Custom Protein-Nanoparticle Conjugation Service
What is Protein-Nanoparticle Bioconjugation?
Bioconjugation of protein and nanoparticles is the covalent or non-covalent bonding of proteins with nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are usually at the nanoscale, and these can be coupled to proteins to yield conjugates which contain properties of both components. These include biological activity and recognition elements of proteins such as antibodies, enzymes, antigens, receptors, growth factors etc., and for the nanoparticle physical properties like its tunable size, shape, surface chemistry, optical, electrical and magnetic properties. The conjugate often exhibits new synergistic properties that surpass what is possible from either component alone.
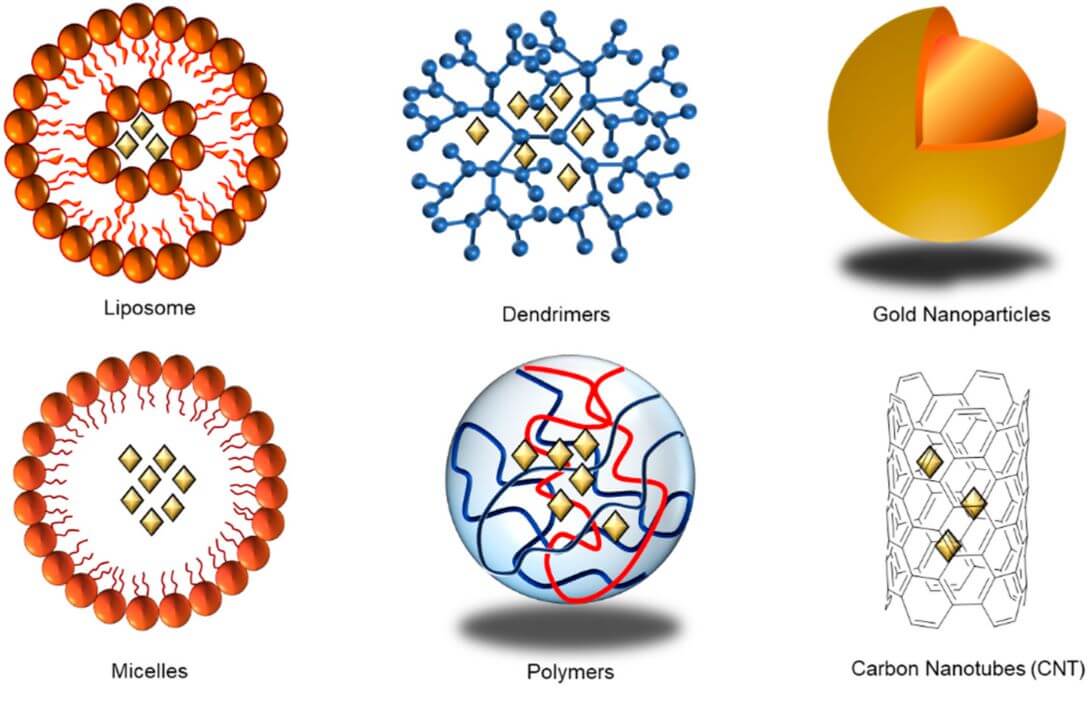 Figure 1 Types of nanoparticles used to carry drug or protein delivery into cells.1,3
Figure 1 Types of nanoparticles used to carry drug or protein delivery into cells.1,3
Technology in Protein-Nanoparticle Bioconjugation
Methods used for protein conjugation to nanoparticles varies from physical to chemical methods. Also, several options are available concerning characterization of the product. The method chosen for conjugation varies with the protein, nanoparticle material and their respective application.
Carbodiimide Chemistry (EDC/NHS)
The carboxyl-containing molecule is covalently conjugated to the amine-containing molecule through the formation of an amide bond. EDC, first activates the carboxyl group by forming an O-acylisourea intermediate that is "captured" and stabilized by NHS forming an ester which is very reactive with primary amines.
Maleimide-Thiol Chemistry
This is an efficient approach based on the maleimide and thiol reaction on different molecules such as cysteine residues. Maleimides reactive towards free thiols form stably thioether conjugated products. This method is preferred for site-specific conjugations when proteins have non-essential, quite accessible, cysteine residues or when cysteine residues are engineered in a manner that do not alter protein function.
"Click" Chemistry
"Click" bioconjugation methods are relatively new and with remarkable efficiency, extreme selectivity as well as orthogonality while working under mild biochemical condition are changing the field. Probably best known is the copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC), which produces very stable triazole rings. For this conjugation to be done in a controlled manner at specific sites, protein and nanoparticle must first be covalently modified with azide and alkyne respectively.
Common Bioconjugation Strategies
![]()
These kinds of bonds are formed through covalent chemical reactions between linker molecules and nanoparticle. The linkers contain functional groups that are able to react with protein molecule or nanoparticle. The linkers form highly stable conjugates which do not dissociate under biological conditions.
![]()
This method takes advantage of binding affinity interaction such as electrostatic charge interaction, hydrophobic interaction and van der Waals forces. They are relatively non damaging to the structure of the proteins.
Characterization and Quality Control of Protein-Nanoparticle Bioconjugation
It is necessary to characterize them after synthesis which allows evaluating whether the process was successful as well as capture all relevant attributes of interest in a bioconjugate. Some methods include:
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy and Fluorescence Spectroscopy: To follow binding changes for both protein as well as nanoparticle alongside tracking evolution in protein structure.
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS): In determining hydrodynamic diameter size and polydispersity index (PDI) before and after conjugation, increase in size can serve as an indicator for successful conjugation while also mitigating risk of aggregation.
- Zeta Potential Measurement: Evaluating change of surface charge postoperative conjugation enables assessing modification done on surface serving as an indirect measure watching change on surface coating.
- Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): To directly visualize the morphology of the nanoparticles and the presence of a protein corona.
- Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blotting: To confirm protein integrity and successful conjugation.
- Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy: To assess changes in secondary structure of the protein upon conjugation.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) or Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI): To verify the preserved biological activity (e.g., binding affinity) of the conjugated protein.
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)/Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): To purify and analyze conjugate homogeneity.
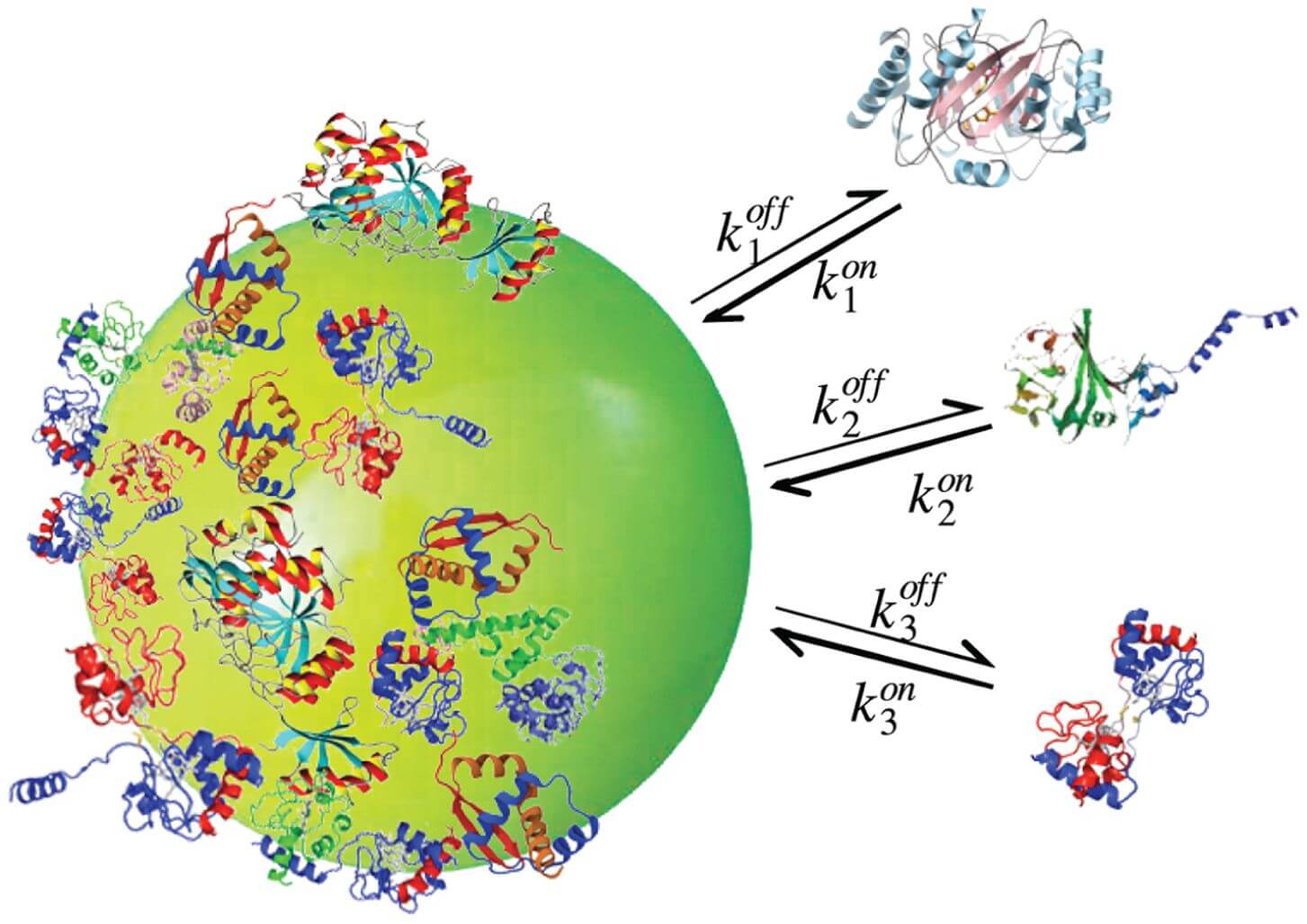 Figure 2 Schematic of nanoparticle-protein corona formation process.2,3
Figure 2 Schematic of nanoparticle-protein corona formation process.2,3
Applications of Protein-Nanoparticle Bioconjugation
Bioconjugation of proteins to nanoparticles has relevance in various biomedical applications, which often capitalize on the unique properties of both the protein and nanoparticle moieties. The following are representative examples of such applications:
-
Enhanced Stability and Bioactivity
Protein stability and bioactivity may be better maintained when proteins are engineered for presentation on the surface of nanoparticles, which can shield them from denaturation or degradation. A sample case for this is the attachment of enzymes to nanoparticles to enhance their stability and reusability in biocatalysis. -
Targeted Delivery
Nanoparticles can be modified with targeting proteins, such as antibodies or aptamers, for targeted delivery to particular cells or tissues. Such a method may be used for targeting therapeutics or diagnostics to a desired location. An instance is the Herceptin-attached nanoparticles which are employed for selective chemotherapeutic agents' delivery to breast cancer cell. -
Multivalency and Enhanced Avidity
Nanoparticles have a high surface area-to-volume ratio, which enables multivalent attachment of proteins to their surfaces. This multivalency can significantly increase the avidity of protein interactions, such as the detection of low-abundance biomarkers or simultaneous binding to multiple cell surface receptors.
Protein-Nanoparticle Bioconjugation Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs is an industry-leading expert in bioconjugation and has unrivaled experience in providing a full range of protein-nanoparticle conjugation services to meet all of your academic and pharmaceutical needs. Our cutting-edge facilities, expertise and dedication to science guarantee that you will receive the highest quality, functional conjugates for your needs.
- Customized Nanoparticle Synthesis: We can synthesize a wide variety of nanoparticles including gold nanoparticles, silver nanoparticles, quantum dots, magnetic nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles (PLGA, PEG-PLGA), liposomes, and mesoporous silica nanoparticles.
- Optimized Conjugation Chemistry: We select and optimize the conjugation strategy based on the properties of the protein, the type of nanoparticle, and the desired application in order to achieve maximum conjugation efficiency and minimal loss of protein activity. We have extensive experience with site-specific bioconjugation, in order to avoid interfering with the protein's active sites as much as possible.
- Application-Specific Conjugate Design: Whether you are interested in targeted drug delivery, enhanced diagnostic sensitivity, bioimaging, or next-generation vaccine development, we work with you to design conjugates that are custom-made for your intended application.
Our Service Advantages
Choosing Creative Biolabs for your protein-nanoparticle conjugation needs has several advantages and will simplify your R&D efforts and get you to discovery faster:
- Expertise: Experts in bioconjugation, protein engineering and nanotechnology. We work with precision and expertise on every project even if the task is most complex.
- Customization: Services are highly customized to the needs of your project. This includes everything from the choice of nanoparticle to the conjugation chemistry.
- One-stop-shop: We handle the entire process from nanoparticle synthesis to protein expression to conjugation and purification and on to characterization.
- Quality: We have strict quality control standards and ensure purity, homogeneity, stability and retained biological activity of your conjugates.
- Bioconjugation Technology: We are constantly investing in the latest technologies and most advanced instrumentation for cutting edge solutions.
- Dedicated Support: A dedicated project manager is assigned to your project for clear communication and flexible support at all times.
Protein-nanoparticle conjugates are used in many applications, such as diagnostics, therapeutics, and bioimaging. The nanoparticles for conjugation with proteins can be gold nanoparticles, magnetic nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, quantum dots, etc. depending upon the intended use. Creative Biolabs provide Protein-nanoparticle Conjugation service. The service involves custom synthesis of nanoparticles, optimization of conjugation methods, and characterization of the conjugates. If you are interested in our biojugation services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
- Yau A, Lee J, Chen Y. Nanomaterials for protein delivery in anticancer applications. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(2): 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020155
- Darabi Sahneh F, Scoglio C, Riviere J. Dynamics of nanoparticle-protein corona complex formation: analytical results from population balance equations. PloS one, 2013, 8(5): e64690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064690
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
