Custom Small Molecule-Peptide Nucleic Acid Conjugation Service
Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) Introduction
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is a synthetic polymer. It is a DNA or RNA mimic in which the phosphate-ribose backbone is replaced by a polypeptide backbone. The polypeptide backbone is formed by repeating the unit N-2-(aminoethyl)-glycine linked by peptide bonds and bases are connected to the backbone by methylene carbonyl bonds. As in a polypeptide chain, PNA has an N-terminal (nitrogen terminus) and a C-terminal (carbon terminus). Peptide nucleic acid is a stable structure, and resistant to nuclease and protease degradation. PNA can bind to single-stranded nucleic acid in a sequence that is base complementary and has low cytotoxicity. It is also possible to use it for molecular biology research or for medical treatment; for example, it can be used as a gene probe. Peptide nucleic acid can be used in the form of an antisense sequence for gene function, gene expression regulation and other research. The bioconjugation of small molecules to PNA via peptide carriers is an emerging strategy to enhance the delivery, targeting, and functionality of PNA-based therapeutics.
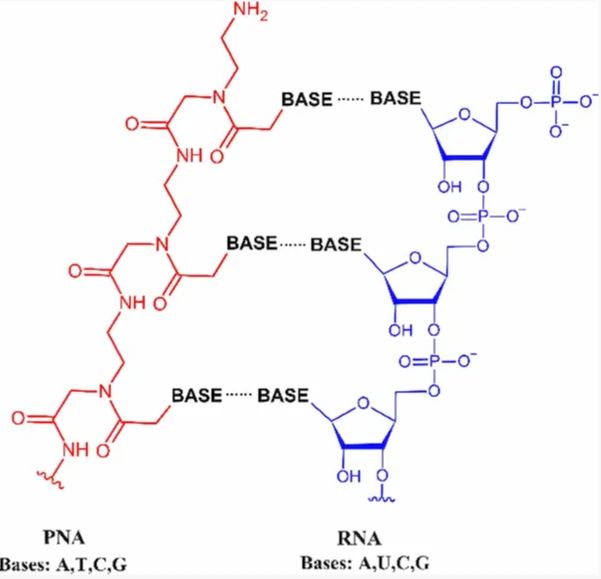 Figure 1 Comparison of the PNA and RNA structures.1
Figure 1 Comparison of the PNA and RNA structures.1
Why Conjugate Small Molecules to PNAs?
The peptide like skeleton of PNA enables it to resist enzymatic degradation and bind complementary DNA and RNA with high affinity and specificity. PNA is a potential anti gene and anti-sense therapeutic drug, but its application in the in vivo environment is hindered due to its poor intracellular delivery ability. The coupling of PNA with molecules with high lipid solubility can solve the problem of inability to reach the target within cells.
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is a nucleic acid mimetic with high specificity and binding affinity to natural DNA or RNA and resistance to enzymatic degradation. PNA sequences can be designed to selectively silence gene expression, making PNA a highly promising tool for antibacterial applications and drug delivery. PNA can reduce the enzymatic degradation of molecules and maintain drug activity by coupling with small molecules.
Design Strategies for Small Molecule-Peptide Nucleic Acid Conjugation
The successful design of small molecule-PNA conjugates is paramount to their efficacy and involves careful consideration of several key factors, including the choice of small molecule, the PNA sequence, the linker chemistry, and the intended application.
-
Small molecule selection:
The spatial structure and chemical properties of the small molecules must be considered during selection. -
Chelators selection:
If the molecule is being designed for use in diagnostic imaging or radiotherapy the chelators DOTA, DTPA or NOTA can be used to conjugate PNA to form radionuclide 64Cu, 99mTc or 177Lu complexes. -
PNA sequence and length:
PNA sequences can range from 10-20 nucleobases in length, however longer sequences will provide increased specificity. The increased specificity will help to reduce off-target effects and PNA chemical structure can be modified if necessary. -
Linker chemistry:
The linker between the small molecule and PNA is a critical design feature that can impact the stability, solubility and activity of the final conjugate. -
Linker length and flexibility:
The length and flexibility of the linker can affect the ability of the small molecule to interact with the target and the PNA to hybridize effectively. The most suitable linker should be able to avoid steric hindrance while allowing the two components to function independently without increasing undesirable clashes.
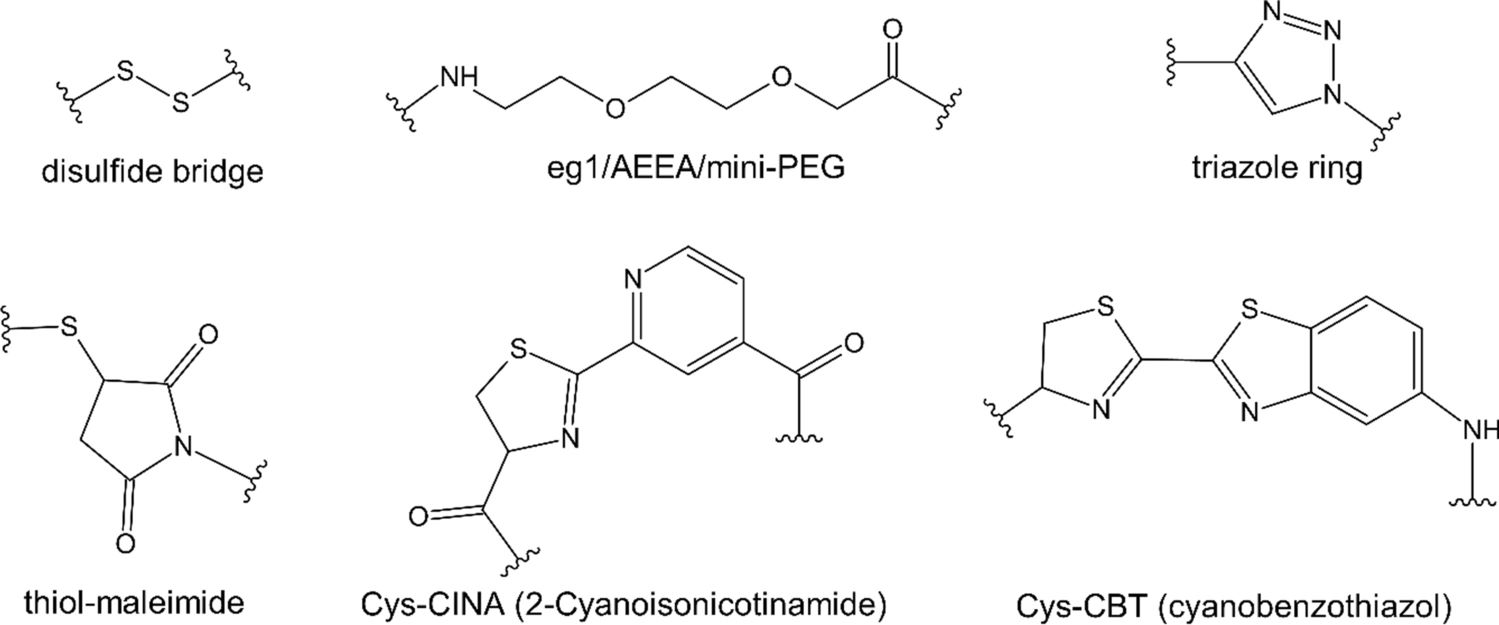 Figure 2 Linkers used for PNA conjugation.1
Figure 2 Linkers used for PNA conjugation.1
Small Molecule Conjugation Methods
| Method | Mechanism | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CuAAC | Cu⁺-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition | High yield (>95%), rapid kinetics | Cu⁺ toxicity, ROS generation |
| SPAAC | Strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition | Copper-free, biocompatible | Slow kinetics (k ≈ 0.1–1 M⁻¹s⁻¹) |
| Thiol-Maleimide | Michael addition | Site-specific, pH-insensitive | Serum instability |
| Enzymatic Ligation | Transglutaminase-mediated | Native linkage, traceless | Substrate specificity |
Photobleaching of Conjugated Small Molecules
Photobleaching is the photochemical destruction of a fluorescent molecule. Photobleaching of fluorophores during microscopy is an unwanted phenomenon since the photobleached fluorophores are effectively damaged and will no longer emit light. Photobleaching thus makes time-lapse microscopy difficult to study. Photobleaching in fluorescence imaging can be reduced with the help of small molecules such as cycloheptatriene and N-dioctyl-1,4-dihydro-o-toluamide. The small molecules work by either quenching reactive oxygen species, deactivating excited states, or shielding fluorophores. Small molecules, including fluorescent dyes, can be conjugated to PNAs for imaging and diagnostic applications. The light-based properties of such small molecules should be considered.
Small Molecule-Peptide Nucleic Acid Conjugation Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs provides custom small molecule-PNA conjugation solutions based on deep expertise in bioconjugation chemistry, peptide synthesis, and nucleic acid science. Our laboratory facilities and research team have the capabilities needed to support projects of varying scales, aiming to provide the highest quality conjugates for our clients' research needs. If you are interested in our service, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Recommended services
- PNA Synthesis and Modification
- Peptide Synthesis and Modification
- Small Molecule Conjugation
- Linker Design and Synthesis
Recommended products
Our Advantages
Creative Biolabs stands out in the field of Small Molecule-PNA Conjugation services for several reasons:
- Advanced Bioconjugation Technology: We invest in the latest technology and equipment to ensure the highest quality of our services. Our state - of - the - art facilities enable us to carry out complex synthesis, purification, and characterization processes with precision and efficiency.
- Custom Bioconjugation: We understand that each customer's research needs are unique. Therefore, we offer highly customized services, tailored to the specific requirements of our customers. Whether it's a simple conjugate design or a complex multi - step project, we can meet the customer's expectations.
- Quality control of Bioconjugation: We have a strict quality control system in place to ensure that all our products and services meet the highest standards. Our characterization and biological evaluation processes are designed to detect any potential issues and ensure the reliability of the conjugates.
Small molecule-PNA conjugates can inhibit gene expression, enhance drug penetration, and reduce enzyme solubility. Small molecule-PNA conjugates can be used as new tools for gene regulation, drug development, and diagnosis. Creative Biolabs is a company that has long focused on the research and exploration of protein labeling technology. Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive small molecule-PNA conjugation services. We have an experienced team of experts and provide customized small molecule-PNA conjugation solutions to meet the unique needs of your project. If you are interested in our biojugation services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Tsylents U, Siekierska I, Trylska J. Peptide nucleic acid conjugates and their antimicrobial applications—a mini-review. European Biophysics Journal, 2023, 52(6): 533-544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-023-01673-w. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
