Product List Background HE4 Aptamer Analysis
Background
HE4, a protein belonging to the WFDC domain family, contains the WAP signature motif characterized by eight cysteines forming four disulfide bonds. Secreted as a glycoprotein in the bloodstream, HE4 inhibits serine, aspartyl, and cysteine proteases. Associated diseases include ovarian cancer and ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. HE4 is involved in pathways related to kidney and nervous system development, potentially playing a role in sperm maturation.
Its Gene ID: 10406, UniProtKB ID: Q14508, and OMIM ID: 617548.
HE4 Modulates Malignant Behaviors in Ovarian Cancer via Several Pathways
Recent studies involving overexpression and knockout of HE4-related genes have demonstrated that malignant behaviors such as cell adhesion, invasion, and proliferation in ovarian cancer cell lines are modulated via the EGFR-MAPK signaling pathway. Knockout of the HE4 gene alters phosphorylation levels of EGFR and Erk1/2, which are restored upon adding HE4 to the culture. The underlying mechanism remains unclear. The Lewis y antigen, a component of the EGFR structure, enhances EGFR and HER2/neu receptor tyrosine kinase activity, activating the PI3K/Akt and Raf/MEK/MAPK pathways. This activation accelerates HER2/neu gene transcription, stimulates DNA synthesis, and promotes cell proliferation, bypassing the G1 phase.
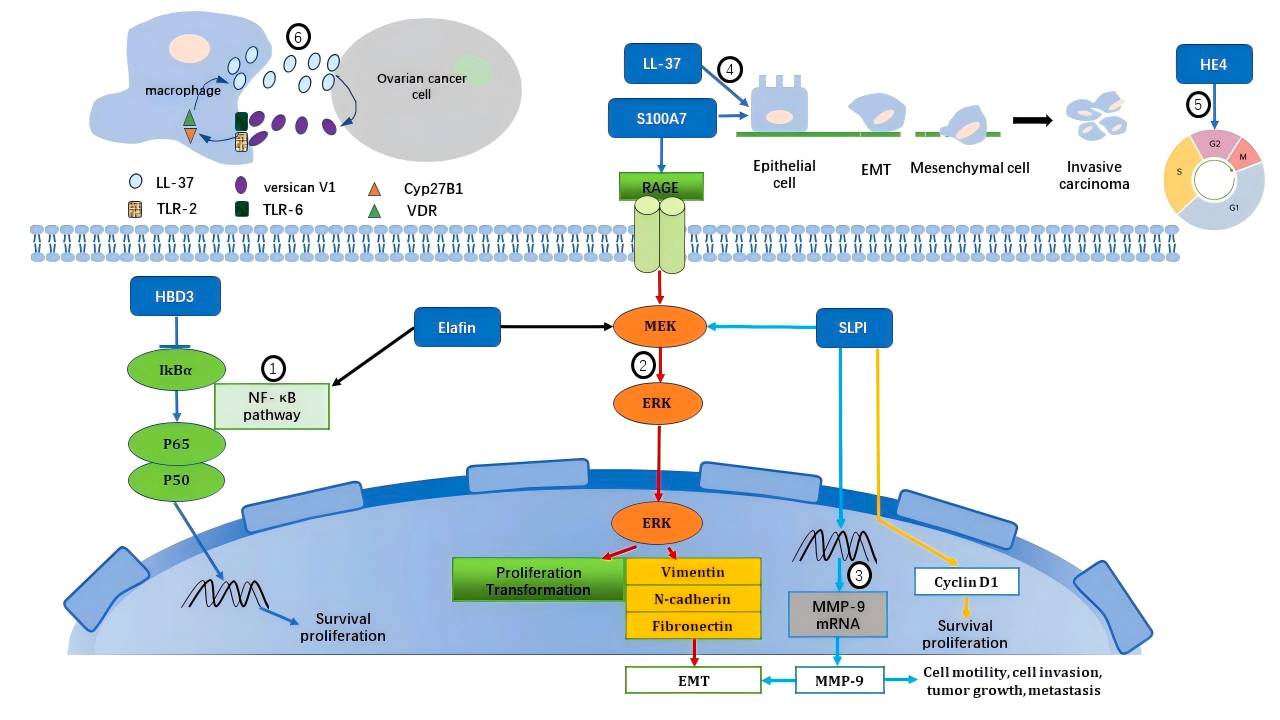 Fig.1 HE4's role in tumorigenic and pro-metastatic mechanisms as an antimicrobial peptide in gynecological cancers.1,3
Fig.1 HE4's role in tumorigenic and pro-metastatic mechanisms as an antimicrobial peptide in gynecological cancers.1,3
Applications of HE4 Products
Development of High-Affinity Anti-HE4 Aptamers for Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
Ovarian cancer, the most lethal gynecological malignancy, suffers from poor prognosis due to late-stage diagnosis, primarily attributed to non-specific symptoms and lack of practical diagnostic tools. Thus, novel diagnostic approaches are imperative. Urine, as a non-invasive source of cancer biomarkers, presents HE4 as a promising candidate, overexpressed in ovarian cancer but average in benign conditions. HE4 in urine offers high stability and diagnostic value. Aptamers, cost-effective single-stranded oligonucleotides with high target affinity, have emerged for cancer detection. Studies have utilized Hi-Fi SELEX to select DNA aptamers against human HE4 in urine, demonstrating high nanomolar affinity through thermofluorimetry. These aptamers show potential for future diagnostic applications and biosensor development for ovarian cancer.
Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Assessment of HE4 Protein Expression by Anti-HE4 Antibody
Initially identified as an epididymis-specific gene via Northern blot and in situ hybridization, HE4 protein distribution has been examined in benign and malignant tissues using HE4-specific antibodies. Immunohistochemical examination has revealed HE4 distribution within the epididymal duct characterized by a distinct granular apical pattern, without detectable presence in the adjacent stromal tissue or vascular structures. Specific immunoprecipitation of glycosylated HE4 by these antibodies has further validated their specificity. In formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues, HE4 expression is predominantly restricted to the epididymis and female reproductive tract.
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive range of HE4-related products, including assay kits and aptamers tailored for precise HE4 detection. Additionally, we offer customized solutions, such as bespoke bispecific antibodies, designed to address specific requirements and needs.
HE4 Aptamer Analysis
Anti-HE4 aptamers are synthetic nucleic acid molecules that specifically bind to HE4, a glycoprotein biomarker linked to ovarian cancer and other diseases as above described. These aptamers serve as powerful tools in diagnostics, offering high specificity for HE4 detection. They are crucial for early cancer diagnosis, monitoring, and targeted therapeutic development.
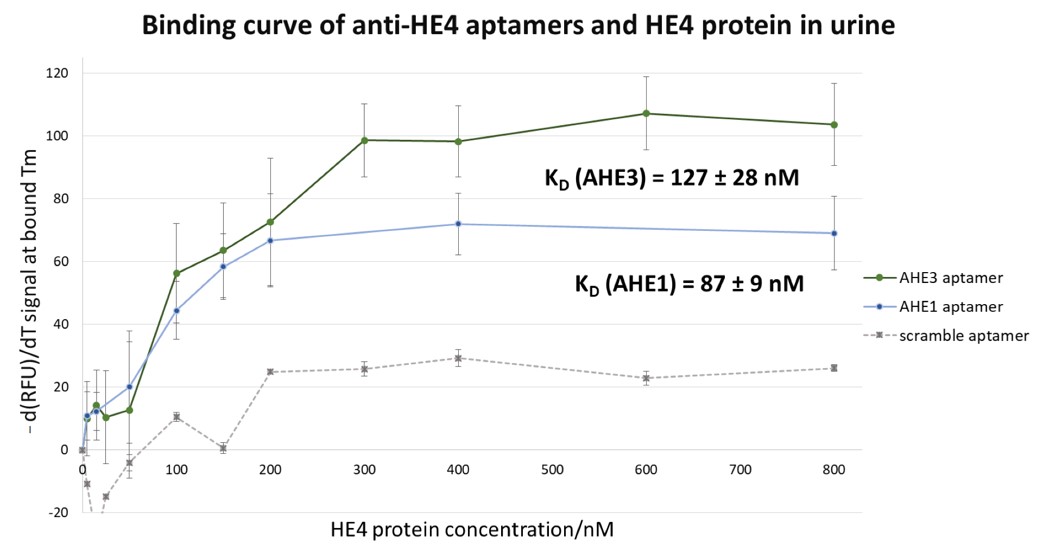 ig.2 The binding specificity of anti-HE4 aptamers targeting HE4.2,3
ig.2 The binding specificity of anti-HE4 aptamers targeting HE4.2,3
Anti-HE4 aptamers are widely used in various HE4-related detection assays, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and biosensors, providing high sensitivity for HE4 quantification in clinical samples. They are essential for exploring the role of HE4 in ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, and other malignancies. These aptamers aid in early cancer detection, helping to identify patients at high risk or in need of treatment monitoring. In functional research, anti-HE4 aptamers assist in exploring tumor progression, metastasis, and therapeutic efficacy. By targeting HE4, these aptamers also contribute to evaluating new cancer treatments and investigating potential biomarkers for personalized medicine and clinical decision-making.
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive service of customized aptamer design, conjugation, and detection assays. Our anti-HE4 aptamers feature high specificity, stability, and ease of use. Customers benefit from advanced research solutions, expert support, and reliable tools for cancer diagnosis and treatment development, enhancing the efficiency of their research efforts.
References
-
Zhao, Chongyi, et al. "Roles of antimicrobial peptides in gynecological cancers." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.17 (2022): 10104.
-
Hanžek, Antonija, et al. "Identification and characterization of aptamers targeting ovarian cancer biomarker human epididymis protein 4 for the application in urine." Cancers 15.2 (2023): 452.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 HE4's role in tumorigenic and pro-metastatic mechanisms as an antimicrobial peptide in gynecological cancers.1,3
Fig.1 HE4's role in tumorigenic and pro-metastatic mechanisms as an antimicrobial peptide in gynecological cancers.1,3
 ig.2 The binding specificity of anti-HE4 aptamers targeting HE4.2,3
ig.2 The binding specificity of anti-HE4 aptamers targeting HE4.2,3
