Click Reagents
Click Reagents Introduction
Click chemistry has been prominently applied in pharmaceutical and biotechnology research and development. Due to its biocompatibility and faster reaction speed, it is becoming increasingly popular. Clicking on chemical reagents has accelerated the progress of chemical biology, biological coupling, and the discovery of azides, alkynes, and ligand drugs.
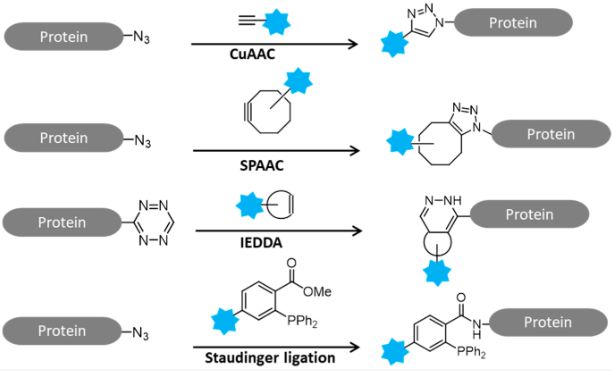 Figure 1 Schematic reactions of click chemistry.1
Figure 1 Schematic reactions of click chemistry.1
What is Clicking Chemistry?
Pharmaceutical science typically relies on the ability to synthesize and purify molecules with specific properties. Clicking chemistry provides some hope for easier connection of synthetic molecular fragments to synthesize larger and more complex molecular structures. The click reaction must exhibit characteristics such as modularity, wide range, high yield, and stereospecificity, and produce almost no by-products that can be removed by non-chromatographic methods. These reactions are typically carried out under simple conditions, such as insensitivity to water or oxygen, use of readily available reagents, minimal or no solvent waste, and simple product separation. The most common click reaction is the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction between azides and terminal alkynes. These molecules aggregate together to form 1,2,3-triazoles.
Click Reagents Overview
Chemical reactions cannot take place without reagents. In click chemistry, the choice of reagents is also of paramount importance. In fact, these special chemical compounds are used to achieve an optimal degree of precision and selectivity when assembling molecules. In this way, click chemistry goes beyond theory to provide really scientific and technological breakthroughs. Creative Biolabs provides information about clicking on chemical reagents.
- Click Chemistry Introduction
- What is Click Chemistry Reagent?
- Latest Research Progress on Click Reagents
Types of Chemical Reagents
Clicking on chemical reagents has completely changed the way scientists handle chemical reactions and has become an indispensable tool in various scientific fields. From biological coupling and drug development to materials science and chemical biology, these reagents possess multifunctionality, selectivity, and efficiency.
Azide
Nitrides are organic compounds with azide functional groups (- N3). They are the foundation of all click chemistry reactions and are primarily used in copper catalyzed azide alkyne cycloaddition reactions (CuAAC). Nitrides readily react with alkynes to form stable triazole linkages, which is why they are priceless in the field of biological interaction, drug discovery and materials science.
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon carbon triple bond (C ≡ C). They are the complementary components to azides in the CuAAC reactions. The alkyne group under the catalysis of copper creates triazole bonds with azide groups, which is the origin of its applications' success for various click chemistry labels and surface modifications of biomolecules.
Cyclooctyne
Cycloalkyne is a strained cyclic alkyne that is used in the strain promoted azide alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC) reaction and is a copper free analog of CuAAC. The inherent strain in the ring allows cycloalkynes to react readily with azides without copper catalyst. The SPAAC reaction has become a popular choice for bioorthogonal chemistry due to its negligible cytotoxicity and ease of biological system compatibility.
Thiols
Thiol is a sulfur-containing compound with the structure (R-SH). Thiols react with olefins in a thioene reaction. Thioene chemistry has important applications in biological coupling and materials science since the thioether bonds that can be formed between the two molecules are stable. Thiols also react with azides in the Staudinger connection to form amide bonds.
Dienes
Dienes are hydrocarbons containing two double bonds (C=C=C). They are essential for Diels Alder click chemistry reactions, which are cycloaddition processes resulting in the formation of cyclohexene rings. The Diels Alder reaction is used for the synthesis of complex organic structures and functional materials.
Phosphines
Phosphine is a phosphorus-containing chemical compound used in Staudinger linkages. In this click chemistry reaction, phosphine reacts with azides to form amide bonds. Staudinger connections are a common bioorthogonal chemistry reaction with a wide range of application in biomolecule labeling and biological conjugation.
Diazides
Diazenes are compounds that have two azide functional groups (-N3). These functional groups are used in Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, a form of click chemistry that reacts with alkynes to form triazole rings. This reaction forms the basis for the CuAAC reaction.
Clickable Handles
The clickable controller is used to introduce the target functional groups or moieties into the molecules to allow the click chemistry to proceed. For example, in biological coupling, azide and alkyne functionalized handles allow for the biomolecules to be precisely labeled and modified.
Major Click Chemistry Reactions
| Reaction | Description | Required Reagents | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC) | The "classic" click reaction. | Azide, alkyne, and a copper(I) catalyst. | In vitro bioconjugation, polymer synthesis. |
| Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (SPAAC) | The "copper-free" or bioorthogonal version. | Azide and a strained alkyne (like a cyclooctyne). | Live-cell imaging, in vivo labeling, where a copper catalyst would be toxic. |
| Ligation Between Tetrazine and Alkene (Trans-Cyclooctene) | This high-speed reaction is also copper free which is ideal for in vivo cell labeling. | Tetrazine and an alkene (e.g., trans-cyclooctene, TCO). | Live-cell imaging, in vivo bioconjugation, fast labeling of biomolecules. |
Choosing the Right Click Reagent
- Compatibility: Look at reaction type (CuAAC or SPAAC) and where the reaction will occur (in vitro or in vivo).
- Target Molecule: What are the functional groups (amines, thiols, carboxyl groups, etc.) on the molecule that is going to be labeled?
- Linker: Discuss the importance of the linker (e.g., PEG) for solubility and preventing steric hindrance.
Key Applications of Click Reagents
Biological coupling and labeling: This is probably the most used application. Click the reagent to enable (fluorescent dyes, biotin, or other functional molecules, etc.) to be accurately and effectively covalently bound to biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.). This is a very important step in widespread molecular and cell biology research, as it provides an alternative that is highly specific, unlike traditional labeling methods.
Drug discovery: In drug discovery, click chemistry can be used to synthesize more complex molecular scaffolds with greater efficiency. A key technology here is called in situ click chemistry. This involves the assembly of small molecular fragments onto biological targets such as enzymes in their native environment. This allows a large number of potential candidate drugs to be screened directly in the target environment and even highly effective inhibitors to be discovered.
Materials Science: Click Chemistry offers new and powerful tools for the design, synthesis and modification of advanced materials. The high efficiency and orthogonality of click reactions, for example, allows precise polymer synthesis, the construction of complex hydrogels for tissue engineering and the functionalization of surfaces with defined chemical properties. The level of control over materials that this affords is invaluable for the development of smart materials, coatings and drug delivery vehicles.
Overview of What Creative Biolabs Can Provide
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive set of services centered around bio coupling and advanced biotechnology. We specialize in a wide range of customized coupling services, including coupling services that connect various molecules such as fluorescent dyes, biotin, and oligonucleotides with proteins, antibodies, and nanoparticles using click chemistry methods such as CuAAC and SPAAC. If you are interested in our bioconjugation services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Recommended products
Reference
- Yao T, Xu X, Huang R. Recent advances about the applications of click reaction in chemical proteomics. Molecules, 2021, 26(17): 5368.https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175368. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
