Custom Magnetic Bead-Protein Conjugation Service
Magnetic bead-protein conjugates are powerful reagents indispensable in modern biomedicine. At Creative Biolabs, we combine deep scientific expertise with cutting-edge conjugation technology to provide customised magnetic bead solutions. These solutions are not just reagents, but precision tools meticulously crafted for success.
Magnetic Bead-Protein Conjugation
Magnetic bead-protein coupling refers to the precise covalent or high-affinity attachment of bioactive proteins to the surface of superparamagnetic particles. Superparamagnetism is a key property; these magnetic beads exhibit strong magnetic susceptibility in an external magnetic field, but retain no residual magnetism once the field is removed. It prevents bead aggregation and allows for rapid, efficient dispersion and recovery without centrifugation, minimizing sample shear forces and preserving the integrity of fragile biomolecules such as antibodies, enzymes, and receptors.
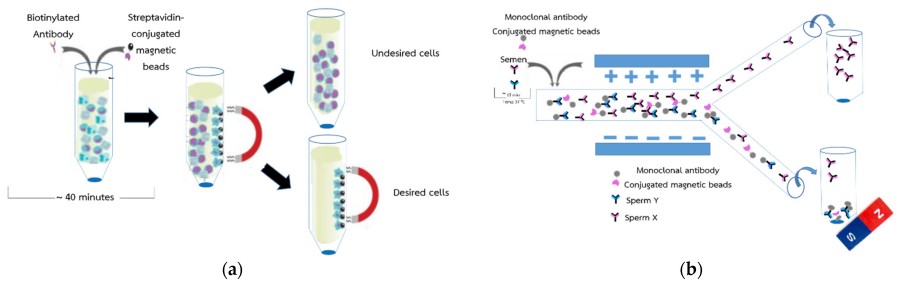 Figure 1.The conceptual of the sorting of sperm X and Y (a) shown the method for separation efficiency of protein by magnetic beads and (b) shown the method for separation efficiency of sperm by magnetic beads.1
Figure 1.The conceptual of the sorting of sperm X and Y (a) shown the method for separation efficiency of protein by magnetic beads and (b) shown the method for separation efficiency of sperm by magnetic beads.1
A successful conjugation must:
The core scientific challenge lies in establishing a stable functional interface between the inorganic magnetic bead surface (typically polystyrene, silica, or carboxylated materials) and the complex tertiary structure of proteins.
- Maximize binding capacity: Achieve high-density, directional functional proteins.
- Maintain protein function: Ensure active sites (e.g., antigen-binding fragments of antibodies) remain accessible and unchanged.
- Ensure stability: Prevent leakage and degradation under various buffer conditions and temperatures.
- Minimize nonspecific binding: Construct bio-inert surfaces to avoid nonspecific interactions that cause background noise.
Types of Magnetic Bead-Protein Conjugates: A Toolkit for Diverse Applications
![]()
Antibody Magnetic Beads
A mainstay in immunomagnetic separation. They are used for highly specific cell sorting (e.g., CD4+ T cell isolation), pathogen capture, and immunoprecipitation (IP). Antibody orientation is crucial; strategies such as periodate oxidation are employed for Fc-specific glycosylation coupling to ensure the Fab region can freely bind to the antigen.
![]()
Streptavidin/Avidin Magnetic Beads
These conjugates utilize the strongest known non-covalent interaction in nature (Kd ~ 10⁻¹⁵ M), namely the interaction between biotin and streptavidin. They are universal capture tools for any biotinylated molecule, including nucleic acids, antibodies, or receptors. Their tetravalent nature allows them to amplify the signal.
![]()
Protein A/G/L Magnetic Beads
These bacterial proteins bind with high affinity to the Fc regions of antibodies from different species and subclasses. They are essential for antibody purification and immunoprecipitation. The choice between protein A, protein G, or chimeric protein A/G depends on the antibody species and subclass to achieve optimal binding.
![]()
Enzyme-Magnetic Beads
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP) conjugate magnetic beads are used for automated immunoassays, enabling magnetic separation combined with chemiluminescence detection.
![]()
Antigen-Magnetic Beads
Used for reverse purification or removal of specific antibodies from serum or hybridoma cultures.
Applications of Magnetic Bead-Tagged Proteins
Drug Screening and Target Identification
Magnetic bead-tagged proteins can be used for drug screening and target identification. By binding candidate drugs to target proteins on magnetic beads, the affinity and specificity between the drug and the target protein can be assessed, thus aiding in the screening of compounds with potential therapeutic effects.
Cell Therapy
Magnetic bead-tagged proteins have applications in cell therapy. By labeling specific proteins onto magnetic beads, therapeutically significant cells or cell subpopulations can be selectively labeled and enriched. These labeled cells can be used in cell transplantation, gene therapy, and stem cell research to improve the efficacy of cell therapies.
Phage Display Technology
After the magnetic bead-tagged protein specifically binds to the target molecule and is then attached to the phage-displayed protein, the phage particles displaying the target protein can be separated using a magnetic field. This allows for the easy acquisition of phages displaying the target protein for subsequent analysis, such as structural studies, affinity assays, and enzyme activity assays.
Overview of What Creative Biolabs Can Provide
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive magnetic bead labeling development services, including magnetic bead modification and protein conjugation. Leveraging our unique expertise in chemical synthesis and biochemistry, we are confident in providing a one-stop bioconjugation service to meet your specific needs.
Custom Magnetic Bead-Protein Conjugation
Creative Biolabs leverages its deep expertise in bioconjugation to provide truly customized and reliable services for magnetic bead-protein conjugation. We are not just a supplier, but also your strategic partner in molecular detection development.
Magnetic Bead Surface Modification Service
Creative Biolabs offers a magnetic bead surface modification service. First, select magnetic beads of suitable size and magnetic properties and wash them with appropriate washing buffers to remove surface impurities. Then, incubate the magnetic beads with a chemical crosslinking agent (e.g., EDC/NHS) to activate the reactive functional groups on the bead surface. Finally, react the target binding molecule with the activated magnetic beads to form a covalent bond.
Protein Binding Service
Incubate the protein sample to be labeled with modified magnetic beads under appropriate conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, etc.) to allow the target protein to specifically bind to the binding molecules on the magnetic bead surface.
Conjugation Technology
The coupling method directly determines the performance, stability, and specificity of the final product. Creative Biolabs employs a range of advanced chemical approaches, chosen based on the functional groups available on magnetic beads and proteins.
 EDC/NHS Carbodiimide Chemistry
EDC/NHS Carbodiimide Chemistry
This is the gold standard for coupling proteins to carboxylated magnetic beads. EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide) activates the surface carboxyl groups, forming an unstable O-acylisourea intermediate. In the presence of NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide), this intermediate is converted into a stable NHS ester, which readily reacts with a primary amine (lysine residue) on the protein to form a stable amide bond.
 Click Chemistry
Click Chemistry
To achieve unparalleled specificity and bioorthogonality, we offer copper-catalyzed azido-yne cycloaddition (CuAAC) or strain-promoted cycloaddition (SPAAC) variants. Magnetic beads are functionalized with azide groups, and proteins are modified with cyclooctyne groups (or vice versa). This results in pure, specific triazole linkages, ideal for site-specific coupling where preservation of critical lysine residues is required.
 Streptavidin-Biotin System
Streptavidin-Biotin System
Although not covalently linked, its extremely high affinity makes it functionally irreversible in most applications. We use the method described above to couple streptavidin to magnetic beads, providing a platform to capture any biotinylated protein with perfect orientation and activity.
 Site-Specific Conjugation
Site-Specific Conjugation
To achieve the highest level of control, we employ techniques such as maleimide chemistry to modify thiol groups (cysteine residues) or use enzymatic labeling. This ensures the homogeneity of the conjugates, where each protein is linked in a predetermined orientation, thereby maximizing functional yield.
Analysis Features of Magnetic Bead-Protein Conjugates
- Standardized Protocols: Following validated and optimized protein immobilization protocols is crucial for ensuring experimental reproducibility.
- Optimal Protein Orientation: Coupling methods (e.g., using Protein G, streptavidin-biotin, or specific chemical linkers) can affect protein orientation, thus impacting capture efficiency.
- Minimizing Inhibitors: Ensuring the final conjugated product is free of residual chemicals or buffer components from the coupling process prevents interference with downstream enzymatic reactions or analysis.
- Automation: Using automated platforms improves reproducibility and throughput, especially for high-volume applications.
Protocol of Magnetic Bead-Protein Conjugation
While our proprietary protocols are optimized for each project, the general workflow is as follows:
- Magnetic Bead Activation: Activate carboxylated magnetic beads with fresh EDC/NHS solution (dissolved in MES buffer, pH 5.5–6.0).
- Protein Preparation: Transfer the target protein via buffer exchange to a suitable conjugation buffer (e.g., PBS, pH 7.4, amine-free, such as Tris).
- Conjugation: Incubate the activated magnetic beads with the protein solution for a specified time with gentle mixing.
- Termination: Terminate the reaction with a high-concentration amine buffer (e.g., Tris) to block any residual active esters.
- Washing: Thoroughly wash the magnetic beads with storage buffer to remove unbound protein and reaction byproducts.
- Blocking:To minimize nonspecific binding, incubate the magnetic beads with a blocking agent (e.g., BSA or a proprietary synthetic blocking agent).
- Formulation and Storage: The final conjugate is suspended in an optimized protein-stabilizing storage buffer, typically containing an antimicrobial agent.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can expired Protein G magnetic beads still be used?
A: We strongly recommend against using any expired magnetic bead conjugates. Shelf life is determined by real-time and accelerated stability studies. Over time, degradation leads to:
- Decreased binding capacity: due to protein denaturation or leakage.
- Increased nonspecific binding: disruption of the blocking matrix.
- Inconsistent results: leading to unreproducible data and sample waste.
- To ensure the integrity of your studies, always use reagents within their expiration date.
Q: How long can Protein G magnetic beads be stored?
A: Unopened Protein G magnetic beads are generally stable for 12-24 months when stored at 2-8°C in the recommended storage buffer provided by Creative Biolabs. Once opened, be sure to avoid microbial contamination and strictly follow the storage instructions to maximize their shelf life. Do not freeze the beads, as this will damage the bead matrix and inactivate the proteins.
Q:Can large amounts of protein be bound to the magnetic beads?
A: "Yes, but there are some key considerations." The number of reaction sites on the surface of the magnetic beads is limited. Excessive coupling can lead to:
- Stereohindrance: Densely packed proteins can obstruct active sites, reducing functional activity.
- Protein aggregation: This can result in multilayered structures that are unstable and prone to dissolution.
- Increased nonspecific binding: Crowded protein surfaces become more "sticky."
- Our optimized workflow determines the saturation point and then the optimal coupling density that maximizes functional yield (not just the total amount of bound protein).
Q: How to remove proteins from magnetic beads for co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)?
A: For Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), if you want to analyze the co-precipitated protein rather than the antibody or bait protein itself, the most common method is to use Laemmli SDS-PAGE loading buffer and elute at 70-95°C for 5-10 minutes. This step denatures all proteins, releasing the bait and target proteins into the supernatant for subsequent Western blotting or mass spectrometry analysis.
Conslusion
The need for rapid, efficient, and reproducible bioseparation and diagnostic tools continues to drive innovation in the field of bioconjugation. Customized magnetic bead-protein conjugates, combining the specificity of biorecognition with the efficiency of magnetic separation, are indispensable tools in molecular biology. At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to precision and high performance. We offer more than just products; we provide fully optimized and characterized reagents tailored to your specific application, ensuring high functional yields and assay reliability—crucial for accelerating your biomedical discoveries and achieving your business goals. Don't hesitate to contact us!
Reference
- Phiphattanaphiphop C, Leksakul K, Wanta T, et al. Antibody-conjugated magnetic beads for sperm sexing using a multi-wall carbon nanotube microfluidic device. Micromachines, 2022, 13(3): 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030426 Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
