Custom Lipid-Drug Conjugation Service
What is Lipid Drug Conjugation?
Lipid drug conjugates (LDCs) are drug molecules covalently modified with lipids. The binding of lipids to drug molecules increases lipophilicity and also alters other properties of the drug. These conjugates have several advantages, including increased oral bioavailability, improved targeting of the lymphatic system, enhanced tumor targeting, and reduced toxicity. Based on the chemical properties of drugs and lipids, various conjugation strategies and chemical linkers can be used to synthesize LDCs. The linker and/or coupling method determine how drugs are released from the least developed countries and is crucial for optimal performance in these regions.
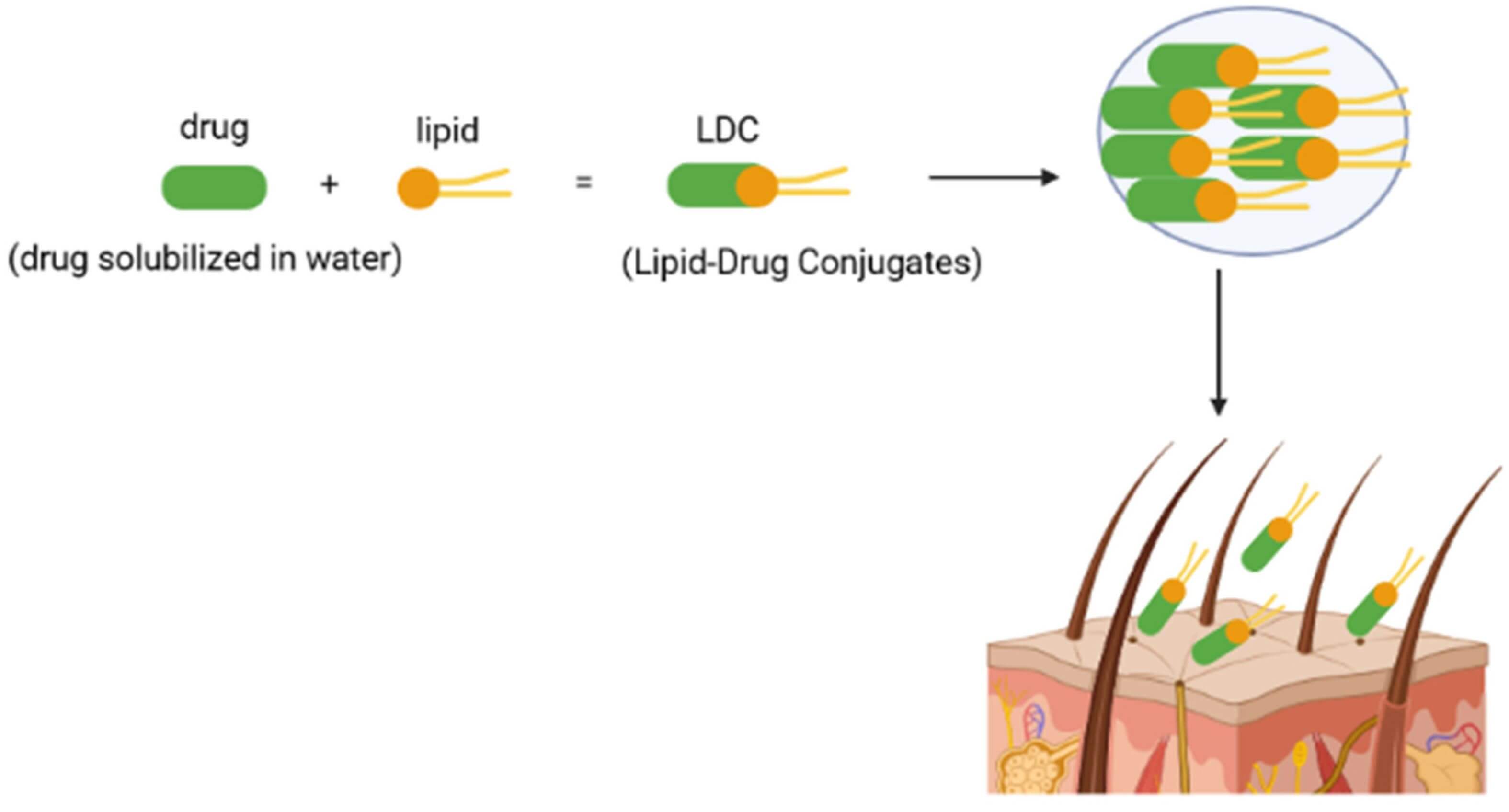 Figure 1 Schematic representation of the lipid-drug conjugates mechanism of action.1
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the lipid-drug conjugates mechanism of action.1
Delivery Systems for Lipid-Drug Conjugate
 Carrier-Free System
Carrier-Free System
A carrier free system refers to a system that does not use delivery carriers to administer LDCs. Linking lipids with hydrophilic drugs forms amphiphilic molecules that can self-assemble into nanoparticles without or with minimal use of stabilizers.
 Emulsions
Emulsions
O/w lotion are also frequently used to deliver LDCs. Lotion is a biocompatible carrier, allowing LDC to be mixed into oil droplets. Lotion improves LDC delivery by dissolving drugs, reducing toxicity and drug clearance.
 Liposomes
Liposomes
Liposomes are a drug delivery system that allows hydrophilic drugs to be embedded in aqueous cores and lipophilic prodrugs to be incorporated into lipid membranes. Liposomes serve as the second protective layer of active agents, preventing premature metabolism of prodrugs.
 Micelles
Micelles
Micelles are composed of amphiphilic macromolecules that self-assemble into core-shell structured nanocarriers. Hydrophobic nuclei can encapsulate hydrophobic drugs through non covalent interactions. Combining drugs with lipids can significantly improve their interaction with the micelle core.
 Lipid Nanoparticles
Lipid Nanoparticles
Lipid nanoparticles (NPs) can encapsulate LDCs within lipophilic cores. The lipid core serves as an effective reservoir for loading lipophilic drugs. Hydrophilic drugs need to be converted into lipid drug conjugates to enhance the loading of lipid NPs.
 Polymer Nanoparticles
Polymer Nanoparticles
Poly (lactic acid glycolic acid) copolymer (PLGA) nanoparticles have been widely used for the delivery of LDCs. The binding of hydrophobic palmitate to siRNA enhances the loading of siRNA in NP. Therefore, a lower polymer/siRNA ratio is required to effectively concentrate siRNA.
Lipid Conjugated Pro Drug
Lipid binding prodrugs are a special type of LDC designed to release active drugs in vivo without pharmacological activity until the lipid portion is cleaved. This is the true definition of prodrug strategy. The prodrug method is particularly valuable in the following aspects:
- Masking toxicity: Reduce the side effects associated with the active drug before it reaches its target.
- Improve permeability: Enhance transport across biological membranes such as intestinal mucosa or blood-brain barrier.
What Makes Creative Biolabs Your Top Choice
Lipid drug conjugates are an emerging nanoscale drug delivery system with potential applications in drug delivery and targeting specific sites, particularly for these water-soluble/hydrophilic drug components. With a wide and comprehensive platform and a pharmaceutical professional team, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing the best customized services to global customers, including but not limited to:
- Customized conjugation strategy design
- Liposome development service
- LNP development service
- Custom lipid synthesis Service
- Lipid and linker synthesis
- Conjugate and purification
- Analysis and characterization service
Why Need Lipid-Drug Bioconjugation?
-
Lipid-Drug Conjugate for Enhancing Drug Delivery
Lipid drug conjugates can be used to overcome various drawbacks of conventional drug delivery systems. The conjugation of drug with lipid can help to prolong the half-life, slow down the clearance rate of drugs, and improve their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Drug lipid conjugates are also used to improve the drug delivery to the targeted site which otherwise are difficult to reach such as tumor and the brain.
-
Lipid-Drug Conjugates for Enhanced Oral Drug Delivery
Oral route of administration is the most preferred route of drug administration for patients due to its ease. Low oral bioavailability is the main drawback for the administration of most of the drugs due to low aqueous solubility or high first pass metabolism. The oral bioavailability of such drugs can be greatly improved by conjugating drugs with lipids. The mechanism of action is the absorption of drug by lymphatic system, avoiding hepatic clearance by entering the blood vessels present in the intestinal lymph vessels. The improvement of oral bioavailability has been seen in many drugs for various therapeutic applications, including antiviral and anticancer drugs.
-
Lipid-Drug Conjugate Improves Biopharmaceutical Profile
The biopharmaceutical properties of the drug mainly decide the success of a drug. LDC greatly helps in improving this characteristic of a drug. The ADME of a drug can be greatly improved by coupling with the lipid. Coupling with lipids also helps to reduce systemic toxicity by ensuring the targeted delivery and controlled release at the site of the lesion. It also helps to increase the half-life of the drug, reducing the frequency of administration.
Why You Should Trust Creative Biolabs
Expertise
Team of PhD and experienced scientists with deep expertise in biological coupling, medicinal chemistry and drug delivery.
Technology
We use the latest methods and techniques to ensure a conjugation process is efficient and state of the art characterization
Tailored Services
One size does not fit all, we understand this and our services are extremely flexible to fit the needs of your project.
Intellectual Property
We value the privacy and IP of our clients and all our work is covered by strict NDAs.
Detailed report
A detailed final report is provided with all synthesis and analysis methods, in addition to biological data in a format ready for inclusion in regulatory submission packages.
Proprietary Lipid Library
We have a proprietary synthetic and natural lipid libraries, with a unique focus on drug delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can lipid binding be used for targeted delivery to specific organs or cell types?
A: Yes, targeted delivery is one of the main interests of the least developed countries. By selecting appropriate lipids (such as cholesterol for LDL receptor targeting) and, if necessary, binding LDCs to specific delivery systems, we can achieve high specificity for the desired organ or cell type.
Q: What is the typical turnaround time for the synthesis and characterization of concept validation LDC?
A: A typical feasibility project, from design to delivery of characterized conjugates, can be completed within 4-8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the chemistry.
Q: Can lipid drug bioconjugation services be customized to meet the specific needs of different drugs and diseases?
A: Of course, lipid drug bio coupling services are essentially customizable, as the success of lipid drug conjugates (LDCs) depends entirely on whether their design is consistent with the unique physicochemical properties of the drug, the biological characteristics of the target disease, and the desired therapeutic outcomes.
Q: How are lipid conjugates synthesized?
A: Lipid conjugates are synthesized through chemical or enzymatic reactions, carefully designed to maintain the function of lipids and attached biomolecules.
Reference
- Zielińska A, Cano A, Andreani T, et al. Lipid-drug conjugates and nanoparticles for the cutaneous delivery of cannabidiol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(11): 6165.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116165. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
