Product List Background
Background
The HDLM2 cell line is derived from the pleural effusion of a patient with Hodgkin's disease. Cultures of HDLM2 predominantly consist of mono- or binucleated cells alongside prominent giant cells possessing between two to ten nuclei. HDLM2 cells do not exhibit a characteristic immunophenotype linked to a specific cell lineage but are positive for HeFi-1, Tac, and HLA class II markers. Cytochemical, enzymological, and functional analyses yield inconclusive results but do not align with a monocyte/macrophage profile. Genetic analysis reveals rearranged T-cell receptor δ and γ-chain genes, while immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes remain in germline configuration, collectively suggesting a T-cell origin for HDLM2 cells.
Signaling Pathways in Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells
Researchers have utilized HDLM-2 cells to investigate the genetic and molecular alterations characteristic of Hodgkin lymphoma. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells employ various strategies to neutralize anticancer immunity. They secrete IL-13, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1, and lactate, which inhibit Teff functions, expand Tregs, and promote immunosuppressive M2-TAM polarization. Additionally, HRS cells produce TGF-β, M-CSF, and lactic acid to convert monocytes or TAMs into M2-TAMs (PD-L1+ and IDO+), which in turn secrete TGF-β, IL-10, CCL17, and CCL22, inducing exhaustion in PD-1+ effector T and NK cells. HRS cells also drive CD4+ T cells towards Tregs by releasing TGF-β, GAL-1, TIMP-1, and PG-E. EADO and EVs from HRS cells further contribute to an immunosuppressive microenvironment by converting fibroblasts into αSMA+ CAFs and releasing bioactive ADAM10. These processes disrupt immune surveillance and hinder immunotherapy efficacy.
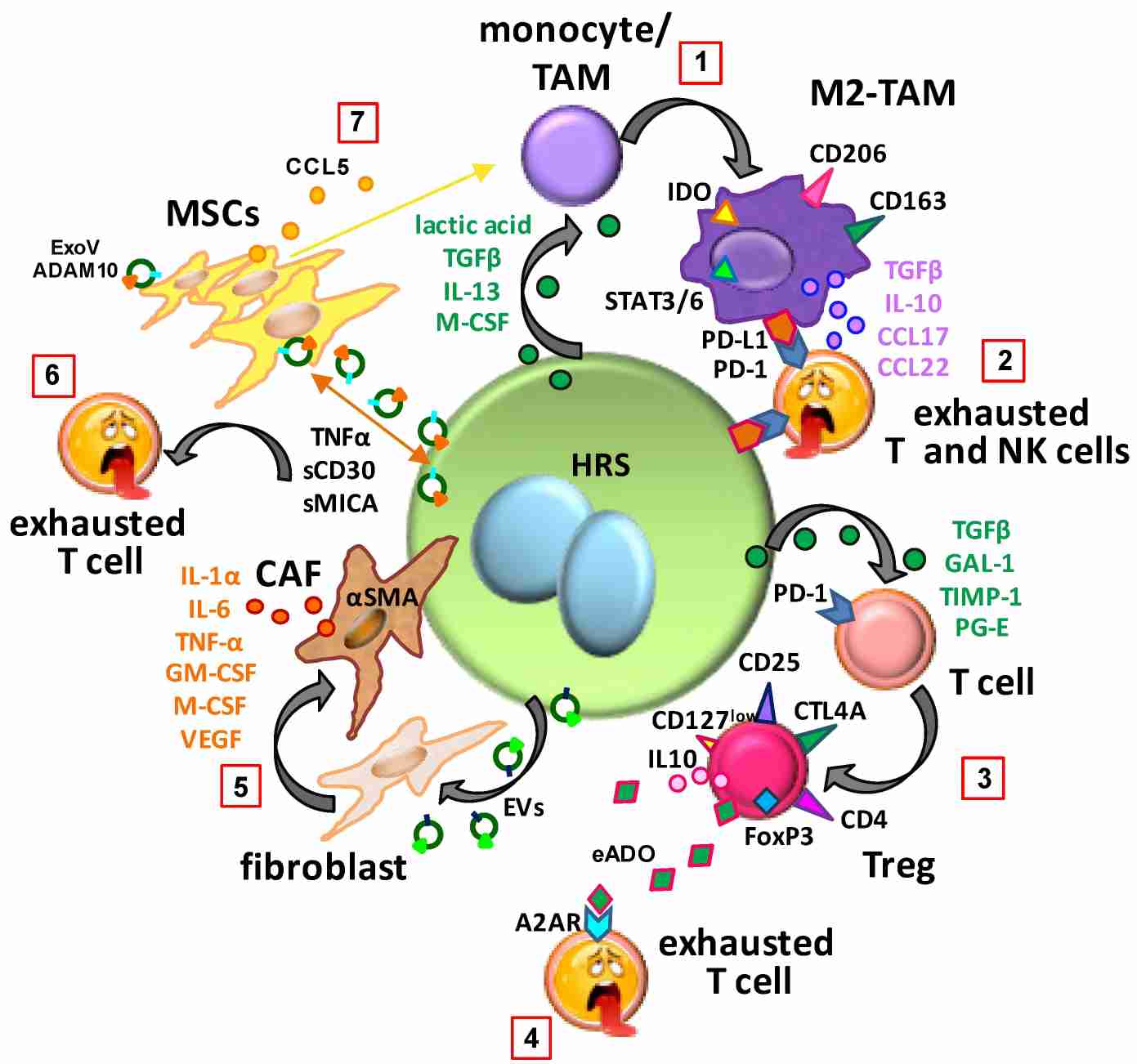 Fig.1 Key cells within the tumor microenvironment of classic Hodgkin lymphoma.1
Fig.1 Key cells within the tumor microenvironment of classic Hodgkin lymphoma.1
Applications of HDLM2 Related Products
Selective Binding and Clinical Potential of Hodgkin Lymphoma Aptamers
Oligonucleotide aptamers exhibit specific binding to target molecules, yet their clinical potential in disease diagnosis remains underexplored. Single-stranded DNA aptamers have been developed for Hodgkin lymphoma tumor cells using a tumor cell-based selection protocol. To assess clinical applicability, HDLM2 cells are diluted from regular donors in fresh human whole blood and double-stained with anti-CD45 antibody and anti-Hodgkin lymphoma aptamer. The aptamers exhibit high-affinity binding to HDLM2 and specifically detect HDLM2 without cross-reacting with other tumors or blood cells in mixed samples. Moreover, their stability in human serum indicates promise for in vivo detection of HDLM2.
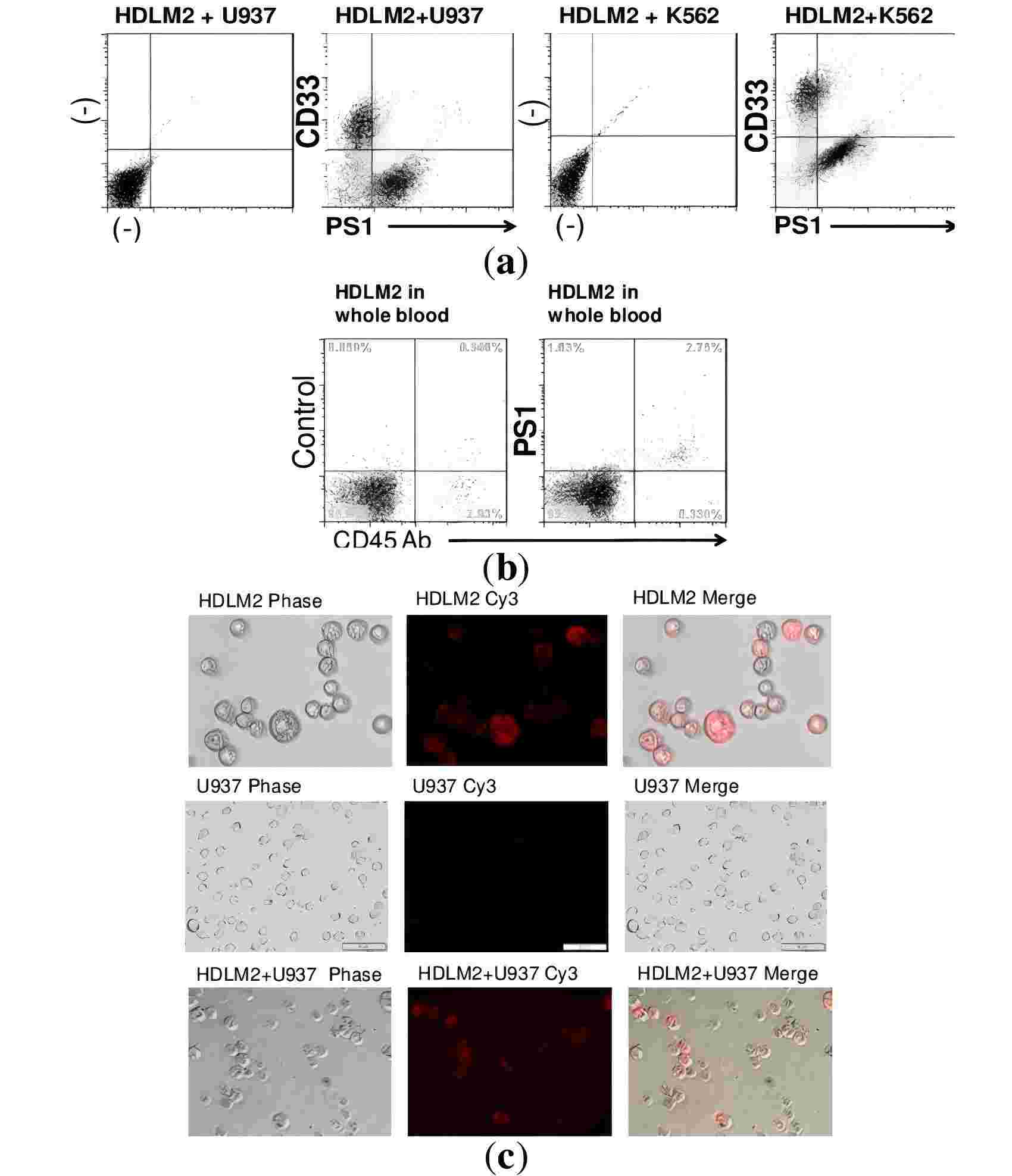 Fig.2 Specific targeting of HDLM2 cells using aptamers.2
Fig.2 Specific targeting of HDLM2 cells using aptamers.2
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of HDLM2-related products, including assay kits and aptamers engineered for accurate HDLM2 detection. Furthermore, we provide bespoke solutions, such as custom bispecific antibodies, designed to meet specific needs and requirements.
References
-
Aldinucci, Donatella, Cinzia Borghese, and Naike Casagrande. "Formation of the immunosuppressive microenvironment of classic Hodgkin lymphoma and therapeutic approaches to counter it." International journal of molecular sciences 20.10 (2019): 2416.
-
Parekh, Parag, et al. "Biostable ssDNA aptamers specific for Hodgkin lymphoma." Sensors 13.11 (2013): 14543-14557.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Key cells within the tumor microenvironment of classic Hodgkin lymphoma.1
Fig.1 Key cells within the tumor microenvironment of classic Hodgkin lymphoma.1
 Fig.2 Specific targeting of HDLM2 cells using aptamers.2
Fig.2 Specific targeting of HDLM2 cells using aptamers.2
