Product List Background CFHR3 Functional Service
Background
Complement factor H (CFH) is an essential regulator of normal complement activity, which inhibits complement alternative pathway activation through the interaction with the C3b fragment. In humans, the CFH family comprises a variant and a group of highly related proteins, including complement factor H related (CFHR) 1, CFHR2, CFHR3, CFHR4, and CFHR5. Based on the N-terminal conserved domains, these proteins are primarily divided into Group I (CFHR1, CFHR2, and CFHR5) and Group II (CFHR3 and CFHR4).
CFHR3 is a plasma protein containing five short consensus repeat (SCR) domains, which is a member of Group II proteins lacking the N-terminal dimerization domain. The SCR1 and SCR2 of CFHR3 share high amino acid homology to SCR6 and SCR7 of CFH, respectively, implying that CFHR3 may bind to C3b fragment like CFH. The SCR3-5 of CFHR3 show high identity to CFHR4. The circulating concentration of CFHR3 is similar to CFHR1, about 70-100 μg/mL. Several CFHR3 variants have been isolated from plasma (ranging from 35 to 56 kDa), which may represent several different glycosylation forms of CFHR3. CFHR3 can bind to the complement C3b, C3d, and heparin with high affinity, which enable CFHR3 to compete with CFH for binding to C3b, thereby inhibiting the complement activation. The CFHR3 variants or mutations have been observed to associate with the atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) and macular degeneration age-related 1.
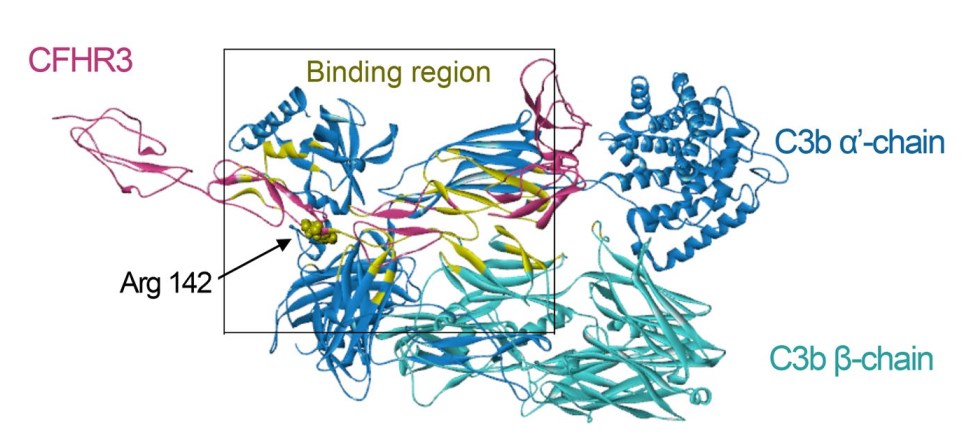 Fig.1 Three-dimensional models of CFHR3/C3b complex.1,3
Fig.1 Three-dimensional models of CFHR3/C3b complex.1,3
CFHR3 Functional Service
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of CFHR3-related products, encompassing CFHR3 ELISA Assay Kits, anti-CFHR3 Antibodies, recombinant CFHR3 Proteins and CFHR3 Blocking Peptides. These products enable precise detection, analysis, and functional studies of CFHR3, facilitating research into complement-related disorders and immune system functions.
CFHR3 functional testing assesses the biological activity and regulatory role of CFHR3 in various cellular and biochemical contexts. This can involve measuring CFHR3 protein expression, analyzing its interaction with other complement proteins, and evaluating its impact on complement activation pathways. Methods for testing include ELISA, Western blotting, flow cytometry, and complement activation assays.
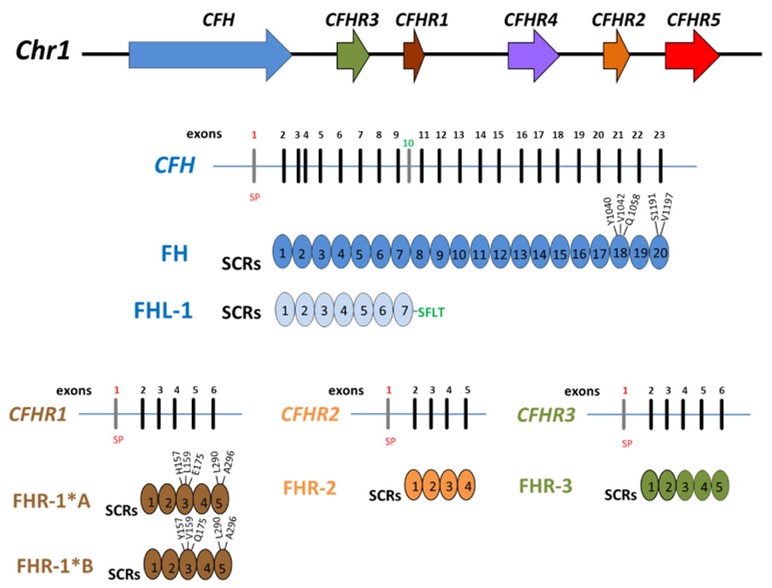 Fig.2 Structure of Factor H family: CFHR3.2,3
Fig.2 Structure of Factor H family: CFHR3.2,3
Our CFHR3 products can be employed in these assays to investigate CFHR3 function in specific research contexts, such as studying the role of CFHR3 in autoimmune diseases or understanding the mechanisms of complement-mediated tissue injury. Research has demonstrated CFHR3’s involvement in complement dysregulation in AMD, showing that altered CFHR3 function correlates with disease progression. Using our CFHR3 recombinant proteins and blocking peptides, researchers can investigate how CFHR3 influences complement-mediated immune responses, providing valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions.
Creative Biolabs provides CFHR3-functional services, including functional assays, activity analysis, and custom research support. Our services help customers optimize experimental design and achieve accurate results, backed by expert support.
References
-
Ding, Yin, et al. "A haplotype in CFH family genes confers high risk of rare glomerular nephropathies." Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 6004.
-
Piras, Rossella, et al. "CFH and CFHR structural variants in atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: Prevalence, genomic characterization and impact on outcome." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2023): 1011580.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Three-dimensional models of CFHR3/C3b complex.1,3
Fig.1 Three-dimensional models of CFHR3/C3b complex.1,3
 Fig.2 Structure of Factor H family: CFHR3.2,3
Fig.2 Structure of Factor H family: CFHR3.2,3
