Immunopathology of SS Complement Activation in SS Complement Molecular Mechanisms Related Products Hot Services Q&A Resources
Are you struggling with the complexities of systemic sclerosis (SS) and the limited efficacy of current treatments? The complex interactions among inflammation, fibrosis, and vascular dysfunction in SS pose considerable challenges for treatment. At Creative Biolabs, our cutting-edge research and development in complement therapeutics offer a promising avenue for targeted intervention, helping you develop novel and effective treatments to address the underlying pathogenic mechanisms of SS through innovative complement-targeting strategies.
Immunopathology of Systemic Sclerosis
Systemic sclerosis (SS), alternatively termed systemic scleroderma, diffuse scleroderma, or progressive systemic sclerosis, is an autoimmune disorder targeting connective tissues. Characterized by an overabundance of collagen deposition, its pathology leads to fibrosis in both the skin and internal organs. CREST syndrome—comprising calcinosis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia—denotes a limited variant of scleroderma. SS is frequently identified in individuals aged 30 to 50, with women exhibiting a higher incidence than men. SS is classified into two main categories: localized (limited) SS, affecting only the skin of the face, hands, and feet, and systemic (diffuse) SS, which inflicts severe damage on internal organs, particularly the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart, and lungs.
Signs and Symptoms of Systemic Sclerosis
Beyond the thickening and shiny areas in the skin, there are a number of other symptoms of SS disease, which can be divided into two categories: skin symptoms and organs symptoms.
-
Skin symptoms
Mainly include: tight, reddish, or scaly of the skin; severe and recurrent itching of large skin areas; calcium deposits, or white lumps under the skin; small, dilated blood vessels under the skin’s surface.
-
Organs symptoms
Diffuse scleroderma can cause musculoskeletal, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, renal and other complications. Mainly include joint pain; shortness of breath; a dry cough; diarrhea; constipation; difficulty swallowing; esophageal reflux; abdominal bloating after meals.
SS patients may suffer from various complications, mainly include heart failure, cancer, kidney failure, and high blood pressure.
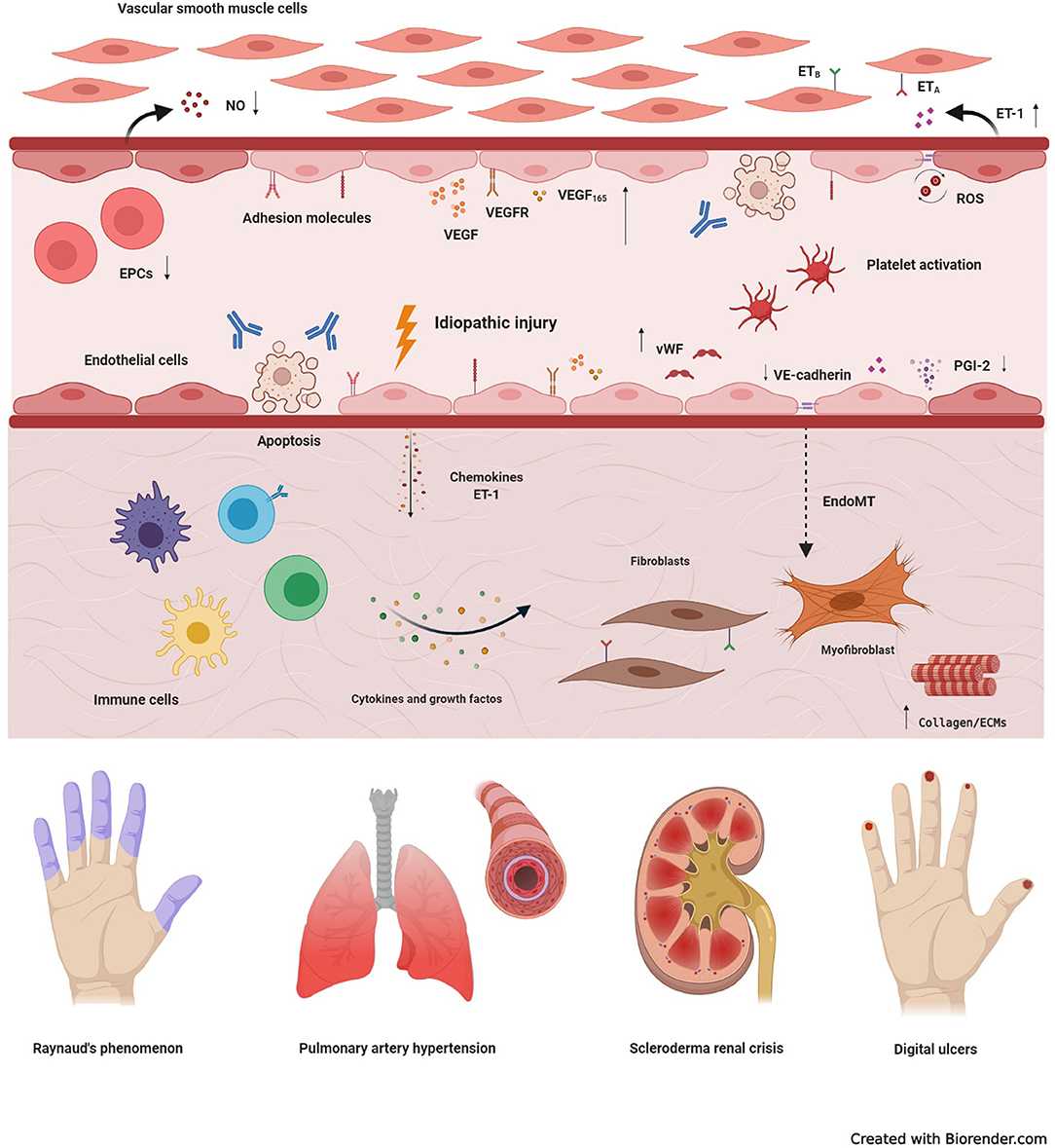 Fig. 1 Fundamental mechanisms underlying vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis.1, 3
Fig. 1 Fundamental mechanisms underlying vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis.1, 3
Complement Activation Pathways and SS Pathogenesis
The complement system, a crucial arm of the innate immune system, is increasingly recognized for its significant role in the pathogenesis of SS. Emerging evidence highlights the involvement of all three pathways in the complex cascade of events that characterize SS.
In SS, complement may be activated or inherently abnormal. C1q, C2, C3, C4A, C3bBbP, C5, C6, C7, C9, and factor B were significantly increased in skin biopsies of SS patients but not in healthy subjects.
Table 1 Complement activation pathways in SS.
|
Complement Activation Pathways
|
Description
|
Therapeutic Relevance
|
|
Classical Pathway
|
Initiated by immune complexes (IgG/IgM) from autoantibodies, leading to increased activation markers and causing inflammation/tissue damage. C3 Convertases Formation leads to the generation of C3a and C3b.
|
Targeting autoantibody production/immune complexes
|
|
Lectin Pathway
|
Initiated by MBL/ficolins, with potential links to vascular dysfunction, and some evidence of elevated MBL levels. C3 Convertases Formation leads to the generation of C3a and C3b.
|
Targeting MBL/ficolin activity
|
|
Alternative Pathway
|
Initiated by spontaneous activation/dysregulation, with increased complement components/activation products, driving inflammation/fibrosis. C3 Convertases Formation leads to the generation of C3a and C3b.
|
Targeting spontaneous activation or regulatory components
|
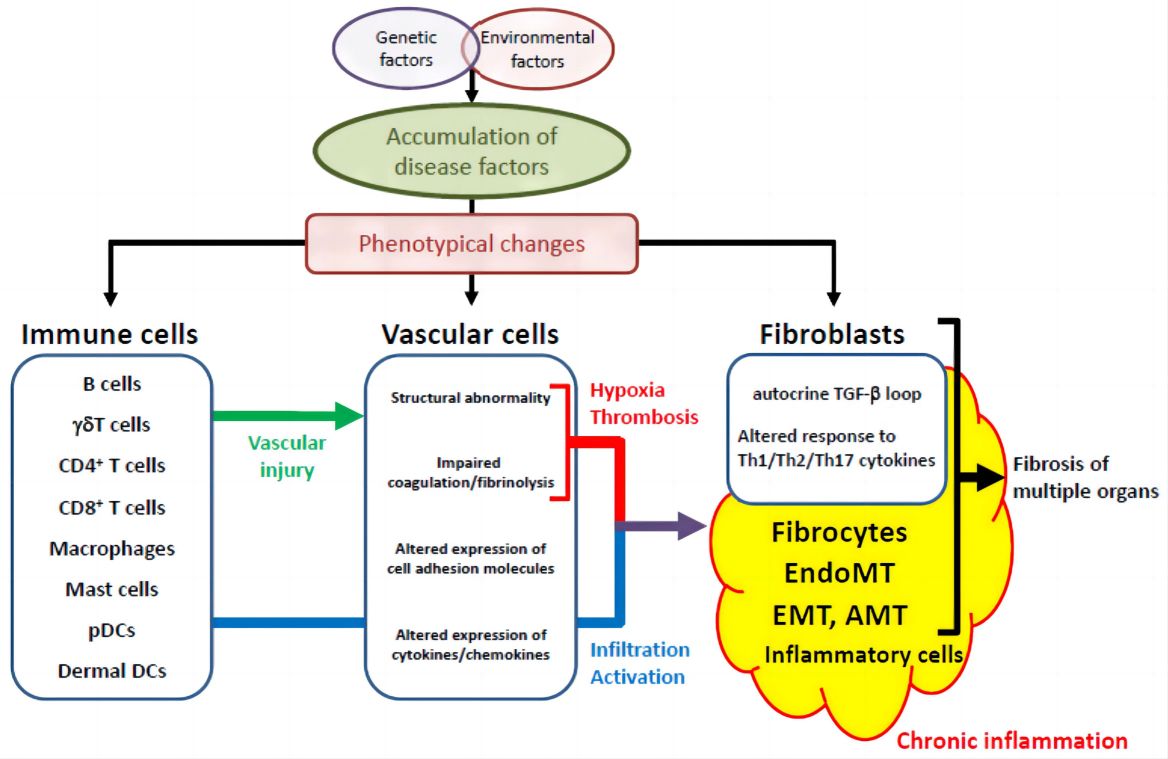 Fig. 2 The shared pathological cascade in various organs specific to systemic sclerosis.2, 3
Fig. 2 The shared pathological cascade in various organs specific to systemic sclerosis.2, 3
Complement Molecular Mechanisms in SS
Table 2 Molecular mechanisms of complement-mediated.
|
Key Complement Components
|
Functions
|
|
C3a, C5a
|
-
Directly bind to their receptors on fibroblasts, stimulating their proliferation, differentiation into myofibroblasts, and the production of excessive extracellular matrix components.
-
Recruit various immune cells to sites of complement activation in SSc tissues, amplifying the inflammatory response.
-
Trigger the release of histamine, prostaglandins, and other inflammatory mediators from mast cells and basophils, contributing to systemic inflammation and vascular permeability.
|
|
MAC Formation (C5b-9)
|
Sublytic MAC can also induce pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic signaling in endothelial cells.
|
|
C3a and C5a Receptor
|
Activation on endothelial cells leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules, promoting leukocyte recruitment and vascular inflammation.
|
Related Hot Products
Our comprehensive complement platform offers an extensive and cost-effective array of complement-associated products. For further information, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Table 3 Featured products.
Related Hot Services
Table 4 Complement test services for SS-related complement studies.
All assays are intended exclusively for research purposes and are fine-tuned for superior specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility. The complement system’s role is now acknowledged as pivotal in the pathogenesis and progression of SS. Focused complement analysis can yield crucial insights into:
-
Disease mechanisms
-
Biomarker discovery
-
Treatment evaluation
Creative Biolabs has established advanced Complement Therapeutics Platform including antibody engineering platform, protease inhibitor platform, and drug discovery platform, and is equipped to offer a full range of biotherapeutics development services regarding drug discovery and validation for SS. Please contact us for detailed information.
Resources
References
-
Zanin-Silva, Djúlio César, et al. "Management of endothelial dysfunction in systemic sclerosis: Current and developing strategies." Frontiers in Medicine 8 (2021): 788250.
-
Asano, Yoshihide. "The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: An understanding based on a common pathologic cascade across multiple organs and additional organ-specific pathologies." Journal of clinical medicine 9.9 (2020): 2687.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Fundamental mechanisms underlying vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis.1, 3
Fig. 1 Fundamental mechanisms underlying vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis.1, 3
 Fig. 2 The shared pathological cascade in various organs specific to systemic sclerosis.2, 3
Fig. 2 The shared pathological cascade in various organs specific to systemic sclerosis.2, 3