Immunopathology Pathogenesis Treatment Related Products Hot Services Q&A Resources
Are you struggling with the complexities of Hashimoto's disease and seeking innovative therapeutic avenues? Complement system dysregulation significantly contributes to the pathogenesis of this autoimmune thyroiditis, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Creative Biolabs empowers your research by providing cutting-edge tools and expertise to investigate and target complement pathways, ultimately accelerating the development of novel therapeutics for Hashimoto's disease through advanced immunological assays, high-quality complement protein reagents, and custom antibody development services.
Immunopathology of Hashimoto's Disease
Hashimoto's disease, or Hashimoto's thyroiditis, exemplifies autoimmune thyroiditis, notable for the painless swelling of the thyroid. Histopathological examination reveals diffuse lymphocytic infiltration, fibrosis, and atrophic modifications. This diffuse phenomenon involves epithelial cell damage, lymphocyte penetration, and fibrotic changes, ultimately resulting in the progressive destruction of the thyroid gland. Research indicates that middle-aged women exhibit greater susceptibility compared to men and children.
Early Indicators and Symptoms of Hashimoto's Disease
Initially, individuals with Hashimoto's disease often remain asymptomatic. However, over time, the thyroid gland may enlarge, eventually leading to the development of hypothyroidism characterized by a constellation of signs and symptoms. After many years, the thyroid may generally decrease in size, and there is a potential risk of developing thyroid lymphoma. The clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism associated with Hashimoto's disease include:
-
Fatigue and sluggishness
-
Increased sensitivity to cold
-
Constipation
-
Pale, dry skin
-
A puffy face
-
Brittle nails
-
Hair loss
-
Enlargement of the tongue
-
Unexplained weight gain
-
Muscle aches, tenderness, and stiffness
-
Joint pain and stiffness
-
Muscle weakness
-
Excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
-
Depression
-
Memory lapses
Fig. 1 Hashimoto's disease/ thyroiditis is one of thyroid diseases.1, 3
Factors in the Pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s Disease
-
Antithyroid Antibodies
The antibodies against thyroperoxidase (anti-TPO), antithyroglobulin (anti-Tg) and more rarely TSH-stimulation blocking antibody (TSBAb), are positively correlated with an increased inflammatory reaction in the thyroid and with the development of Hashimoto’s disease. Antithyroid antibodies have an ability to fix complement and thus promote complement-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity leading to more damage to thyroid tissue.
-
T and B Lymphocytes
In patients with Hashimoto’s disease, B cells from thyroid tissue are activated to secrete antithyroid antibodies, the major pathogenic factors. It is acknowledged that excessively stimulated T cells CD4+ play the main role in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s disease. Moreover, T helper cells (Th1, Th2, and Th17) are also involved in the development of Hashimoto’s disease. Th2 cells lead to excessive stimulation and production of B cells, resulting in antithyroid antibodies accumulation. While Th1 cells activate cytotoxic lymphocytes and macrophages, leading to direct effects on thyroid tissue by destroying thyroid follicular cells.
-
Complement Components
As an important parameter of Hashimoto’s disease, thyroperoxidase consists of a large N-terminal myeloperoxidase-like module followed by a complement control protein (CCP)-like module and an epidermal growth factor-like module. C4 may bind to thyroperoxidase and activate the complement pathway in autoimmune thyroiditis. Autoantibodies against complement C1q (anti-C1q) are correlated with parameters of thyroid function and anti-TPO, anti-Tg and TSBAb. The researches of C3 in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s disease shows that the severity and duration of the thyroid dysfunction correlate with the degree of complement activation.
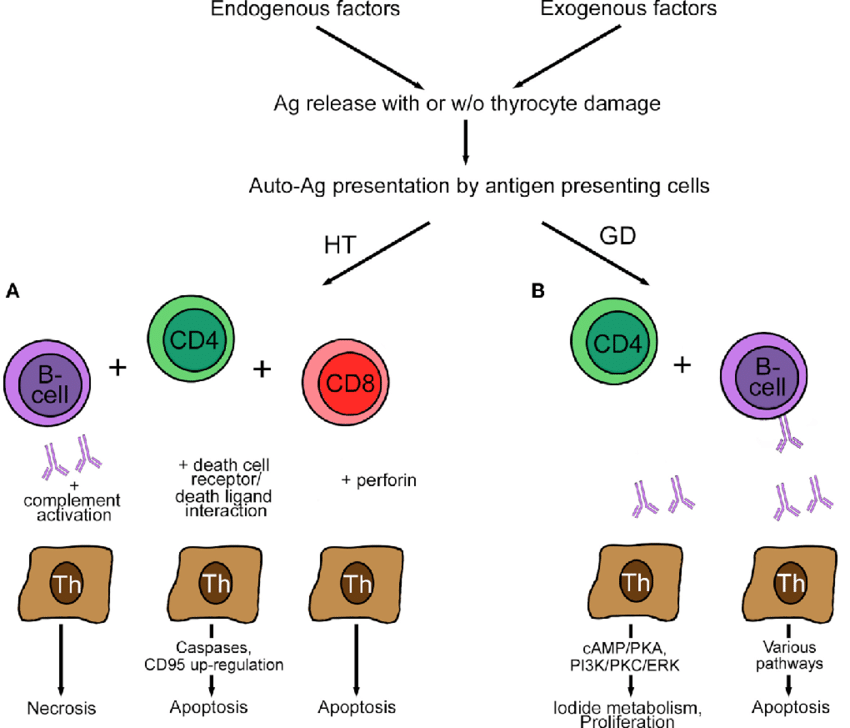
Fig. 2 Pathogenesis of Hashimoto's disease.2, 3
Treatment of Hashimoto's Disease in Complement Therapeutics
Table 1 Complement factors in Hashimoto's Disease treatment.
|
Complement molecules/pathways
|
Potential Therapeutic Approaches
|
|
C1q (Classical Pathway Initiation)
|
C1q Inhibitors (small molecules, antibodies, etc.)
|
|
MASPs (Lectin Pathway)
|
MASP Inhibitors
|
|
C3 (Core of All Pathways)
|
C3 Inhibitors (small molecules, antibodies, peptides, etc.)
|
|
C3 Convertase
|
C3 Convertase Inhibitors
|
|
CFB, CFD (Alternative Pathway)
|
CFB Inhibitors, CFD Inhibitors (small molecules, antibodies, etc.
|
|
C5 (Initiation of Terminal Pathway)
|
C5 Inhibitors (monoclonal antibodies)
|
|
C5 Convertase
|
C5 Convertase Inhibitors
|
|
MAC (C5b-C9)
|
MAC Formation Inhibitors
|
Creative Biolabs has established advanced Complement Therapeutics platform including antibody engineering platform, protease inhibitor platform, and drug discovery platform, and is equipped to offer a full range of biotherapeutics development services regarding drug discovery and validation for Hashimoto’s disease. Please contact us for detailed information.
Related Hot Products
Our comprehensive complement platform offers an extensive and cost-effective array of complement-associated products. For further information, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Table 2 Featured products.
Related Hot Services
Table 3 Complement test services for Hashimoto's Disease-related complement studies.
Resources
References
-
Macvanin, Mirjana T., et al. "New biomarkers: prospect for diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid disease." Frontiers in Endocrinology 14 (2023).
-
Fröhlich, Eleonore, and Richard Wahl. "Thyroid autoimmunity: role of anti-thyroid antibodies in thyroid and extra-thyroidal diseases." Frontiers in immunology 8 (2017): 521.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: