Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? Published Data FAQs Related Products Featured Services
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in developing highly specific therapeutics for complement-mediated diseases, or struggling with the complexities of targeting the classical complement pathway? Our Complement Therapeutic Target-C1q services at Creative Biolabs help you accelerate the discovery and development of novel C1q-modulating biologics, ensuring high-quality and precisely targeted solutions through advanced antibody engineering and functional assay platforms.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system constitutes an essential element of innate immunity, serving an integral function in defending against microbial invaders and removing immune complexes and apoptotic cells. However, dysregulation of the complement system can contribute to the pathogenesis of numerous inflammatory, autoimmune, and neurodegenerative diseases. Complement component 1q (C1q) functions as the recognition subunit within the C1 complex, tasked with triggering the classical complement pathway. C1q binds to immune complexes, apoptotic cells, and certain pathogen surfaces, triggering a cascade of events that leads to inflammation, opsonization, and cell lysis.
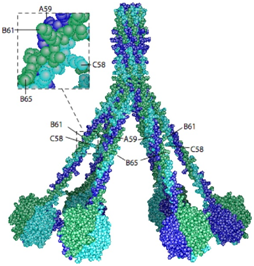 Fig.1 The 3D model of human C1q.1,3
Fig.1 The 3D model of human C1q.1,3
C1q is a large, multi-domain protein composed of 18 polypeptide chains organized into six identical globular heads (gC1q) and six collagen-like stalks (cC1q) that converge into a central stem. This unique structure allows C1q to bind to various activators through its gC1q domains, while its cC1q domains interact with C1r and C1s proteases, leading to their activation. Beyond its classical role in immunity, C1q has been implicated in a diverse array of physiological and pathological processes, including synaptic pruning in the central nervous system, tissue repair, and the progression of various diseases.
Dysregulated C1q function constitutes a major contributor to the pathogenesis of numerous severe disorders. These encompass autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, wherein abnormal C1q function promotes chronic inflammation and tissue injury through impaired clearance of immune complexes or provoking maladaptive immunity. Additionally, C1q critically influences atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), a rare yet critical illness marked by dysregulated complement activation causing microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute renal impairment. Regarding neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and glaucoma, C1q acts as a central mediator of synaptic elimination and neuroinflammatory amplification, frequently by opsonizing synapses for pathological microglial eradication. This participation solidifies C1q as a promising therapeutic focus for these incapacitating conditions. Therapeutic modulation of C1q—whether suppressing detrimental actions or augmenting protective functions—offers a viable approach for creating innovative, precisely directed treatments potentially capable of arresting or reversing disease advancement.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to support your Complement Therapeutic Target-C1q projects:
-
C1q Protein Production: High-quality recombinant human and animal C1q proteins for research, assay development, and screening purposes.
-
High-Throughput Screening for C1q Modulators: Efficient screening platforms to identify small molecules or biologics that modulate C1q activity from large libraries.
-
C1q Binding / Interaction Profiling: Evaluating binding kinetics/specificity of therapeutic candidates against C1q using advanced biophysical techniques.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of complement therapeutic development, offering unparalleled expertise and cutting-edge platforms for targeting C1q. Our commitment to scientific excellence and client success distinguishes us in the field.
-
Deep Scientific Expertise: Our team comprises seasoned biologists and immunologists with extensive experience in complement biology and therapeutic development, ensuring a nuanced understanding of C1q's complex roles.
-
Advanced Antibody Engineering: We leverage state-of-the-art antibody discovery and engineering platforms to generate highly specific and potent anti-C1q antibodies or other C1q modulators, optimized for therapeutic applications.
-
Comprehensive Functional Assays: Our robust suite of functional assays allows for precise characterization of C1q-modulating candidates, including classical pathway inhibition assays, C1q binding assays, and cell-based functional readouts.
-
Integrated Discovery Workflow: From target validation to lead optimization, we offer an integrated workflow that streamlines the development process, saving you time and resources.
-
Quality and Reliability: We adhere to stringent quality control standards at every stage, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of our data and the high quality of our deliverables.
-
Proven Track Record: Our success stories, supported by Published Data, demonstrate our capability to deliver effective solutions for challenging therapeutic targets, including complement components.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Published Data
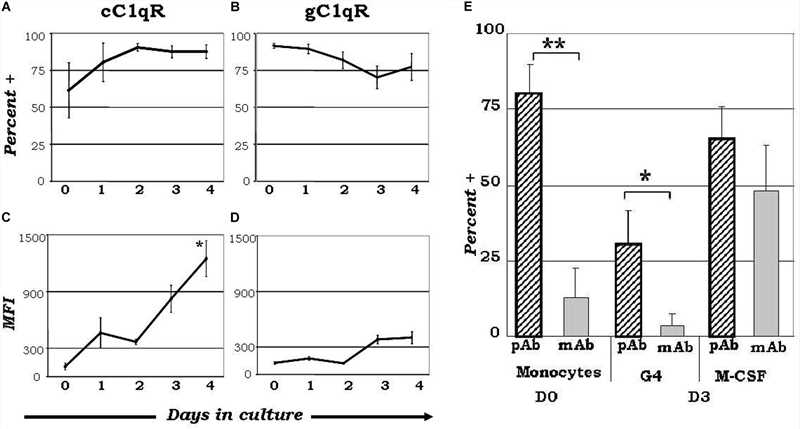 Fig.2 Expression diversity of C1q receptors and orientation of surface-bound C1q on monocyte-derived dendritic cell precursors potentially influence dendritic cell differentiation processes.2,3
Fig.2 Expression diversity of C1q receptors and orientation of surface-bound C1q on monocyte-derived dendritic cell precursors potentially influence dendritic cell differentiation processes.2,3
Understanding the role of C1q and its receptors (C1qRs) in inflammation linked to diseases such as infections, cancer, and autoimmune disorders is key for advancing therapeutic strategies. Elucidating how C1q/C1qR interactions switch from a homeostatic to an inflammatory state may reveal novel therapeutic avenues. Compounds that disrupt C1q and cC1qR binding, or replicate C1q's engagement with gC1qR, offer potential as drug templates to mitigate C1q-induced inflammation. The N-terminal region of C1q's collagen tail, binding cC1qR, presents a promising drug target. Already, specific monoclonal antibodies targeting gC1qR are in development, demonstrating efficacy in reducing tumor growth and enhancing apoptosis.
FAQs
Q: How can targeting C1q specifically benefit therapeutic development compared to broader complement inhibitors?
A: Targeting C1q offers the advantage of selectively inhibiting the classical complement pathway, which is often implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, while potentially preserving the beneficial functions of the alternative and lectin pathways. This selectivity can lead to fewer off-target effects and a more focused therapeutic intervention.
Q: What types of diseases or conditions are most likely to benefit from C1q modulation?
A: Conditions where the classical complement pathway plays a significant pathological role are prime candidates. These include various autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis), certain neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer's disease, glaucoma), and specific inflammatory conditions where C1q-mediated immune complex deposition or tissue damage is prominent.
Q: Are there any potential challenges or considerations when developing C1q-targeting therapeutics?
A: Key considerations include ensuring high specificity to C1q to avoid unintended interactions with other complement components or physiological processes. Additionally, understanding the precise mechanism of action (e.g., inhibiting C1q binding, preventing C1 activation, or promoting C1q clearance) is crucial for optimizing therapeutic efficacy and safety.
Q: How is the efficacy of C1q-modulating agents typically evaluated in preclinical studies?
A: Efficacy is often evaluated using a combination of in vitro functional assays (e.g., classical pathway hemolytic assays, C1q binding assays, complement activation assays in serum) and in vivo disease models that mimic the human condition where C1q dysregulation is a driver of pathology. Biomarker analysis of complement activation products can also provide valuable insights.
Q: What differentiates a C1q-targeting approach from strategies that block downstream complement components like C3 or C5?
A: While blocking C3 or C5 offers broad complement inhibition, targeting C1q provides a more upstream and pathway-specific intervention. This can be advantageous in diseases primarily driven by classical pathway activation, potentially allowing for finer control over complement activity and reducing the risk of broad immunosuppression associated with more downstream inhibition.
Access the Creative Biolabs Edge – Request Your Quote Now
Related Hot Products
Featured Services
References
-
Pflieger, Delphine, et al. "Analysis of human C1q by combined bottom-up and top-down mass spectrometry: detailed mapping of post-translational modifications and insights into the C1r/C1s binding sites." Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 9.4 (2010): 593-610. DOI:10.1074/mcp.M900350-MCP200.
-
Hosszu, Kinga K., et al. "SLE: novel postulates for therapeutic options." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 583853. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2020.583853.
-
Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 The 3D model of human C1q.1,3
Fig.1 The 3D model of human C1q.1,3
 Fig.2 Expression diversity of C1q receptors and orientation of surface-bound C1q on monocyte-derived dendritic cell precursors potentially influence dendritic cell differentiation processes.2,3
Fig.2 Expression diversity of C1q receptors and orientation of surface-bound C1q on monocyte-derived dendritic cell precursors potentially influence dendritic cell differentiation processes.2,3