Custom Folic Acid-siRNA Conjugation Service
Folic Acid–siRNA Conjugates are sophisticated bioconjugates formed by the covalent attachment of folic acid (also known as vitamin) to an siRNA molecule. Creative Biolabs is a global leader in bioconjugation, offering a comprehensive suite of services for the design, synthesis, and characterization of Folic Acid–siRNA Conjugates.
What is Folic Acid-siRNA Conjugate?
Folate-siRNA conjugates are a class of targeted therapeutics bioconjugates combining folate targeting ligands with small interfering RNAs for the gene-specific silencing of target proteins. The therapeutic complex utilizes folate-mediated pathways to achieve selective delivery and cellular uptake of therapeutic nucleic acids to target cells overexpressing folate receptors. Figure 1 shows typical approaches. Folic Acid–siRNA Conjugate includes a small-molecule vitamin (folate, FA) conjugated to an oligonucleotide (siRNA) via a chemical linker. Depending on the method of synthesis, the conjugation can be covalent or noncovalent.
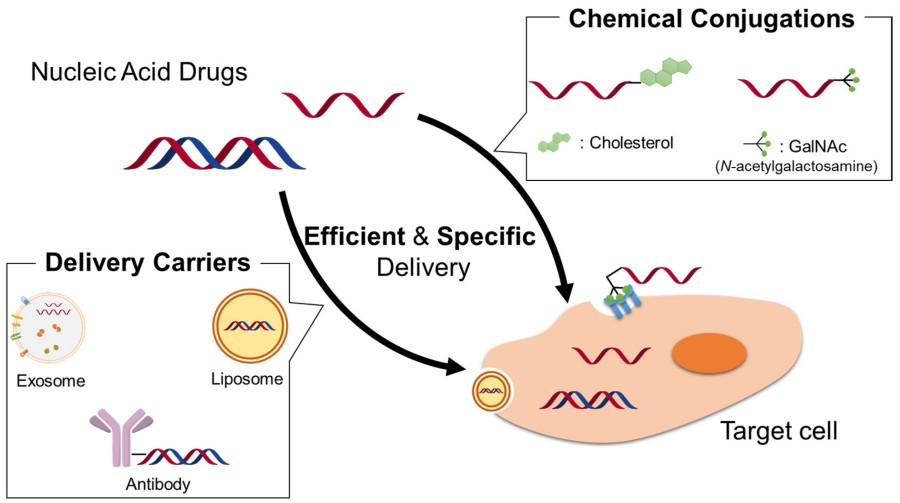 Figure 1. Schematic illustrations of delivery carriers and chemical conjugation strategies for nucleic acid drugs.1
Figure 1. Schematic illustrations of delivery carriers and chemical conjugation strategies for nucleic acid drugs.1
Key Advantages of Folic Acid for Delivery
Folic acid offers several compelling advantages as a targeting ligand for siRNA delivery, particularly in cancer therapy.
- High Specificity for Cancer Cells: The folate receptor (FR) is significantly overexpressed (up to 300-fold) in a variety of human cancers, including ovarian, breast, lung, kidney, and brain tumors, while expression in normal tissues is generally limited. This differential expression provides an excellent therapeutic window for targeted delivery, minimizing off-target toxicity.
- Non-immunogenicity and Biocompatibility: Folic acid is an essential nutrient and, unlike many synthetic ligands or peptides, is inherently biocompatible and non-immunogenic. This naturally occurring molecule is well tolerated in vivo, reducing the risk of adverse immune responses.
- Efficient Internalization: Binding of folate to the FR triggers receptor-mediated endocytosis, a highly efficient and rapid uptake pathway that concentrates the conjugate within target cells, overcoming the membrane barrier challenges associated with naked siRNA.
- Small Molecule Size: Folic acid is a relatively small molecule and generally does not significantly increase the overall size of the conjugate. This small size facilitates tissue penetration compared to larger antibody-based conjugates or composite nanoparticles.
Bioconjugate Technologies for Conjugate Synthesis
Chemical Conjugation
The synthesis of folate-siRNA conjugates utilizes sophisticated bioconjugation chemistry to establish a stable link between the targeting moiety and the therapeutic oligonucleotide. Direct covalent conjugation represents a strategic approach, in which folate derivatives are chemically coupled to siRNA chains through specific functional group interactions. This approach typically utilizes the carboxyl groups of folates to form amide bonds with amine-modified siRNAs, resulting in direct ligand-oligonucleotide conjugates.
Nanocarrier-Based Conjugation
Advanced nanocarrier platforms offer alternative conjugation strategies that address the limitations of direct covalent approaches. Polymeric nanoparticles, particularly those synthesized via controlled free radical polymerization techniques such as aqueous reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT), enable the construction of multivalent folate-siRNA complexes with enhanced functional properties.
Characterization of Folic Acid–siRNA Conjugates
Rigorous characterization is essential to confirm the successful synthesis, stability, purity, and functionality of the bioconjugate.
Conjugation Confirmation and Stoichiometry
- HPLC/FPLC: Used for separation and purification, often followed by UV/Vis spectroscopic analysis to quantify folate and siRNA content, thereby determining the conjugation efficiency.
- Mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/ESI): Essential for determining the precise molecular weight, verifying siRNA integrity, and successful attachment of the folate moiety.
Functional Characterization
In vitro assays using FR-overexpressing cell lines (e.g., KB, HeLa) typically confirm the binding affinity and specificity of the folate moiety by competition with free folate. Gene silencing efficacy: The final test is to measure knockdown of target mRNA and/or protein expression in target cells using qPCR and Western Blot, respectively. Comparison with a non-targeting siRNA control provides evidence of on-target efficacy.
Purity and Stability
- Gel electrophoresis (e.g., PAGE): Confirms the size and charge of the conjugate and detects unreacted siRNA or degradation products.
- Serum Stability Assay: The conjugate is incubated in serum (e.g., fetal bovine serum) followed by HPLC or gel analysis to measure resistance to nuclease degradation, a critical factor for in vivo applications.
Applications of Folic Acid-siRNA Conjugates
Cancer Therapy: This is the most common application. siRNA can be designed to target genes critical for tumor growth, survival, or metastasis.
Inflammatory Diseases: Certain activated immune cells, such as macrophages, overexpress FRβ. Folate conjugates can be used to deliver siRNA to silence pro-inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, thereby treating diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or atherosclerosis.
Imaging and Diagnostics: Folic acid can also be conjugated to diagnostic agents, such as fluorescent dyes, for use with siRNA in theranostic applications, allowing imaging of FRβ-positive tumors and simultaneous monitoring of treatment efficacy.
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs leverages our extensive expertise in bioconjugate chemistry and nucleic acid therapeutics to offer a comprehensive suite of services for the design, development, and characterization of folate-siRNA conjugates. Our integrated platform spans the entire development process, from initial proof-of-concept to preclinical evaluation, providing clients with end-to-end solutions to the challenges of targeted siRNA delivery. We specialize in the rational design of folate-siRNA conjugates optimized for specific therapeutic applications.
✅ Free design of siRNA sequences (four siRNA oligonucleotides)
✅ siRNA oligonucleotide synthesis
✅ Modification of siRNA
✅ Oligonucleotide deprotection and purification
✅ Synthesis and purification of folic acid–siRNA conjugates
✅ Copolymer characterization
Comparison of Folic Acid–siRNA Conjugate Platform Technologies
| Platform Type | Key Components | Conjugation Method | Advantages | siRNA Loading Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Conjugate | Folic acid, modified siRNA | Covalent bond formation | Well-defined structure, low polydispersity | Integral part of structure |
| Polymeric Nanoparticles | Block copolymers, folate ligands | RAFT polymerization, folate conjugation to side chains | Multivalency, biocompatibility, neutral complexes | Electrostatic complexation with cationic blocks |
| Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles | Silica matrix, PEG spacer, folate | Surface amination, PEGylation, folate conjugation | High loading capacity, tunable pore size, stability | Physical adsorption in mesopores |
| Nanovesicles | Phospholipids, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG-Folate | Membrane incorporation | Biomimetic properties, fusion with cell membranes | Aqueous core encapsulation or membrane association |
Why You Should Trust Creative Biolabs
✅ PhD-Level Expertise
Our team of PhD-level scientists specializing in oligonucleotide chemistry and targeted drug delivery ensures the highest scientific rigor for every project.
✅ Proprietary Linker Technology
Access to exclusive, optimized cleavable linkers designed to improve endosomal escape and maximize cytoplasmic siRNA release, a critical bottleneck for RNAi therapeutics.
✅ Success Rate
Our proven track record of successfully synthesizing and characterizing complex bioconjugates with retained biological activity significantly reduces our clients' development timelines.
✅ Quality Assurance
Our proprietary technology portfolio includes patented conjugation methods, specialized nanocarrier platforms, and innovative purification techniques, which together enhance the efficiency, stability, and performance of folate-siRNA conjugates.
Customer Review
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the typical stability of folate-siRNA conjugates in human serum?
A: Stability is highly dependent on the chemical modification of the siRNA backbone (e.g., 2'-O-methyl, phosphorothioate) and the nature of the linker. Well-optimized, chemically modified siRNA conjugates can exhibit serum half-lives of hours to days, significantly superior to naked siRNA, which is rapidly degraded by nucleases.
Q: Can folate-siRNA conjugates be used to target normal cells?
A: Although the folate receptor is overexpressed in many cancer cells, it is expressed at low to moderate levels in some normal tissues, such as the kidney and choroid plexus. This requires careful optimization of dose and route of administration to maintain the therapeutic window. However, the significantly higher FR density on tumor cells still ensures preferential and efficient uptake in target tissues.
Q: How is the siRNA released from the conjugate within the cell?
A: The mechanism depends on the linker chemistry. If a disulfide bond is used, the conjugate is cleaved by the high concentration of glutathione in the cytoplasm (a reducing environment), releasing the free siRNA. If a pH-sensitive linker is used, the acidic environment of the endosome (pH 5-6) triggers cleavage, promoting release and endosomal escape into the cytoplasm.
Q: What is the typical gene silencing efficiency of folate-siRNA conjugates?
A: Silencing efficiency varies depending on the specific construct and cell model, but optimized folate-siRNA conjugates typically achieve a 50-80% reduction in target gene expression under optimal conditions. For example, folate-conjugated silica nanoparticles complexed with VEGF siRNA demonstrated 73% and 50% gene silencing efficiencies in HeLa and MDA-MB-231 cell lines, respectively. Efficacy depends on multiple factors, including folate receptor density, conjugate design, intracellular trafficking efficiency, and siRNA potency.
Conclusion
Creative Biolabs is a leader in the field of biological conjugation, providing comprehensive customized folate siRNA conjugation services. Our technology platform covers everything from optimized siRNA sequence design and various chemical modifications, to high-precision covalent coupling (including complex PEGylation and multi ligand strategies), as well as rigorous HPLC purification and comprehensive quality control. Please contact us to discuss your demands or to request a proposal.
Reference
- Oyama S, Yamamoto T, Yamayoshi A. Recent advances in the delivery carriers and chemical conjugation strategies for nucleic acid drugs. Cancers, 2021, 13(15): 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153881 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)

