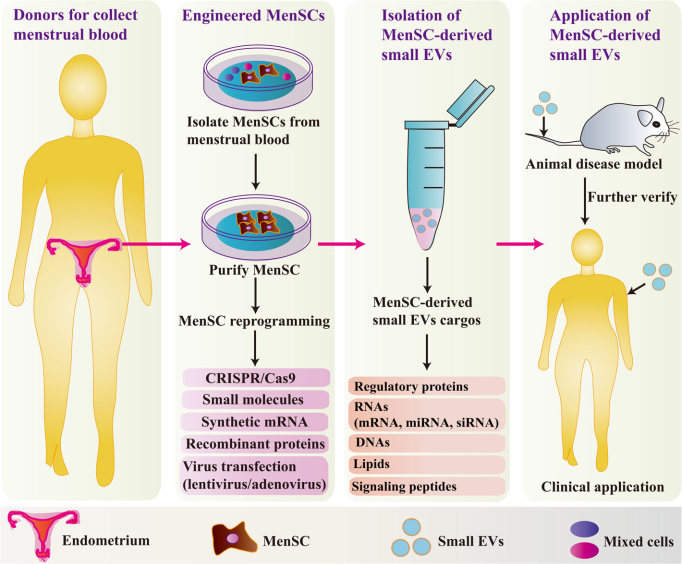 Fig.1 The strategy for developing clinical applications of MenSC-derived small EVs.1
Fig.1 The strategy for developing clinical applications of MenSC-derived small EVs.1
MBMSC-Exos Potential in Therapy Field
Creative Biolabs collected the research data of MBMSC-Exos and summarized how researchers used MBMSC-Exos in therapeutic studies.
-
MBMSC-Exos in Tissue Repair and Regeneration
MBMSC-Exos inherit the pro-regenerative characteristics of their source cells and have shown promising effects in multiple tissue repair models. Preclinical studies have demonstrated their ability to promote neural regeneration by enhancing neurite outgrowth and axonal elongation. In models of pulmonary fibrosis, MBMSC-Exos modulate macrophage activity, suppress oxidative stress, and inhibit apoptosis, in part via the transfer of let-7 family miRNAs. Similarly, hepatoprotective effects have been documented in liver injury models, where MBMSC-Exos suppress hepatocyte apoptosis and restore liver function.
In the context of metabolic disease, MBMSC-Exos have been shown to activate Pdx-1 signaling pathways, restoring β-cell mass and enhancing insulin synthesis—findings that underscore their potential in type 1 diabetes therapy. Moreover, in cutaneous wound healing models, these vesicles accelerate repair by regulating macrophage polarization and promoting collagen deposition.
At Creative Biolabs, we support these applications by offering a full suite of exosome-based research services. Our platform includes exosome isolation, nanoparticle tracking analysis, TEM-based morphology evaluation, and Western blot or flow cytometry-based marker identification. For downstream functional evaluation, we provide in vitro and in vivo bioassays tailored to your specific disease model—whether it's pulmonary injury, liver disease, or metabolic dysfunction. Let us help streamline your preclinical development process.
-
MBMSC-Exos and Tumor Biology
Interestingly, MBMSC-Exos have shown potential not only in regenerative medicine but also in modulating tumor progression. In prostate cancer cells, these exosomes attenuate reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated angiogenesis, leading to suppression of neovascularization and reduced tumor growth. A similar anti-angiogenic effect has been reported in oral squamous cell carcinoma, where MBMSC-Exos downregulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and promote endothelial cell apoptosis.
These findings suggest that MBMSC-Exos may function as biological inhibitors of tumor vascular remodeling—a feature that could be harnessed for anti-cancer therapies targeting the tumor microenvironment. To advance such discoveries, Creative Biolabs offers high-throughput exosomal RNA-sequencing and proteomics profiling, empowering researchers to dissect the molecular underpinnings of these anti-angiogenic mechanisms.
-
Reproductive Function Modulation by MBMSC-Exos
Given their origin, MBMSC-Exos are uniquely positioned to impact reproductive biology. Preclinical data indicate that these exosomes enhance ovarian function by promoting granulosa cell proliferation, activating dormant follicles, and upregulating components of the ovarian extracellular matrix. Moreover, MBMSC-Exos appear to improve embryonic development by modulating oxidative stress-related signaling pathways.
These effects point to new avenues for addressing female infertility, especially in patients with diminished ovarian reserve or age-related reproductive decline. To support research in this area, Creative Biolabs provides transcriptomic and proteomic profiling of MBMSC-Exos, offering insights into the molecular drivers of folliculogenesis and oocyte competence.
Partner with Creative Biolabs
Menstrual blood-derived MSC exosomes represent a transformative step in the field of regenerative and cell-free medicine. Their biological potency, ethical sourcing, and translational flexibility make them ideal candidates for applications spanning tissue repair, oncology, and reproductive health. As research into MBMSC-Exos accelerates, their full clinical utility will undoubtedly become more apparent.
As MBMSC-Exos continue to demonstrate remarkable potential across diverse indications, researchers are increasingly seeking robust, scalable, and customizable tools to support translational studies. That 's where Creative Biolabs comes in.
We offer:
Contact us today to discuss your next project—we're here to help you move from promising research to practical breakthroughs.
FAQs
Q: What analytical services are available for characterizing MBMSC-Exos?
A: Our characterization package includes nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) for size and concentration, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for morphology, western blot or flow cytometry for exosomal markers (CD9, CD63, CD81), and RNA/protein cargo profiling via next-generation sequencing and LC-MS/MS.
Q: How can I enhance the targeting ability of MBMSC-derived exosomes?
A: Through our exosome engineering services, we can modify the surface of MBMSC-Exos with peptides, antibodies, or ligands to improve disease-specific targeting. We also offer cargo-loading technologies (e.g., electroporation, sonication, transfection) to enrich exosomes with therapeutic RNAs or proteins.
Q: What is the turnaround time for exosome isolation and analysis services?
A: Turnaround time depends on the complexity of your project. Standard exosome isolation and basic characterization typically take 4–6 weeks. More advanced services, such as omics profiling or functional assays, may take longer. We provide detailed timelines at project initiation and keep you informed throughout the process.
Reference
-
Chen, Lijun et al. "Small extracellular vesicles from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MenSCs) as a novel therapeutic impetus in regenerative medicine." Stem cell research & therapy vol. 12,1 433. 3 Aug. 2021, doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02511-6. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The strategy for developing clinical applications of MenSC-derived small EVs.1
Fig.1 The strategy for developing clinical applications of MenSC-derived small EVs.1









