Product List Background MAp44 Functional Service
Background
MAp44 is a 44 kDa variation of mannose-binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine protease (MASP) proteins. Encoded by the MASP1 gene, MAp44 lacks enzymatic activity but plays a crucial role in regulating the lectin pathway of the complement system. It contains domains of C1r/C1s/Uegf/bmp1 (CUB), complement control protein (CCP), and calcium-binding EGF-like domain. Its structural features enable modulation of MASP activity, affecting downstream complement-mediated immune processes. MAp44 is expressed primarily in the heart and functions as a regulator of complement activation, influencing innate immune responses against pathogens.
Its Gene ID: 5648, UniProtKB ID: P48740, and OMIM ID: 600521.
MAp44 Formation
MAp44 formation involves the alternative splicing of the primary transcript encoded by the MASP1 gene. Up to now, 5 MASP proteins have been identified: MASP-1, MASP-2, and MASP-3, which activate the complement system, and MAp44 and MAp19, which operate as natural endogenous competitive inhibitors. These proteins are encoded by MASP1 and MASP2 gene. MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 are derived from the MASP1 gene due to alternative splicing, whereas MASP-2 and MAp19 are derived from the MASP2 gene. The gene for MAp44 shares the first eight exons with MASP-1 and MASP-3, encoding domains crucial for interaction with MASP-1 and MASP-2. The ninth exon encodes a unique C-terminal sequence of 17 amino acids specific to MAp44, distinguishing it from other MASP variants. This structural arrangement allows MAp44 to regulate the lectin pathway of complement activation, distinct from its enzymatically active counterparts MASP-1 and MASP-2.
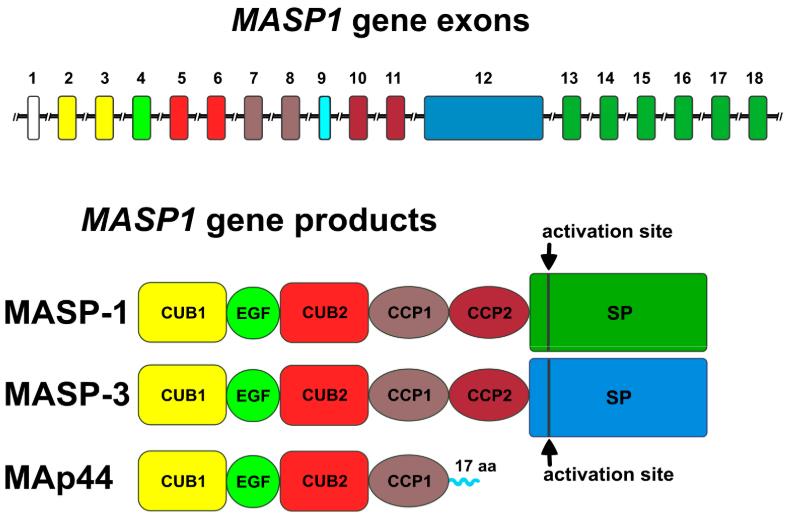 Fig.1 The protein structures of MASP-1, MASP-3 and MAp44 encode by MASP1 gene.1, 3
Fig.1 The protein structures of MASP-1, MASP-3 and MAp44 encode by MASP1 gene.1, 3
Regulation of MAp44 in the Lectin Pathway
MAp44 regulates the lectin pathway of complement activation through several mechanisms. It binds to MBL and three ficolins (M-ficolin, L-ficolin, H-ficolin), forming complexes that modulate pathway activity. MAp44 acts as a competitive inhibitor by binding to MASPs, particularly MASP-1 and MASP-2, thereby preventing their interaction with MBL and subsequent activation of complement cascades, such as avoiding cleavage of C4 and C2. This regulatory role helps fine-tune immune responses by controlling the initiation of complement activation, ensuring that it occurs appropriately in response to pathogenic threats without excessive activation that could lead to tissue damage.
Antibodies Targeting MAp44
Antibodies targeting MAp44 can be utilized in binding studies to understand its interaction with MBL and MASPs. These antibodies help elucidate MAp44's mechanism of action in inhibiting the lectin pathway of complement activation. In research, they facilitate the characterization of MAp44's binding specificity and affinity, aiding in developing therapeutic strategies targeting complement-mediated diseases. Additionally, they serve as tools for assessing MAp44 levels and dynamics in biological samples, providing insights into their role in immune regulation and potential diagnostic applications.
Creative Biolabs offers a high-quality human MAp44 ELISA kit that can be used for sandwich ELISA. Our products are fully validated for complete reliability and ready support.
MAp44 Functional Service
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive range of reagents related to MAp44, featuring ELISA kits designed for MAp44 detection. These tools excel in detecting and analyzing the interactions between various factors and the human MAp44 protein. As such, they are indispensable assets in research dedicated to developing therapeutic strategies for disease management.
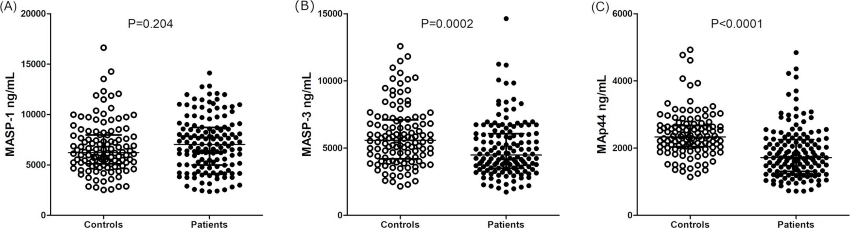 Fig.3 Serum concentrations of MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 in healthy individuals and leprosy patients.2, 3
Fig.3 Serum concentrations of MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 in healthy individuals and leprosy patients.2, 3
The complement system, specifically through the lectin pathway, enhances the phagocytosis of Mycobacterium leprae, with proteins such as MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 playing potential roles in leprosy. Researchers conducted haplotyping of five MASP1 polymorphisms using multiplex sequence-specific PCR, while MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 serum levels were quantified in leprosy patients and controls using time-resolved immunofluorimetric assays (TRIFMA). Key findings revealed that MASP-3 and MAp44 levels were lower in patients versus controls, and in lepromatous compared to non-lepromatous cases. Elevated MASP-3 levels in controls were linked to leprosy resistance, underscoring lectin pathway regulation’s role in host-pathogen interactions.
Creative Biolabs provides specialized expertise in MAp44 functionality, featuring comprehensive analysis of interaction dynamics and extensive functional assessments. These services are precisely designed to align with the specific needs of distinguished clients, significantly advancing clinical and scientific research efforts.
References
-
Lindelöf, Linnea, et al. "A survey of ficolin-3 activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus reveals a link to hematological disease manifestations and autoantibody profile." Journal of Autoimmunity 143 (2024): 103166.
-
Weinschutz Mendes, Hellen, et al. "Adding MASP1 to the lectin pathway—Leprosy association puzzle: Hints from gene polymorphisms and protein levels." PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 14.4 (2020): e0007534.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 The protein structures of MASP-1, MASP-3 and MAp44 encode by MASP1 gene.1, 3
Fig.1 The protein structures of MASP-1, MASP-3 and MAp44 encode by MASP1 gene.1, 3
 Fig.3 Serum concentrations of MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 in healthy individuals and leprosy patients.2, 3
Fig.3 Serum concentrations of MASP-1, MASP-3, and MAp44 in healthy individuals and leprosy patients.2, 3
