Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Source
Introduction Applications Advantages Services FAQs
Hematopoietic Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes (HSC-Exos): A Promising Cell-Free Strategy for Regenerative Medicine
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), primarily residing in the bone marrow but also found in peripheral blood, spleen, liver, and other tissues, are the sole source of all blood and immune cells. However, despite their remarkable clinical utility, HSC-based therapies face critical challenges, including limited donor availability, potential for immune rejection, and difficulties in large-scale manufacturing.
In recent years, exosomes derived from HSCs (HSC-Exos) have emerged as a promising cell-free alternative that retains many of the functional properties of their parent cells. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles, typically 30–150 nm in diameter, secreted by a wide range of cell types, including stem cells. They carry a diverse cargo of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, reflecting the molecular profile of their cells of origin. This cargo enables exosomes to mediate intercellular communication, modulate immune responses, and influence cellular behavior, making them attractive candidates for therapeutic applications.
HSC-Exos, in particular, have garnered increasing interest for their ability to promote hematopoiesis, modulate immune responses, and support tissue repair. Importantly, compared to whole-cell therapies, exosome-based strategies offer several advantages, including lower immunogenicity, improved safety profiles, and greater ease of storage and handling. These features position HSC-Exos as a scalable and versatile tool for advancing regenerative medicine.
As continuous development of cutting-edge technology, Creative Biolabs have made substantial strides in providing exosome technology services, aimed at helping researchers to develop the yield and functionality of HSC-Exos.
Functional Potential of HSC-Exos in Hematopoiesis and Vascular Regeneration
A key feature of HSC-Exos is their ability to inherit critical molecular signatures from their parent cells, including hematopoiesis-related factors such as microRNAs (e.g., miR-126), cytokines, and signaling molecules. MiR-126, in particular, has been implicated in both hematopoietic differentiation and vascular remodeling, suggesting a dual role for HSC-Exos in supporting blood cell formation and promoting angiogenesis.
Emerging studies have demonstrated that HSC-Exos can influence the fate of other stem cells. For instance, co-culturing HSC-Exos with mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) has been shown to enhance hematopoietic lineage differentiation, potentially by modulating the miR-126/Notch1 signaling axis. These findings highlight the potential of HSC-Exos not only as therapeutic agents but also as tools to manipulate stem cell fate for research and clinical applications. Services like exosomal miRNA sequencing, exosomal RNA qPCR analysis and in vitro functional research of exosomes provide tools to quantify and analyze the molecular contents of HSC-Exos that contribute to vascular regeneration.
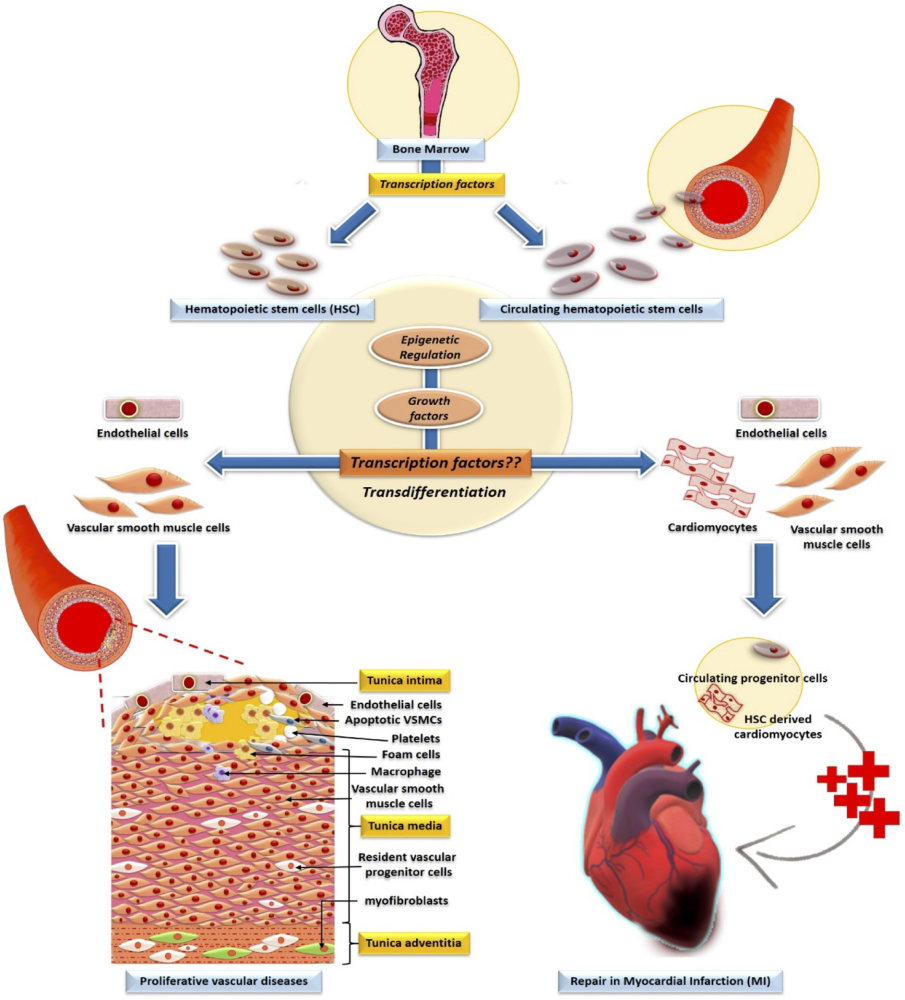 Fig.1 Involvement of transcription factors and their epigenetic modification in the development of HSC.1
Fig.1 Involvement of transcription factors and their epigenetic modification in the development of HSC.1
Furthermore, exosomes derived from CD34+ HSCs—a well-established marker of hematopoietic stemness—have demonstrated pro-angiogenic activity in preclinical models. This angiogenic potential suggests that HSC-Exos could play a role in treating ischemic diseases, where restoring blood supply is critical for tissue recovery. However, challenges remain in scaling up the isolation and characterization of HSC-Exos, given the rarity of HSCs in native tissues and the technical limitations of current exosome production methods. Through exosome characterization via FACS, Western Blotting or ELISA, Creative Biolabs offers robust services for analyzing and identifying the exosome populations with the highest angiogenic potential.
Advantages of HSC-Exos
From a practical perspective, HSC-Exos offer several logistical and biological advantages that could facilitate their transition into clinical use.
1. Reproducible and Scalable
The preparation of HSC-Exos is relatively straightforward, relying on established techniques such as ultracentrifugation and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) to isolate exosomes with high purity and yield. At Creative Biolabs, we provide tailored exosome isolation services optimized for stem cell sources, ensuring reproducible and scalable workflows for HSC-Exos production.
2. Remarkable Stability
HSC-Exos can be stored under a range of conditions—including refrigeration, freezing, or lyophilization—without significant loss of bioactivity. This contrasts with whole-cell therapies, where cell viability and functionality can be severely compromised by cryopreservation or extended storage. Creative Biolabs provides activity and stability tests and large-scale production service.
3. Lower Immunogenicity
The immunological profile of HSC-Exos is more favorable than that of their parent cells. Exosomes generally exhibit lower immunogenicity, reducing the risk of adverse immune responses following administration. This property is particularly relevant for allogeneic applications, where donor-recipient mismatches remain a major hurdle in HSC transplantation.
4. Potential Hematopoiesis Function
The functional potential of HSC-Exos to promote hematopoiesis is supported by their molecular composition. Through services such as exosomal RNA sequencing, proteomics, and miRNA profiling, researchers can characterize the bioactive cargo of HSC-Exos in detail. At Creative Biolabs, we provide a comprehensive suite of analytical tools to support functional evaluation, enabling researchers to link specific exosomal components—such as miR-126 or angiogenic factors—with desired biological outcomes, such as enhanced hematopoietic recovery or improved vascularization.
Creative Biolabs: Supporting the Development of HSC-Exos
At Creative Biolabs, we recognize both the promise and the challenges of translating HSC-Exos into viable therapeutic products. That's why we offer a full spectrum of exosome-related services designed to support every stage of HSC-Exos development—from early discovery to preclinical validation.
Our exosome isolation and purification services leverage cutting-edge technologies like ultracentrifugation, SEC, and immunoaffinity capture to ensure high-purity exosome preparations. We also provide robust characterization platforms, including nanoflow analysis, Western blotting, ELISA, and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), to confirm the identity, size distribution, and surface marker profiles of your HSC-Exos samples.
For researchers aiming to enhance the therapeutic potential of their exosomes, we offer advanced services in exosome engineering, such as cargo loading (e.g., miRNAs, siRNAs, proteins), surface modification for targeted delivery, and functional assays to evaluate hematopoietic and angiogenic activities in vitro and in vivo. Whether you're looking to optimize exosome yields, improve their cargo profiles, or assess functional outcomes in disease models, our team is here to help you navigate the complexities of HSC-Exos development.
If you're exploring the therapeutic potential of HSC-Exos—or any other stem cell-derived exosomes—Creative Biolabs would love to collaborate with you. Please contact us today to learn how our customized solutions can accelerate your research and bring your exosome-based innovations closer to clinical application.
FAQs
Q: How do HSC-Exos improve upon existing stem cell therapies?
A: Think of these nanosized bubbles as concentrated "care packages" from blood stem cells. They pack all the crucial stuff like miRNAs and proteins that drive tissue repair, but ditch the baggage of live cells. No more worrying about immune rejection risks or accidental tumor growth – plus they're shelf-stable and easier to work with than temperamental living cells.
Q: What's your secret for getting clean exosome preps?
A: Typically, HSC-Exos are isolated using ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), or ultrafiltration methods. At Creative Biolabs, we use a single/combination of these techniques to get high-purity exosomes with minimal contamination from other particles. We also run a series of characterization assays (like Western blot, NTA, and FACS) to make sure the exosomes are exactly what they should be.
Q: Can we turn these exosomes into targeted drug couriers?
A: Our team engineers these natural delivery vehicles in two ways: 1) Packing customized payloads (like healing RNAs or anti-inflammatory proteins) into their core, or 2) Giving them "homing beacon" surface tags to zero in on damaged tissues. Imagine creating smart bombs that only attack inflammation hotspots!
Q: When will we see these in actual treatments?
A: The science is moving faster than you'd think. Animal studies already show promise for bone marrow recovery and heart attack repair. While human trials are still on the horizon, the pieces are falling into place – better isolation methods and clearer regulatory pathways could make these exosome therapies mainstream within the next 5-8 years.
Reference
-
Duddu, Sushmitha, et al. "Hematopoietic stem cell transcription factors in cardiovascular pathology." Frontiers in Genetics 11 (2020): 588602. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Involvement of transcription factors and their epigenetic modification in the development of HSC.1
Fig.1 Involvement of transcription factors and their epigenetic modification in the development of HSC.1









