Product List Background BAFF Aptamer Analysis
Background
BAFF, a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family, functions as a ligand binding to receptors TNFRSF13C/BAFFR, TNFRSF17/BCMA, and TNFRSF13B/TACI. This cytokine plays a pivotal role in promoting the viability and developmental progression of B cells. BAFF-deficient mice exhibit a lack of mature B cells. It supports the survival of immature T2 B cells and potentially mature B cells, excluding B1 B cells. Together, these components constitute a pathway involving two ligands and two receptors that modulate B- and T-cell functions, influencing humoral immunity regulation. Given its pivotal role, BAFF represents a significant target for therapeutic interventions.
Its Gene ID: 10673, UniProtKB ID: Q9Y275, and OMIM ID: 603969.
BAFF Signaling Pathways
The BAFF and BAFF-R pathways modulate both canonical and non-canonical NF-κB-dependent signaling routes. The canonical path, reliant on NEMO and the IKK complex, activates NF-κB dimers containing p50 subunits. BAFF stimulates the non-canonical NF-κB2 pathway, which is intricately regulated by the NF-κB inducing kinase NIK. In the absence of BAFF, NIK interacts with TRAF3, leading to its proteasomal degradation mediated by cIAP1/2 and TRAF2/3 complexes. Conversely, BAFF binding to BAFF-R induces receptor clustering, enabling TRAF3 dissociation from the intracellular sequence, and preventing NIK degradation. Accumulated NIK phosphorylates IKK1, promoting NF-κB2 p100 cleavage into active p52, which forms complexes with relB to regulate nuclear genes like ICOSL in activated T cells, crucial for follicular Th cell development. Additionally, BAFF-R activates PI3K-dependent signaling, influencing cytoskeletal dynamics and the AKT/mTOR axis, essential for B cell metabolic processes, including protein synthesis and mitochondrial function.
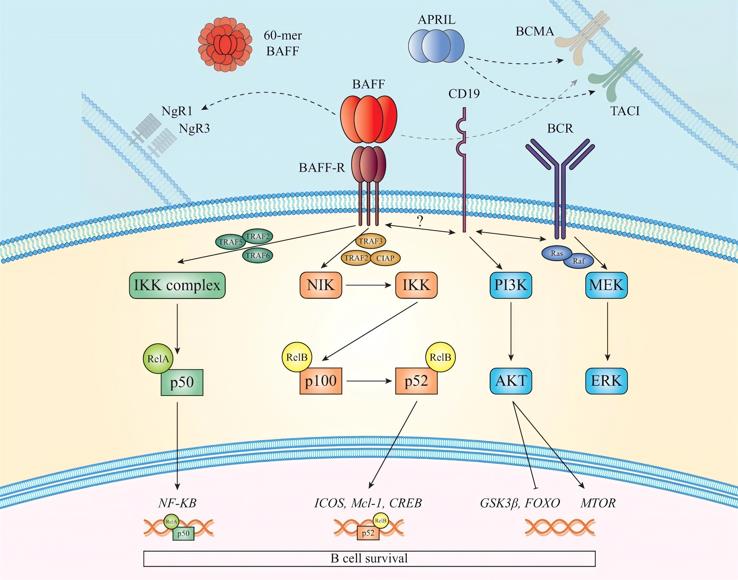 Fig.1 BAFF signaling pathways.1,3
Fig.1 BAFF signaling pathways.1,3
Applications of BAFF-Related Products
High-Affinity Aptamers for BAFF Detection in SLE Treatment
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prevalent autoimmune disease, with BAFF being a critical target for its treatment and detection. Developing novel high-affinity molecular recognition elements for BAFF is crucial. A study has utilized the SELEX technique to identify artificial nucleic acid aptamers targeting BAFF from a single-stranded DNA random library. Following ten rounds of selection, aptamers with high specificity and affinity for BAFF are successfully identified. High-throughput sequencing and binding assays have confirmed their efficacy. A sandwich ELONA using these aptamers and antibodies has been established for BAFF detection, offering new tools for BAFF detection and antagonist studies.
BAFF as a Biomarker in Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
In recent research, children with ocular Myasthenia gravis (MG) have shown significantly higher serum BAFF levels before immunosuppressive therapy (IST) compared to controls; these levels decrease post-IST. A positive correlation between serum BAFF levels and anti-AChR antibody titers is also observed, indicating BAFF's role in both pediatric and adult MG pathogenesis and its potential as a therapeutic marker.
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive range of BAFF-related products, including assay kits and aptamers designed for precise BAFF detection. Additionally, we offer tailored solutions such as custom bispecific antibodies to address specific needs and requirements.
BAFF Aptamer Analysis
Anti-BAFF aptamers are short, synthetic nucleic acids designed to specifically bind to BAFF, a key cytokine in immune regulation. These aptamers play critical roles in immunological research, particularly in studying B-cell activation and autoimmune diseases, and are valuable in developing diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions.
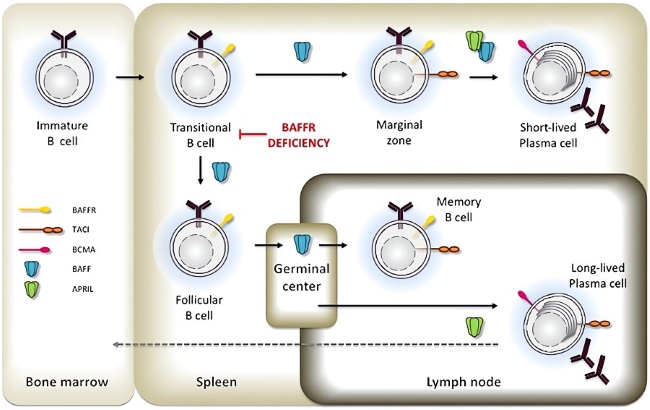 Fig.2 Role of BAFF and BAFF-R in the B cells development.2,3
Fig.2 Role of BAFF and BAFF-R in the B cells development.2,3
Anti-BAFF aptamers can be utilized in BAFF-related detection assays and functional research. By specifically binding to BAFF, they enable precise quantification and analysis of BAFF levels in various biological samples. These aptamers are crucial in studying autoimmune diseases such as SLE and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), where BAFF is often dysregulated. In disease research, anti-BAFF aptamers aid in understanding the role of BAFF in B-cell proliferation and survival, providing insights into the development of targeted therapies. They also support the creation of biosensors for early detection of BAFF-related diseases, improving diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic monitoring.
The anti-BAFF aptamers provided by Creative Biolabs offer high specificity, stability, and low immunogenicity for various functional research. We provide customized aptamers tailored to your research needs, along with optimization and assay development services. With our expertise, you gain reliable, efficient solutions for BAFF-related research and diagnostics, supported by comprehensive customer service.
References
-
Damianidou, Olympia, et al. "Novel contributors to B cell activation during inflammatory CNS demyelination; An oNGOing process." International Journal of Medical Sciences 19.1 (2022): 164.
-
Smulski, Cristian R., and Hermann Eibel. "BAFF and BAFF-receptor in B cell selection and survival." Frontiers in Immunology 9 (2018): 2285.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 BAFF signaling pathways.1,3
Fig.1 BAFF signaling pathways.1,3
 Fig.2 Role of BAFF and BAFF-R in the B cells development.2,3
Fig.2 Role of BAFF and BAFF-R in the B cells development.2,3
