Product List Background ANGPTL4 Aptamer Analysis
Background
Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4, aliases HFARP, FIAF, PGAR, NL2, etc.) is a protein encoded by the ANGPTL4 gene in humans, transcript variants of which caused by alternatively splicing have been reported. It is a secreted, glycosylated protein composed of several domains, including a coiled-coil N-terminal domain, and a fibrinogen-like C-terminal domain. ANGPTL4 is a serum hormone intensively involved in inhibiting lipoprotein metabolism and energy homeostasis under different circumstances, stimulated under low oxygen conditions in various types of cells, being a target of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors.
Its Gene ID: 51129, UniProtKB ID: Q9BY76, and OMIM ID: 605910.
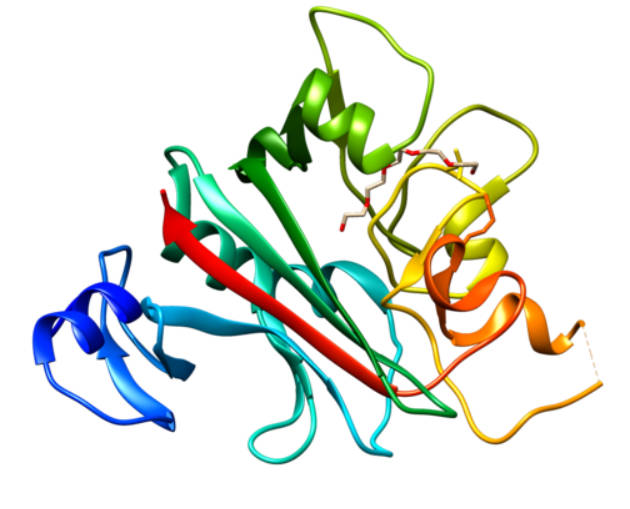 Fig.1 Structure of ANGPTL4. Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Structure of ANGPTL4. Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Functions of ANGPTL4 in Diseases
ANGPTL4 plays a crucial role in various cancers and serves as a modulator of vascular permeability, cancer cell motility, and invasiveness in the process of tumor metastasis. There has also been abundant evidence showing that ANGPTL4 plays essential roles in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases, like type 2 diabetes (T2D) and atherosclerosis, and is directly correlated with the risk of these diseases. Studies in humans and murine have explored the mechanisms of how ANGPTL4 functions in various tissues and the effects on disease development via possible regulations in paracrine or autocrine forms. These findings revealed that ANGPTL4 controls inhibiting the activities of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) to further regulate lipoprotein catabolism and energy distribution in different tissues. In addition to regulating lipid homeostasis, ANPTL4 has also been reported to regulate angiogenesis and vascular permeability.
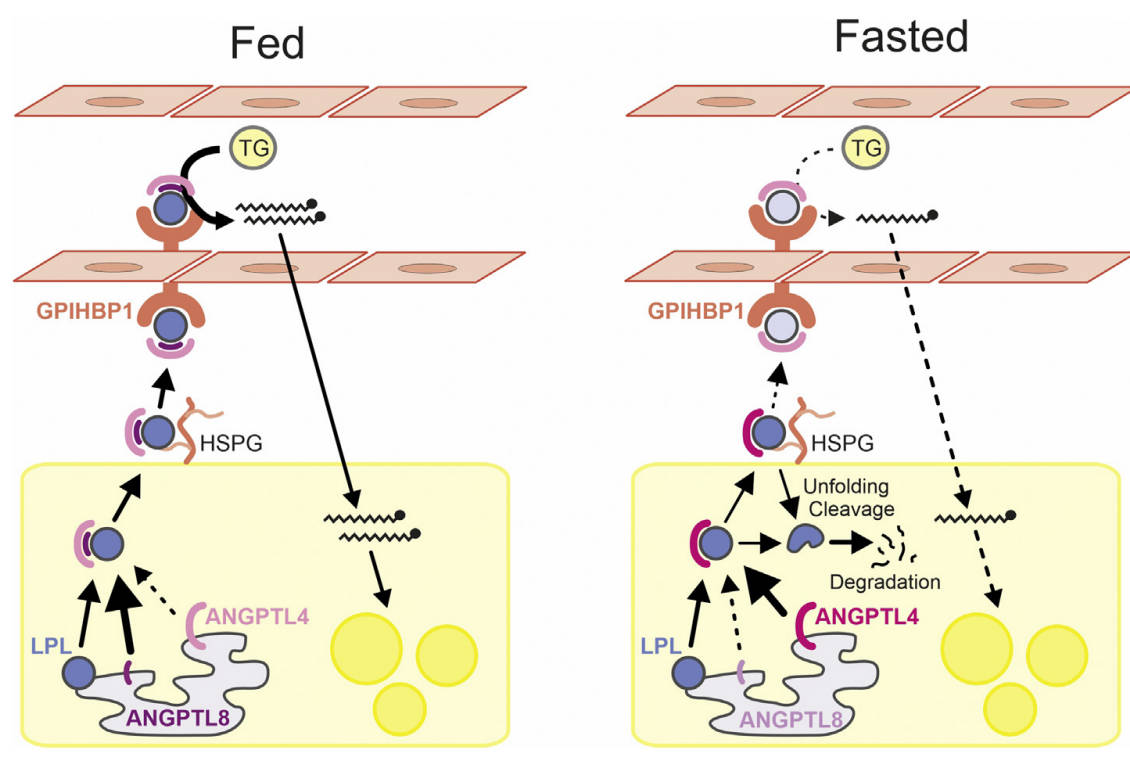 Fig.2 The mechanism of ANGPTL4 in LPL regulation in adipose tissue.1,3
Fig.2 The mechanism of ANGPTL4 in LPL regulation in adipose tissue.1,3
In inflammatory responses, ANGPTL4 is found to play dual roles, demonstrating a complex mechanism and expression pattern across different cell types and tissues, involved in a broad spectrum of processes, including post-translational modification, alternative splicing, cleavage and oligomerization, DNA methylation, and subcellular localization.
Aptamers Targeting ANGPTL4
Aptamers are functional DNA or RNA oligonucleotides selected by the systematic evolution of ligands by SELEX techniques, extensively utilized as robust research tools, components of drug delivery systems, and many other applications. Since the value of ANGPTL4 as a therapeutic target has attracted continuous research interests, aptamers targeting ANGPTL4 have also been obtained and studied. A DNA anti-ANGPTL4 aptamer is reported to be applied to form a simple, accurate, quick, and cost-effective biosensor for detecting ANGPTL4 in clinical samples., shedding light on the diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for many related diseases.
Creative Biolabs offers several products related to ANGPTL4, mainly our high-affinity, high-stability, and low-toxicity aptamer products, to support you for your various research purposes. We also offer customized services for other tailored ANGPTL4-targeting products based on your requirements and needs.
ANGPTL4 Aptamer Analysis
Anti-ANGPTL4 aptamers are synthetic oligonucleotides specifically designed to bind ANGPTL4, which have significant potential in diagnostics and therapies for metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, where ANGPTL4 plays a pivotal role.
Anti-ANGPTL4 aptamers are used in detection assays to quantify ANGPTL4 levels in biological samples, aiding in disease diagnosis. These aptamers can be integrated into biosensors for real-time detection, offering high sensitivity and specificity. For instance, electrochemical and fluorescence-based biosensors have been developed, utilizing anti-ANGPTL4 aptamers for detecting ANGPTL4 in serum, facilitating early diagnosis of diseases like atherosclerosis and obesity.
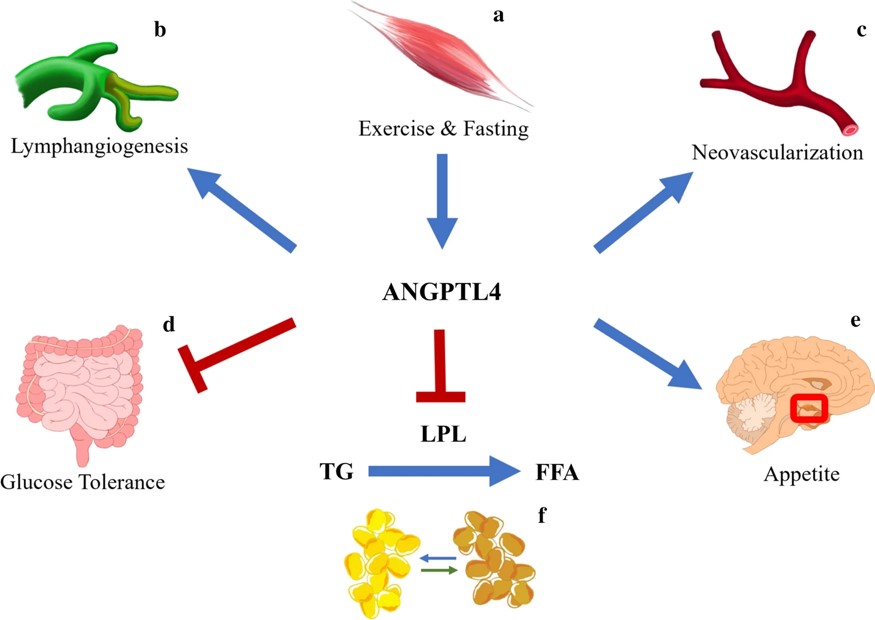 Fig.3 Roles of ANGPTL4.2,3
Fig.3 Roles of ANGPTL4.2,3
In therapeutic applications, anti-ANGPTL4 aptamers can block the interaction between ANGPTL4 and its receptors, potentially reducing the pathological effects of excessive lipid accumulation and endothelial dysfunction. Research has demonstrated that these aptamers can inhibit ANGPTL4-induced vascular leakage and regulate lipid homeostasis, presenting novel therapeutic avenues in cancer and metabolic diseases. Additionally, studies have shown that anti-ANGPTL4 aptamers could serve as targeted drug delivery vehicles, providing precision treatments for diseases involving ANGPTL4 dysregulation.
Creative Biolabs provides custom anti-ANGPTL4 aptamer development, aptamer conjugation, and assay optimization services. Our products feature high specificity and reliability, helping customers efficiently detect and analyze ANGPTL4. We support researchers with tailored solutions to enhance their studies on ANGPTL4-related diseases and therapeutic strategies.
References
-
Kersten, Sander. "Role and mechanism of the action of angiopoietin-like protein ANGPTL4 in plasma lipid metabolism." Journal of Lipid Research 62 (2021).
-
Tong, Zhoujie, et al. "Cross-talk between ANGPTL4 gene SNP Rs1044250 and weight management is a risk factor of metabolic syndrome." Journal of Translational Medicine 19 (2021): 1-12.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Structure of ANGPTL4.
Fig.1 Structure of ANGPTL4. Fig.2 The mechanism of ANGPTL4 in LPL regulation in adipose tissue.1,3
Fig.2 The mechanism of ANGPTL4 in LPL regulation in adipose tissue.1,3
 Fig.3 Roles of ANGPTL4.2,3
Fig.3 Roles of ANGPTL4.2,3
